- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
1994CAP Prize Exam加拿大高中物理大奖赛真题免费下载
历年CAP High School Prize Exam加拿大高中物理大奖赛
真题与答案下载

翰林国际教育全网首发
力争超快速发布最全资料
助你在升学路上一帆风顺
为你
千千万万遍
1994 CAP Prize Exam真题免费下载
共计3小时考试时间
此套试卷由两部分组成
20道选择题
以及3道简答题组成
每道大题含有不同数量的小题
完整版下载链接见文末
部分真题预览:
Data:
Speed of light c =3.00 × 108m/s
Gravitational constant G =6.67 × 10−11N · m2kg2
Radius of Earth RE=6.38× 106 m
Mass of Earth ME=5.98× 1024 Kg
Mass of Sun MS=1.99× 1030 Kg
Radius of Earth's orbit RES=1.50× 1011 m
Acceleration due to gravity g =9.80m/s2
Fundamental charge e =1.60× 10−19 C
Mass of electron me =9.11 × 10−31kg
Mass of proton mp =1.673 × 10−27kg
Planck’s constant h = 6.63 x 10-34 J·s
Coulomb’s constant 1/(4πε0) = 8.99x109 N·m2/C2
Magnetic constant μo=4π × 10−7N/A2
Speed of sound in air vs=340m/s
Part A: Multiple Choice
1)It was once proposed to use a 2Km vertical Sudbury mine shaft for microgravity experiments in a vacuum. How much time would scientists have to do an experiment during one drop?
- 20s
- 63s
- 0.64s
- 198s
2)If the moon were twice as massive as it is now, and it stayed at the same orbital radius about the earth as it has now, its new orbital period(in terms of its current orbital period T) would be,
- T
- T/2
- T/4
- 2T
3)In the following circuit composed of identical capacitors, across which terminals would you connect a battery in order for all the capacitors to charge up.
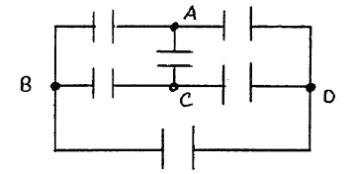
- AB
- AC
- BD
- none of the above
4)Two cylindrical resistors, one of length I and radius r, and the other of length 3I and radius 3r, are made of the same materials. If the resistance of the smaller one is R, what is the resistance of the larger one?
- R/3
- 3R
- 9R
- 27R
5)A simple pendulum consists of a mass m attached to a light string of length I. If the system is oscillating through small angles, which of the following is true?
- The frequency is independent of the acceleration due to gravity g
- The period depends on the amplitude of the oscillation
- The period is independent of the mass m
- The period is independent of the length I
完整版真题资料可以底部二维码免费领取↓↓↓
[vc_btn title="查看更多CAP Prize Exam加拿大物理奥林匹克学术活动相关详情" color="primary" align="center" i_icon_fontawesome="fa fa-globe" css_animation="zoomIn" button_block="true" add_icon="true" link="url:http%3A%2F%2Fwww.linstitute.net%2Farchives%2F92551||target:%20_blank|"]
[products columns="2" orderby="title" order="ASC" ids="310579,310582 "]

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









