- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
CIE IGCSE Biology: 复习笔记:15.1.1 Drugs for Medicine
CIE IGCSE Biology: 复习笔记:15.1.1 Drugs for Medicine
What is a Drug?
- A drug is any substance taken into the body that modifies or affects chemical reactions in the body
- Some drugs are medicinal drugs that are used to treat the symptoms or causes of a disease - for example, antibiotics
- The liver is the primary site for drug metabolism
Antibiotics
- Antibiotics are chemical substances made by certain fungi or bacteria that affect the working of bacterial cells, either by disrupting their structure or function or by preventing them from reproducing.
- Antibiotics are effective against bacteria but not against viruses.
- Antibiotics target processes and structures that are specific to bacterial (prokaryotic) cells; as such they do not generally harm animal cells.
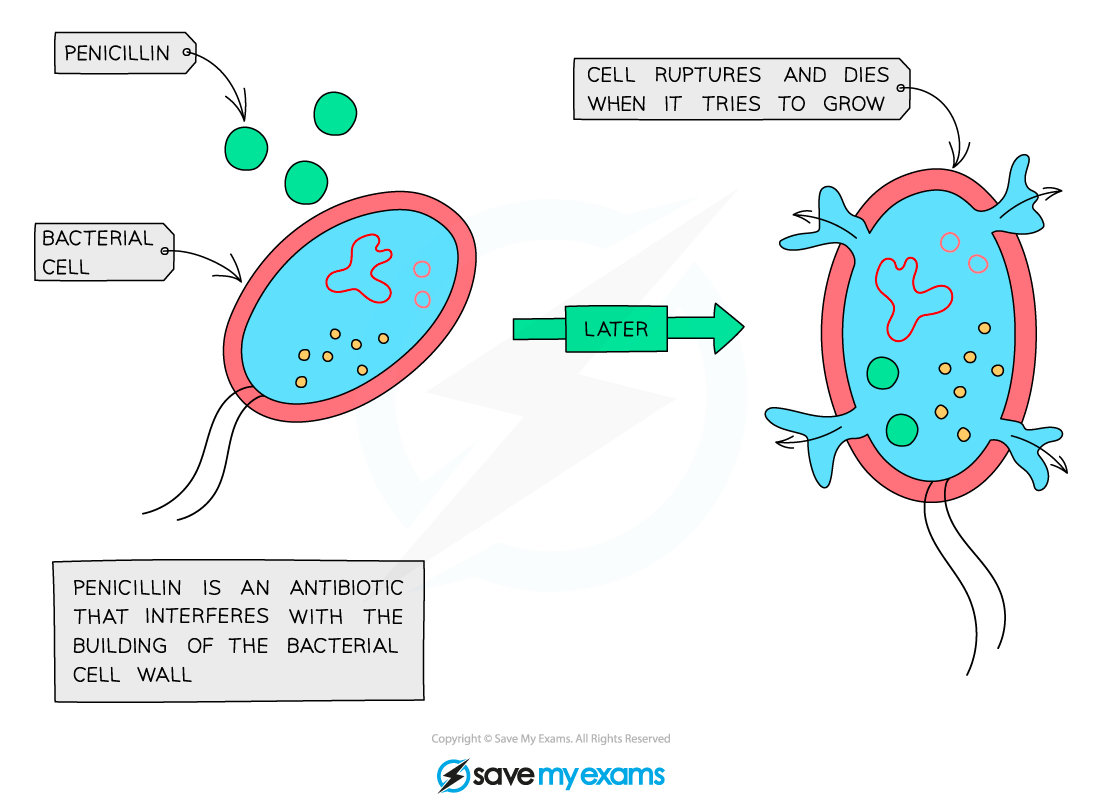 How antibiotics work
How antibiotics work
Antibiotic Resistance & Use: Extended
- Since the first antibiotic was discovered in 1928, many more have been discovered and developed and antibiotics were and are widely overused
- Commonly prescribed antibiotics are becoming less effective due to a number of reasons:
- overuse and being prescribed when not really necessary
- patients failing to complete the fully prescribed course by a doctor
- large scale use of antibiotics in farming to prevent disease when livestock are kept in close quarters, even when animals are not actually sick
- This has led to the effectiveness of antibiotics being reduced, and the incidence of antibiotic resistance increasing
- These bacteria are commonly known as superbugs and the most common is MRSA
- Ways individuals can help prevent the incidence of antibiotic resistance increasing include:
- only taking antibiotics when absolutely essential
- when prescribed a course of antibiotics, ensure that the entire course is completed even if you feel better after a few days
 Antibiotic resistance
Antibiotic resistance

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









