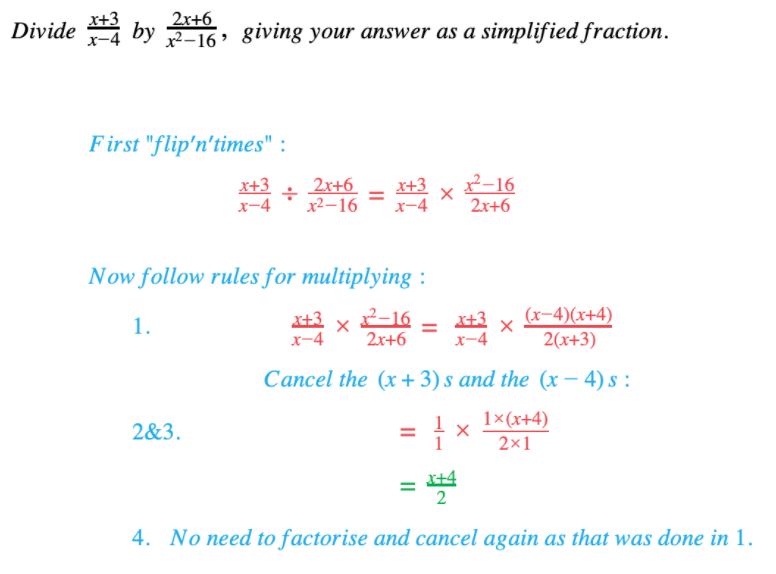
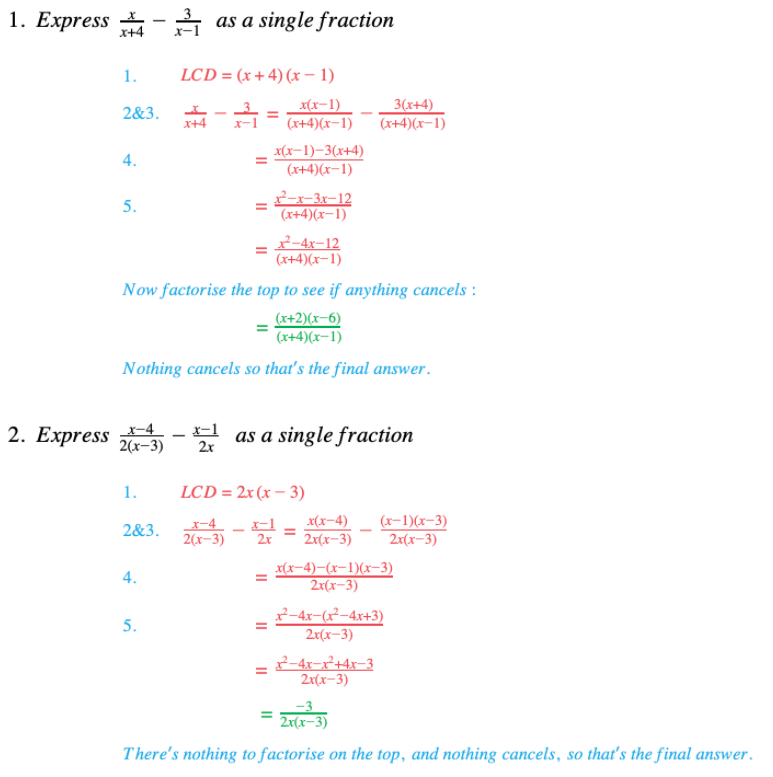
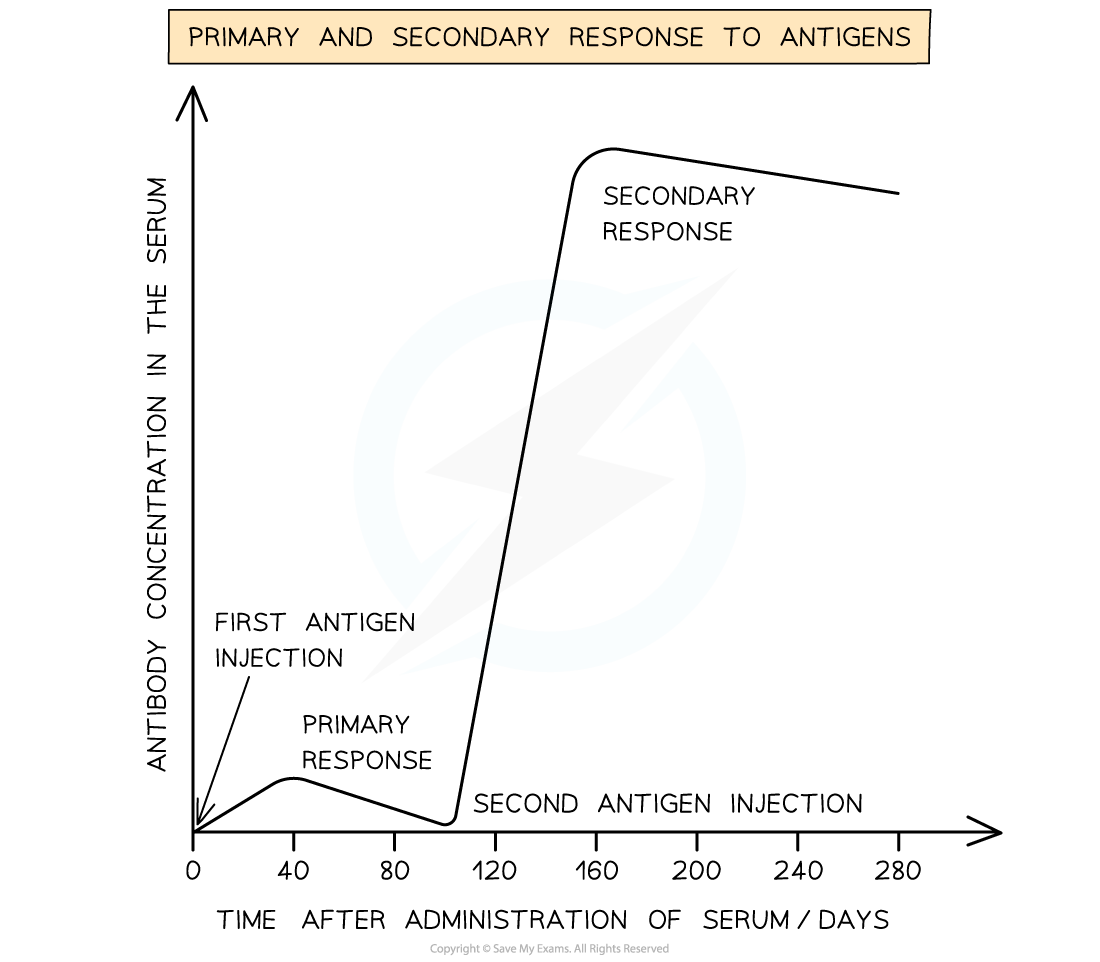
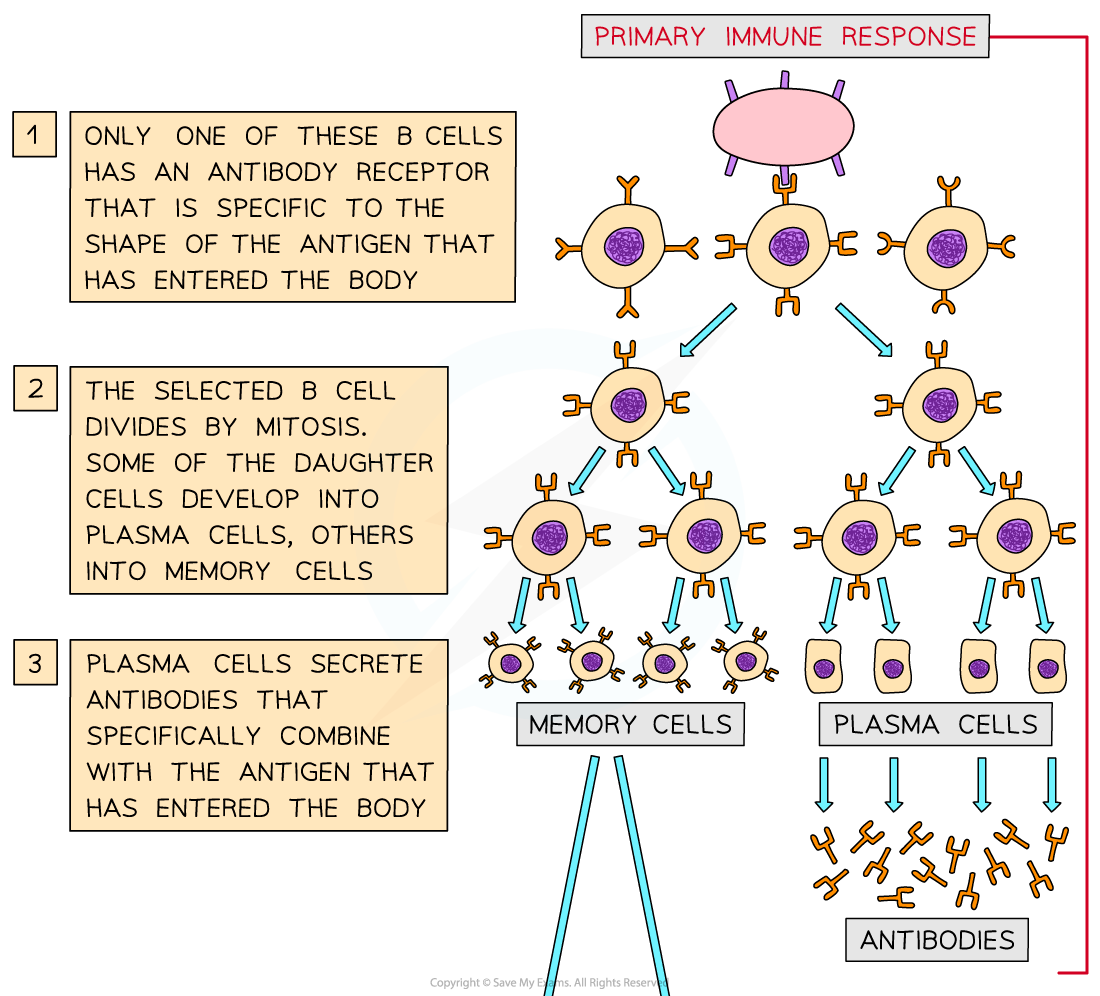
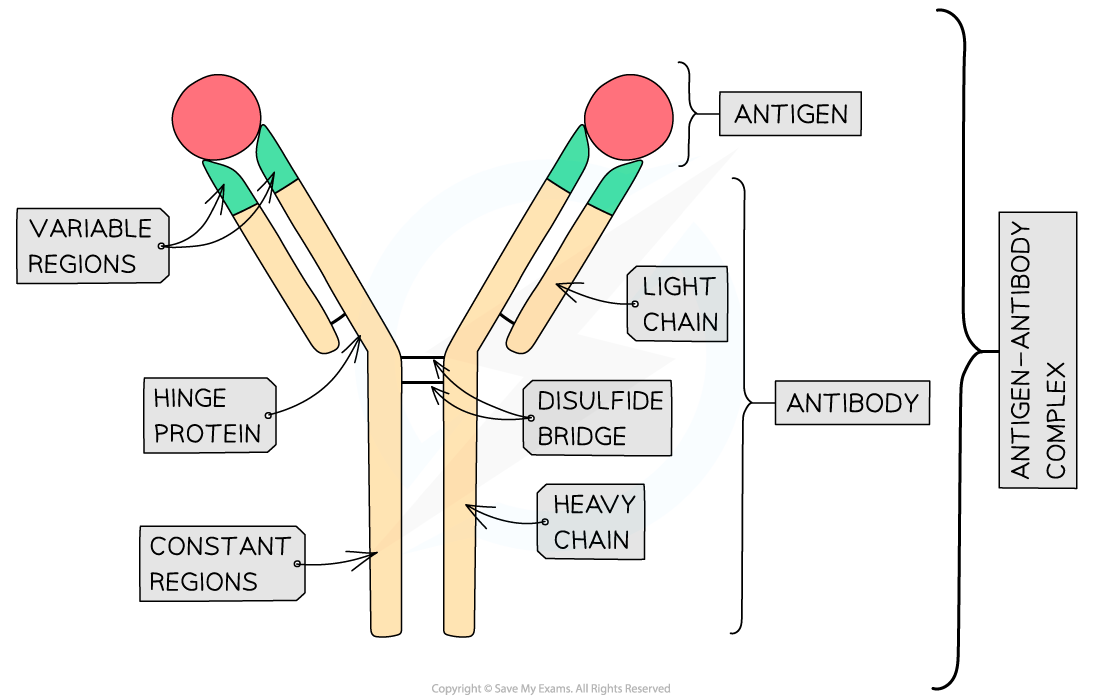
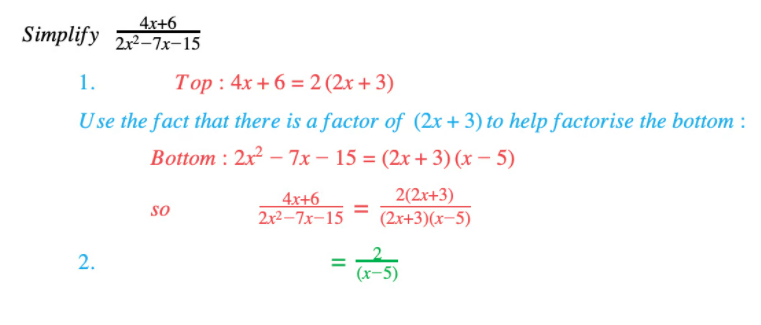Edexcel IGCSE Maths 复习笔记 2.6.3 Algebraic Fractions - Multiplying & Dividing
Edexcel IGCSE Maths 复习笔记 2.6.3 Algebraic Fractions - Multiplying & Dividing What is an algebraic fraction? An algebraic fraction is simply a fraction with an algebraic expression on the top...