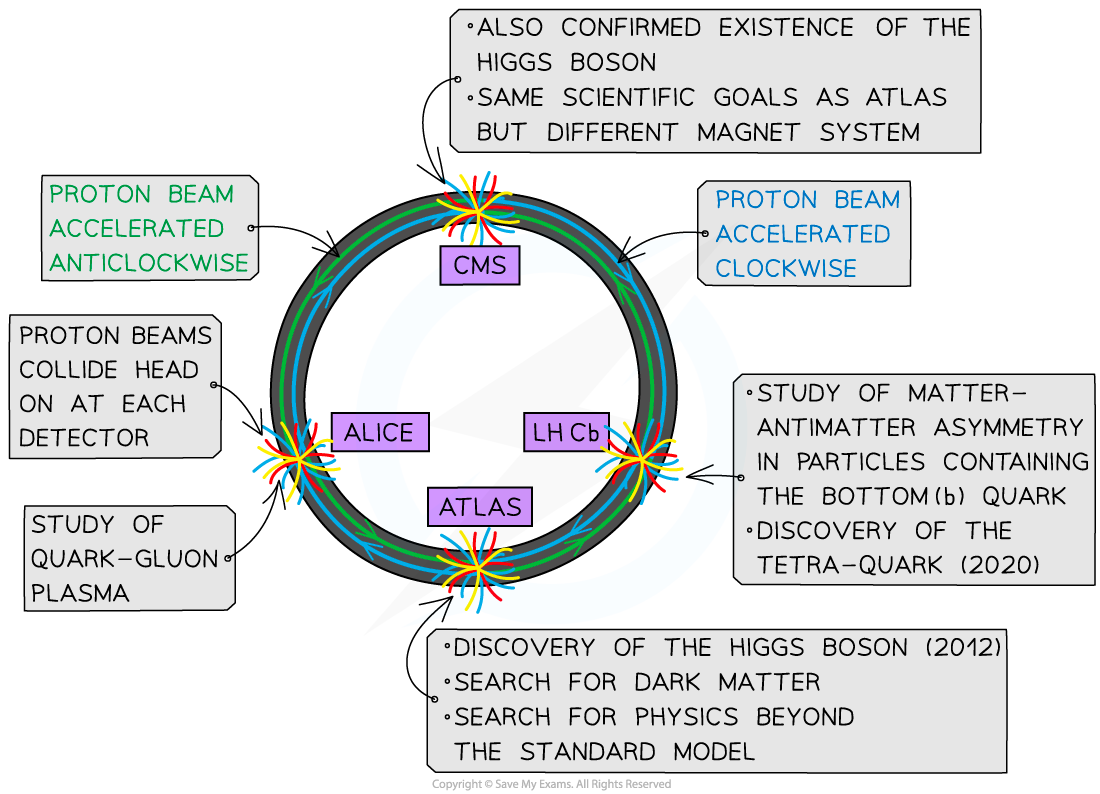
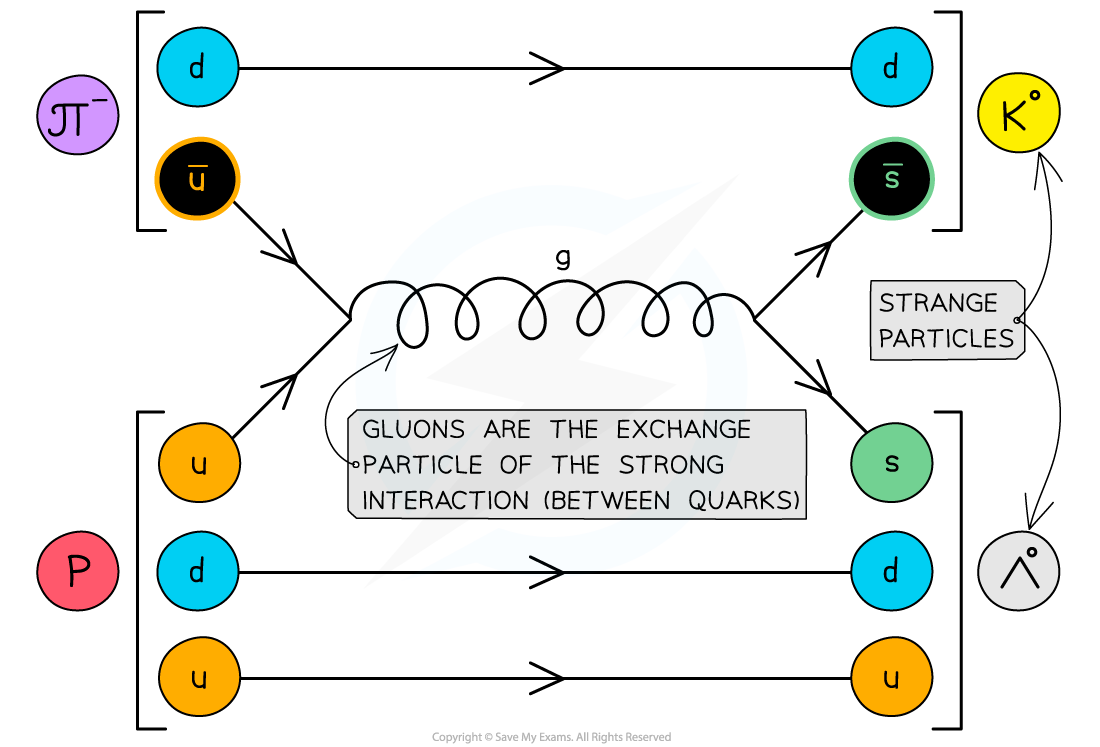
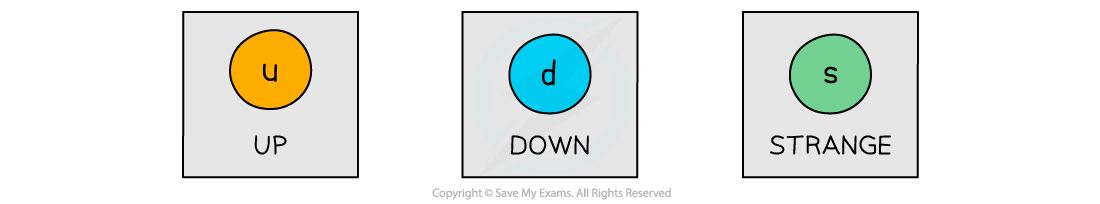
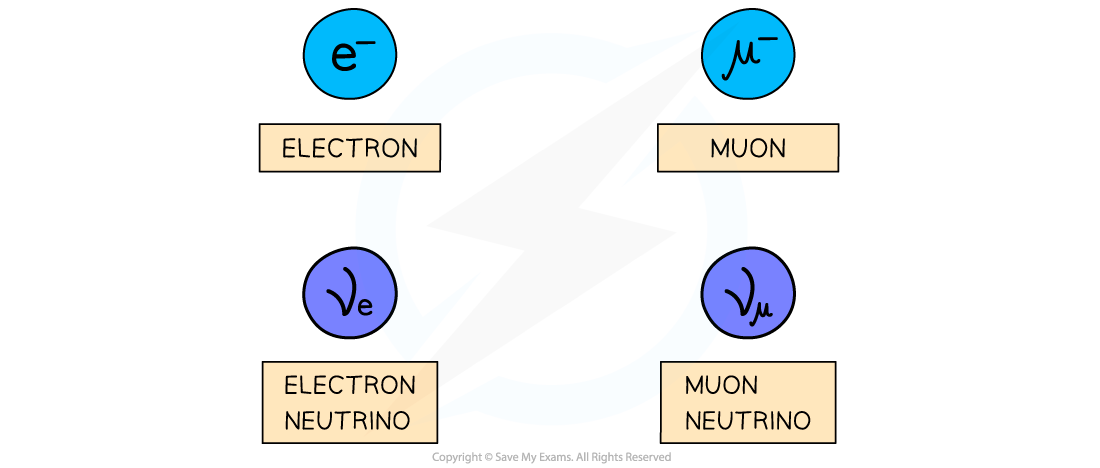
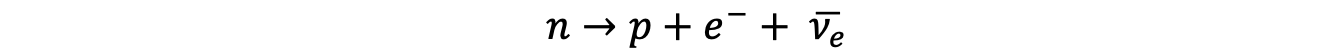AQA A Level Physics复习笔记2.3.5 Application of Conservation Laws
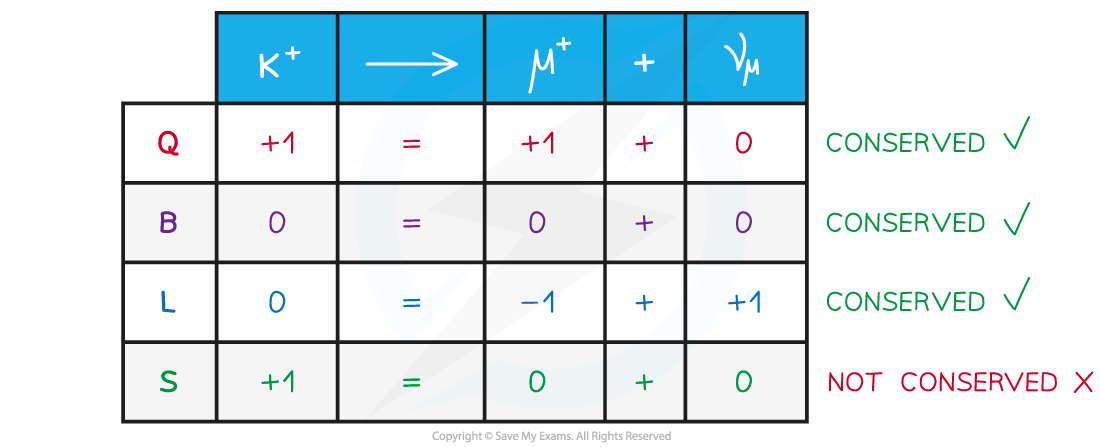
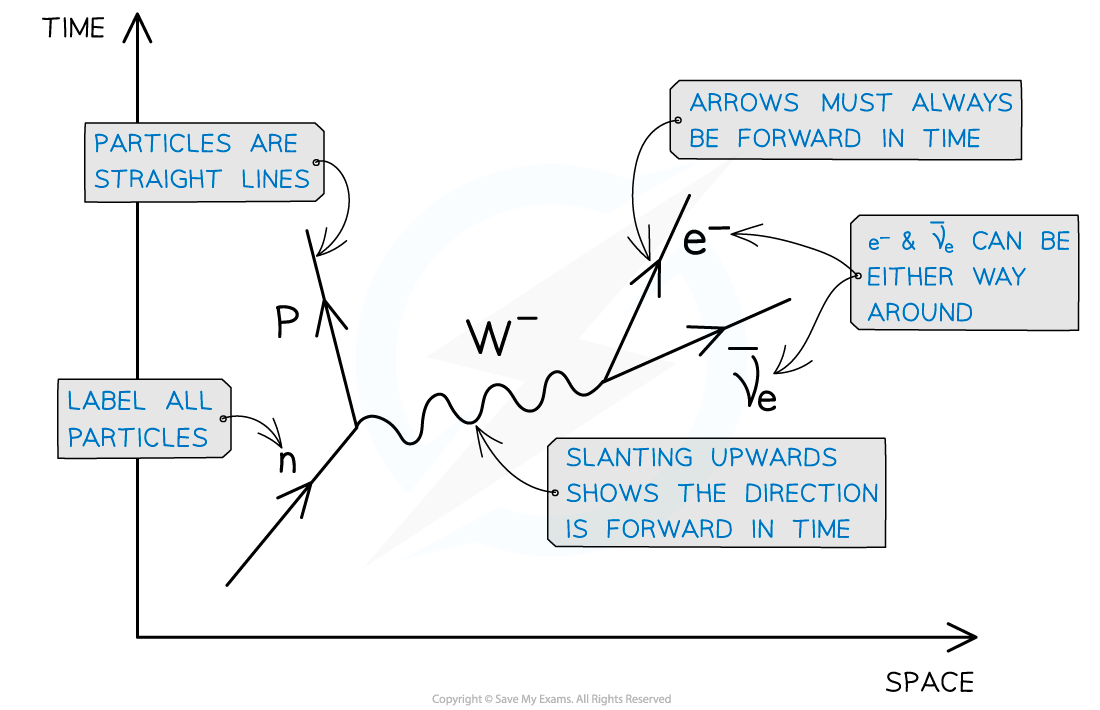
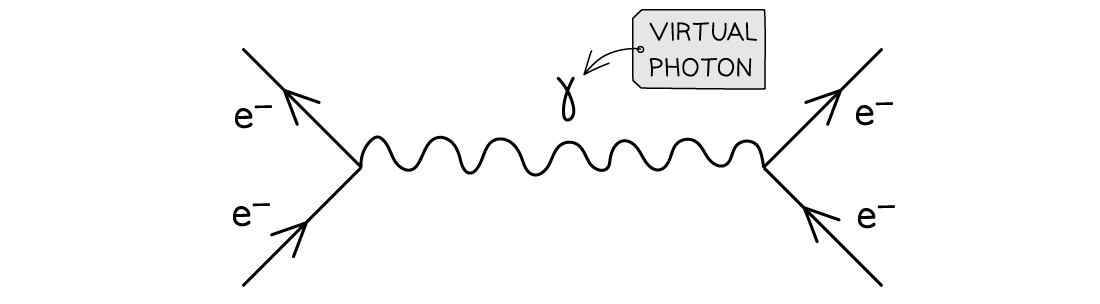
Application of Conservation Laws All particle interactions must obey a set of conservation laws. These are conservation of: Charge, Q Baryon number, B Lepton Number, L Strangeness, S Energy ...