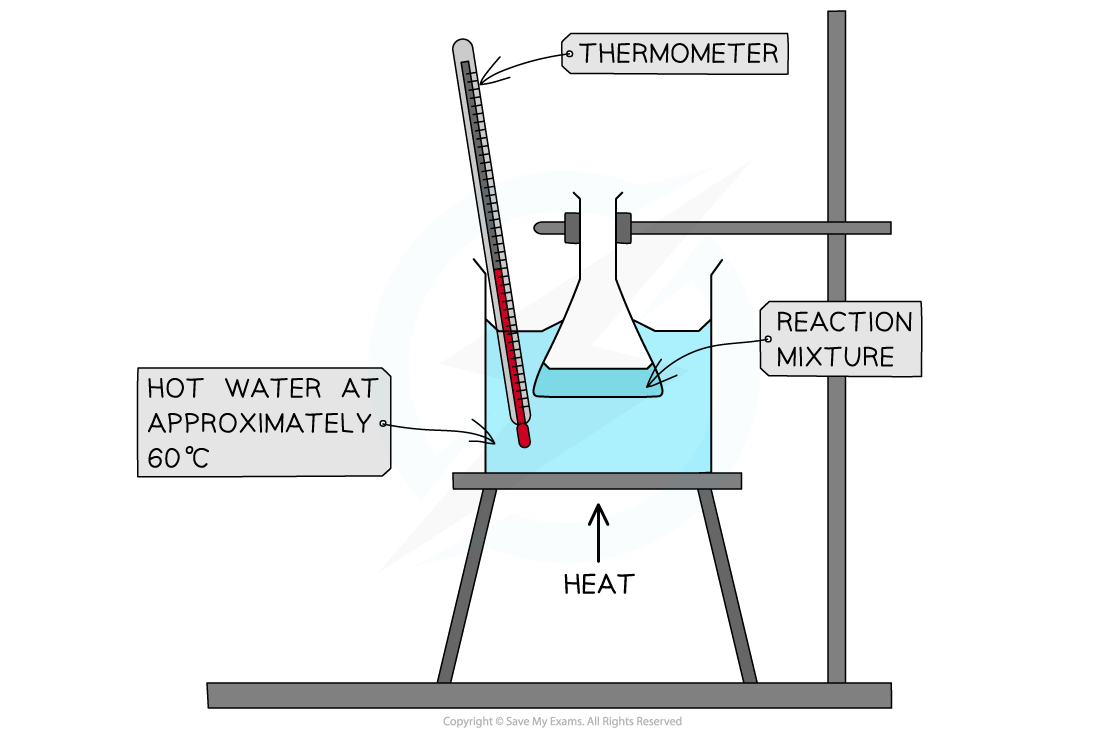
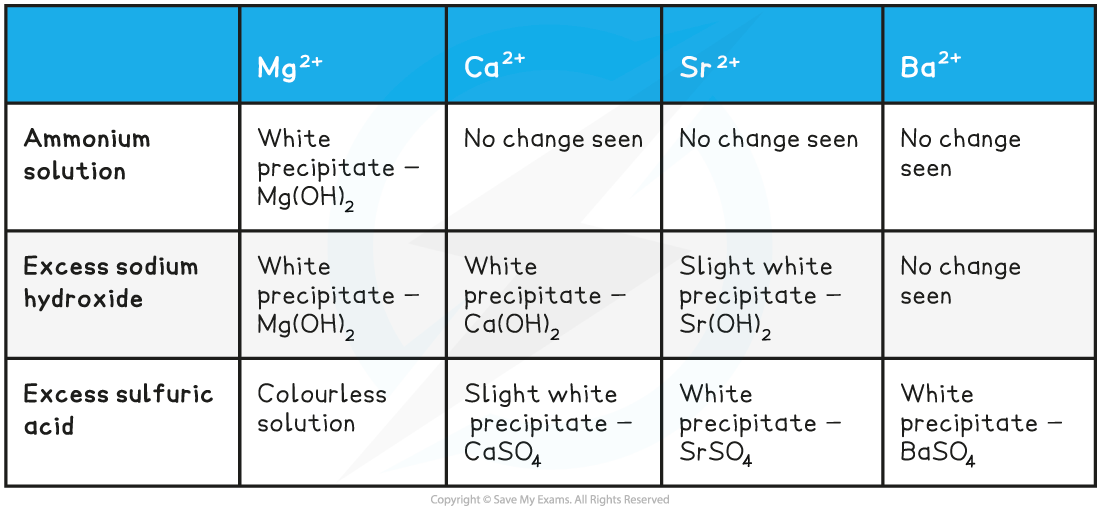
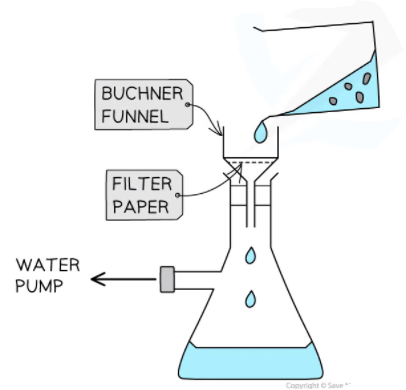
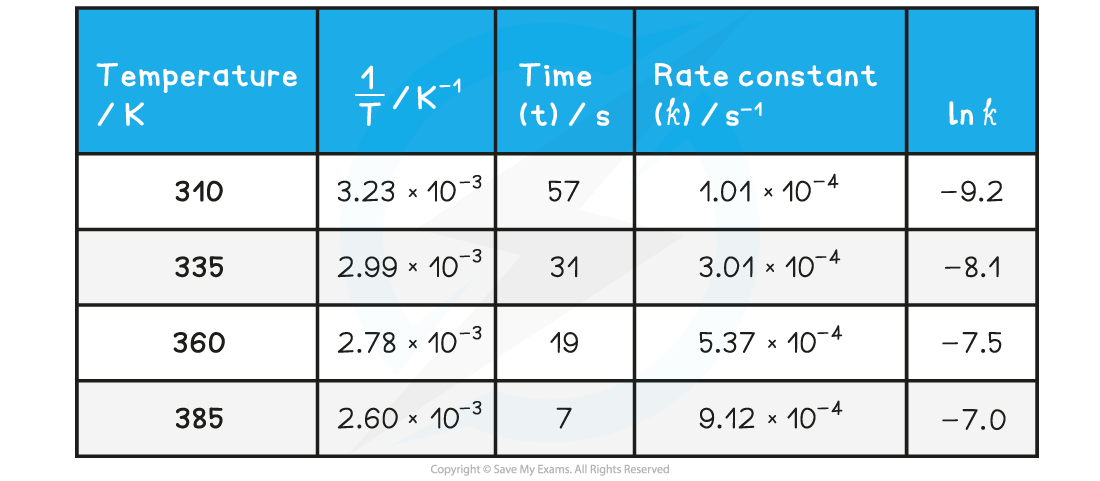
Edexcel A Level Economics A:复习笔记1.1.3 The Economic Problem
The Basic Economic Problem: Scarcity The basic economic problem is that resources are scarce There are finite resources available in relation to the infinite wants and needs that humans have...