- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
CIE IGCSE Biology: 复习笔记:9.1.7 Identifying Structures in the Heart: Extended
CIE IGCSE Biology: 复习笔记:9.1.7 Identifying Structures in the Heart: Extended
Identifying Structures in the Heart: Extended
- The ventricles have thicker muscle walls than the atria as they are pumping blood out of the heart and so need to generate a higher pressure
- The left ventricle has a thicker muscle wall than the right ventricle as it has to pump blood at high pressure around the entire body, whereas the right ventricle is pumping blood at lower pressure to the lungs
- The septum separates the two sides of the heart and so prevents mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
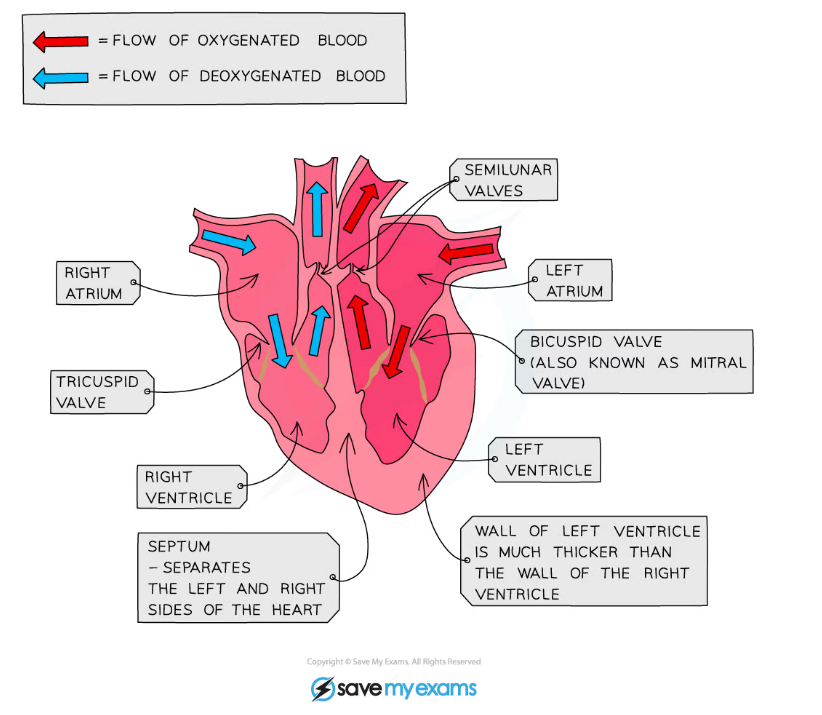 Structure of the heart showing the different valves
Structure of the heart showing the different valves
The function of valves
- The basic function of all valves is to prevent blood from flowing backwards
- There are two sets of valves in the heart:
- The atrioventricular valves separate the atria from the ventricles
- The valve in the right side of the heart is called the TRICUSPID and the valve in the left side is called the BICUSPID
- These valves are pushed open when the atria contract but when the ventricles contract they are pushed shut to prevent blood flowing back into the atria
- The semilunar valves are found in the two blood arteries that come out of the top of the heart
- They are unusual in that they are the only two arteries in the body that contain valves
- These valves open when the ventricles contract so blood squeezes past them out of the heart, but then shut to avoid blood flowing back into the heart
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









