- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
CIE IGCSE Biology: 复习笔记:9.1.6 Coronary Heart Disease
CIE IGCSE Biology: 复习笔记:9.1.6 Coronary Heart Disease
Coronary Heart Disease
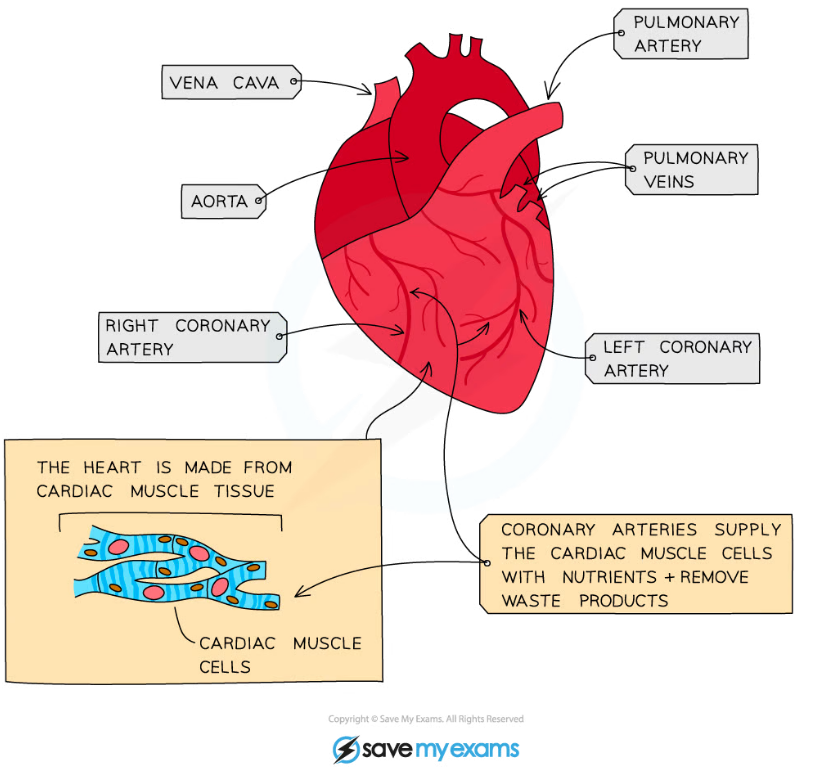 The coronary arteries
The coronary arteries
- The heart is made of muscle cells that need their own supply of blood to deliver oxygen, glucose and other nutrients and remove carbon dioxide and other waste products
- The blood is supplied by the coronary arteries
- If a coronary artery becomes partially or completely blocked by fatty deposits called ‘plaques’ (mainly formed from cholesterol), the arteries are not as elastic as they should be and therefore cannot stretch to accommodate the blood which is being forced through them - leading to coronary heart disease
- Partial blockage of the coronary arteries creates a restricted blood flow to the cardiac muscle cells and results in severe chest pains called angina
- Complete blockage means cells in that area of the heart will not be able to respire and can no longer contract, leading to a heart attack
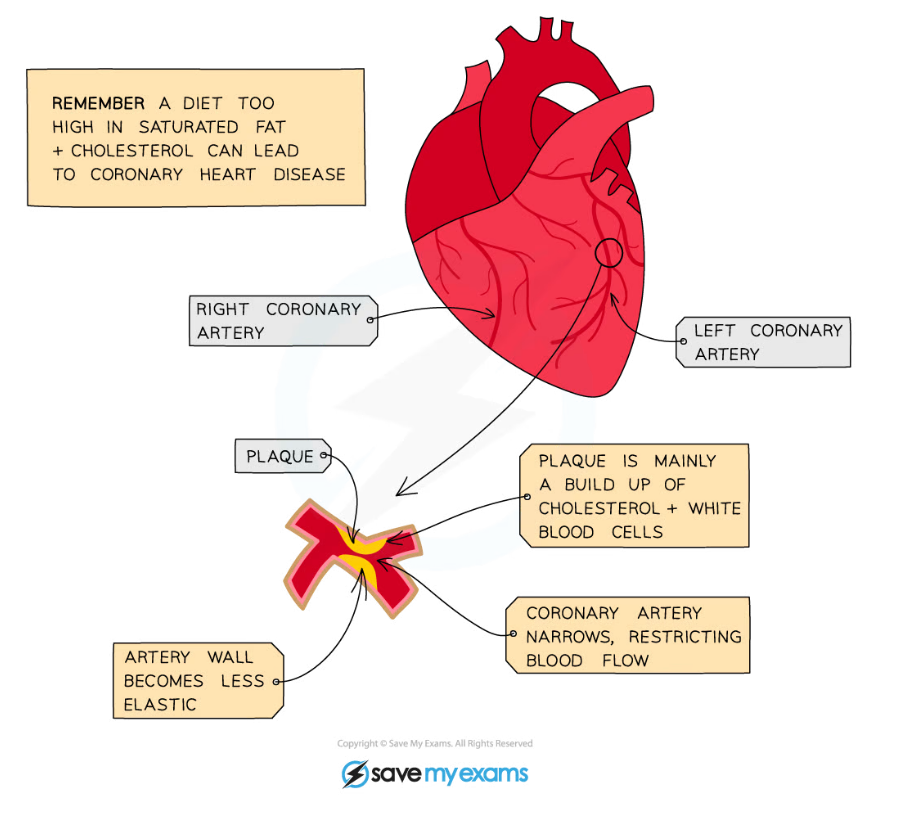 Buildup of plaque in the coronary arteries
Buildup of plaque in the coronary arteries
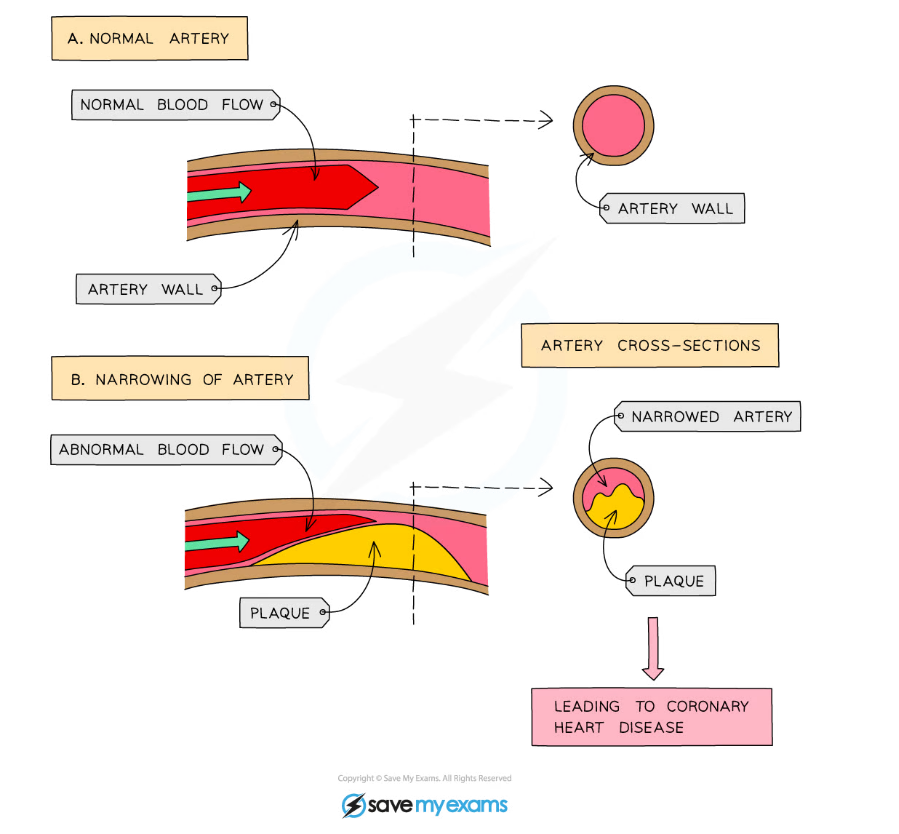 Effect of narrowing of arteries
Effect of narrowing of arteries
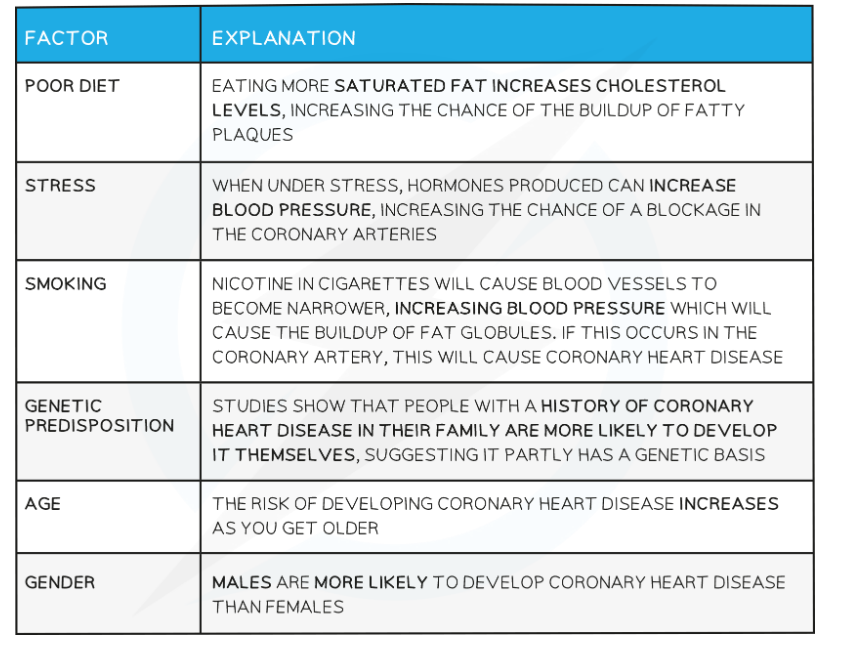
Risk Factors for CHD Table
Diet, Exercise & Coronary Heart Disease
Reducing the risks of developing coronary heart disease
- Quit smoking
- Diet - reduce animal fats and eat more fruits and vegetables - this will reduce cholesterol levels in the blood and help with weight loss if overweight
- Exercise regularly - again, this will help with weight loss, decrease blood pressure and cholesterol levels and help reduce stress

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








