- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
CIE IGCSE Biology: 复习笔记:20.1.5 Sustainability
CIE IGCSE Biology: 复习笔记:20.1.5 Sustainability
Sustainable Use of Resources
- We use many resources from the Earth; some, such as food, water and wood, are sustainable resources
- A sustainable resource is one which is produced as rapidly as it is removed from the environment so that it does not run out
- Some resources, such as fossil fuels (coal, oil and natural gas), are non-renewable because what we use cannot be replaced
- These resources, once used, cannot be produced anymore and so they need to be conserved by reducing the amount we use and finding other, sustainable resources to replace them
- Fossil fuels are being used as an energy source in increasing amounts
- In addition, they are the raw materials for many other products we make - eg almost all plastics that are made start with oil as a raw material
- Some products, especially those made from paper, plastic, glass or metal, can be reused and recycled - this reduces waste in the environment and reduces the amounts of raw materials and energy needed to make new products
- Some resources, such as forests and fish stocks, can be maintained - enabling us to harvest them sustainably so that they will not run out in the future
Sustainable Production Examples: Extended
- Sustainable development is defined as development providing for the needs of an increasing human population without harming the environment
- When developing the way in which we use resources to manage them sustainably, we have to balance conflicting demands - eg:
- the need for local people to be able to utilise the resources they have in their immediate environment with the needs of large companies to make money from resources such as forests and fish
- the need for balancing the needs of humans for resources with the needs of the animals and plants that live in the areas the resources are taken from (preventing loss of habitat and extinction)
- the need to balance what current populations need with what future populations might need - for example if we harvest all the fish we need to feed people now, this might lead to overfishing which would deplete stocks for future generations
- For development to occur sustainably, people need to cooperate at local, national and international levels in the planning and management of resources
Sustaining Forests
- Forests are needed to produce paper products and provide wood for timber
- Much of the world’s paper is now produced from forests which replant similar trees when mature trees are cut, ensuring that there will be adequate supply in the future
- Tropical hardwoods such as teak and mahogany take many years to regrow but are highly desirable for furniture
- Using these types of wood has now been made more sustainable due to the introduction of several schemes designed to monitor logging companies and track the wood produced (eg the Forestry Stewardship Council)
- Education helps to ensure logging companies are aware of sustainable practices and consumers are aware of the importance of buying products made from sustainable sources
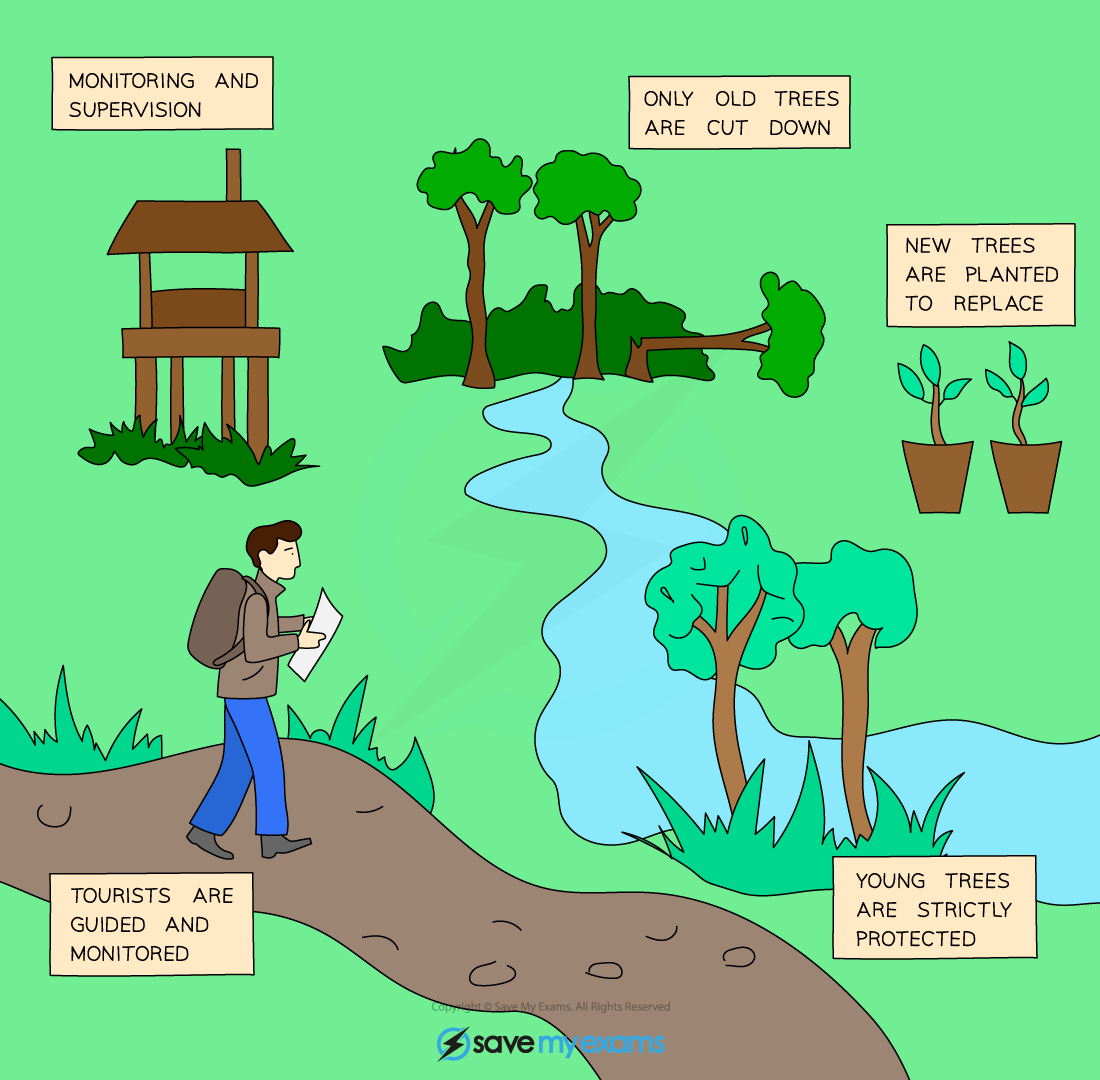 More efforts are being made to manage forests sustainably so consumers know they are not causing damage to forests
More efforts are being made to manage forests sustainably so consumers know they are not causing damage to forests
Sustaining Fish Stocks
- Managing fish stocks sustainably includes:
- Controlling the number of fish caught each year (quotas)
- Controlling the size of fish caught (to ensure there are enough fish of a suitable age for breeding remaining)
- Controlling the time of year that certain fish can be caught (to prevent large scale depletion of stocks when fish come together in large numbers in certain areas to breed)
- Restocking (breeding and keeping offspring until they are large enough to survive in their natural habitat then releasing)
- Educating fishermen as to local and international laws and consumers so they are aware of types of fish which are not produced sustainably and can avoid them when buying fish
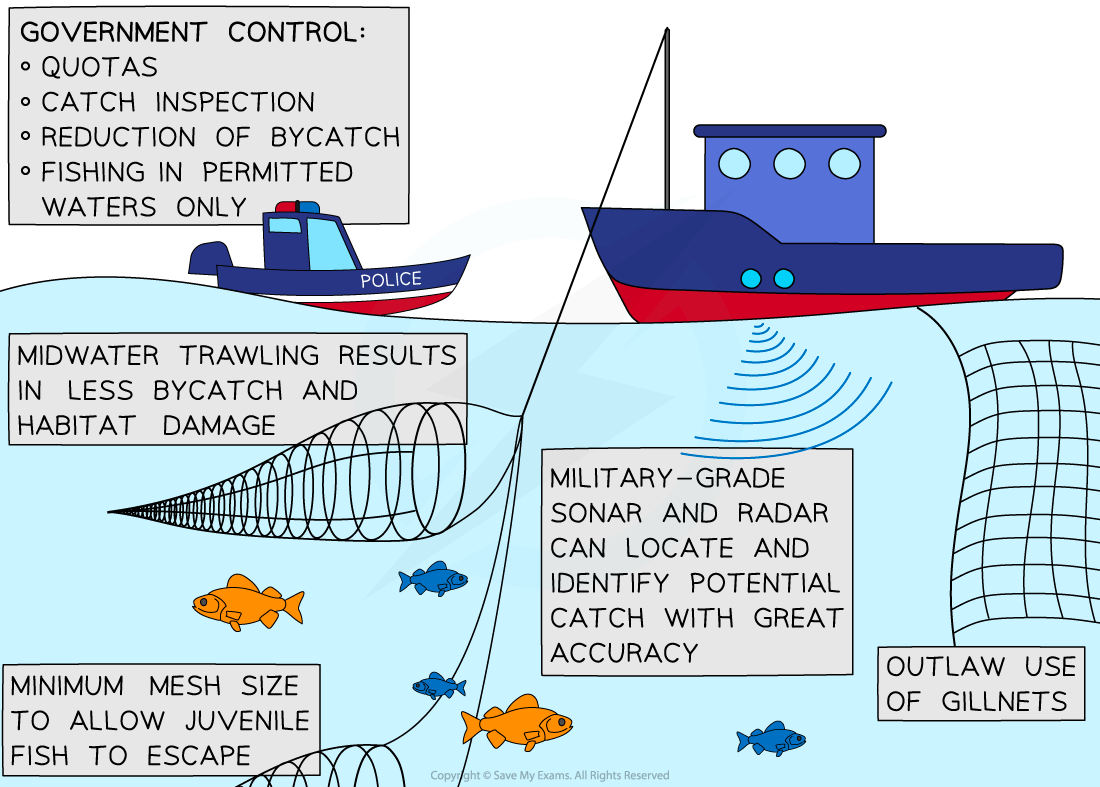
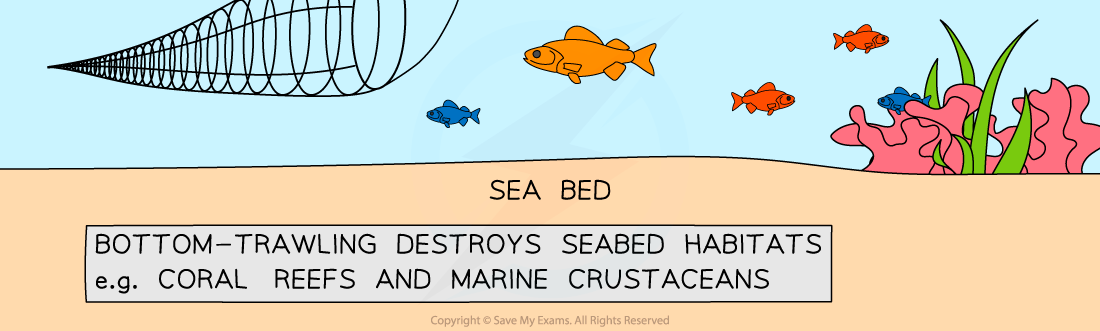
Ways of controlling fishing to make it more sustainable
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








