- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
2016 AP Chemistry化学真题系列之简答题免费下载
历年AP Chemistry化学系列
真题与答案下载

翰林国际教育全网首发
力争超快速发布最全资料
助你在升学路上一帆风顺
为你的未来保驾护航
2016 AP Chemistry Free-Response Questions Free Download
2016 AP 化学简答题部分免费下载
考试时会提供花常用的等式与常量
以及化学元素周期表
此套Section II试卷共7题
每道大题含有不同数量的小题
共计时1小时45分钟
其中1-3题各需23分钟,每题10分
4-7题各需9分钟,每题4分
完整版下载链接见文末
部分真题预览:
1)A student investigates the enthalpy of solution, ΔHsoln, for two alkali metal halides, LiCl and NaCl. In addition to the salts, the student has access to a calorimeter, a balance with a precision of ±0.1g, and a thermometer with a precision of ±0.1°C.
- To measure ΔHsoln for LiCl, the student adds 100.0g of water initially at 15.0°C to a calorimeter and adds 10.0g of LiCl(s), stirring to dissolve. After the LiCl dissolves completely, the maximum temperature reached by the solution is 35.6°C.
- Calculate the magnitude of the heat absorbed by the solution during the dissolution process, assuming that the specific heat capacity of the solution is4.18 J/(g.°C) . Include units with your answer.
- Determine the value of delta ΔHsoln for LiCl in kJ/molrxn.
To explain why ΔHsoln for NaCl is different than that for LiCl, the student investigates factors that affect ΔHsoln and finds that ionic radius and lattice enthalpy (which can be defined as the ΔH associated with the separation of a solid crystal into gaseous ions) contribute to the process. The student consults references and collects the data shown in the table below.
(b) Write the complete electron configuration for the Na+ ion in the ground state.
(c) Using principles of atomic structure, explain why the Na+ ion is larger than the Li+ ion.
(d) Which salt, LiCl or NaCl, has the greater lattice enthalpy? Justify your answer.
(e) Below is a representation of a portion of a crystal of LiCl. Identify the ions in the representation by writing the appropriate formulas ( Li+ or Cl-) in the boxes below.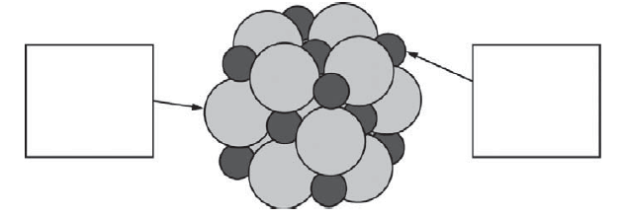
(f) The lattice enthalpy of LiCl is positive, indicating that it takes energy to break the ions apart in LiCl. However, the dissolution of LiCl in water is an exothermic process. Identify all particle-particle interactions that contribute significantly to the dissolution process being exothermic. For each interaction, include the particles that interact and the specific type of intermolecular force between those particles.
完整版真题资料可以底部二维码免费领取↓↓↓
[vc_btn title="查看更多AP Chemistry化学课程相关详情" color="primary" align="center" i_icon_fontawesome="fa fa-globe" css_animation="zoomIn" button_block="true" add_icon="true" link="url:http%3A%2F%2Fwww.linstitute.net%2Farchives%2F25860||target:%20_blank|"]

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









