- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
OCR A Level Biology:复习笔记2.2.4 The Glycosidic Bond
The Glycosidic Bond
Forming the glycosidic bond
- To make monosaccharides more suitable for transport, storage and to have less influence on a cell’s osmolarity, they are bonded together to form disaccharides and polysaccharides
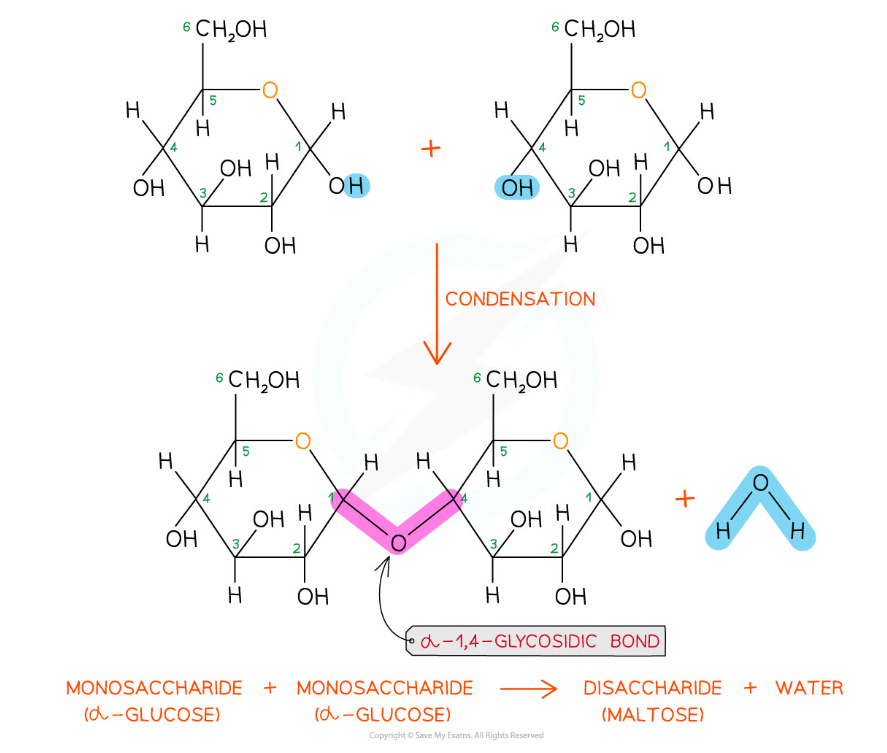
- Disaccharides and polysaccharides are formed when two hydroxyl (-OH) groups (on different saccharides) interact to form a strong covalent bond called the glycosidic bond (the oxygen link that holds the two molecules together)
- Every glycosidic bond results in one water molecule being removed, thus glycosidic bonds are formed by condensation
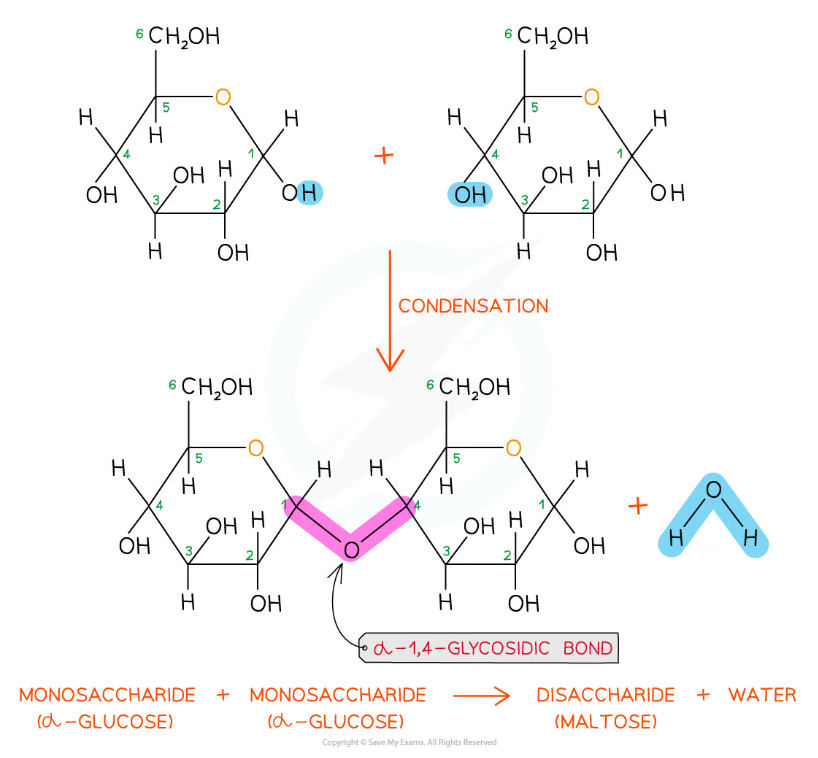
The formation of a glycosidic bond by condensation between two monosaccharides (glucose) to form a disaccharide (maltose)
- Each glycosidic bond is catalysed by enzymes specific to which OH groups are interacting
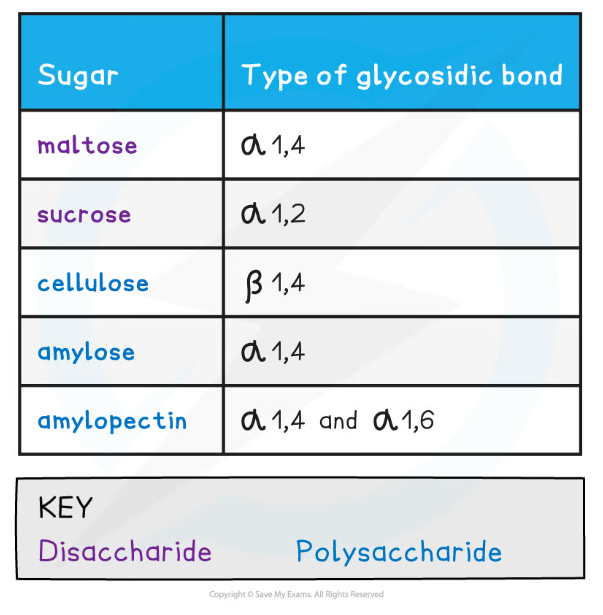
- As there are many different monosaccharides this results in different types of glycosidic bonds forming (e.g maltose has a α-1,4 glycosidic bond and sucrose has a α-1,2 glycosidic bond)
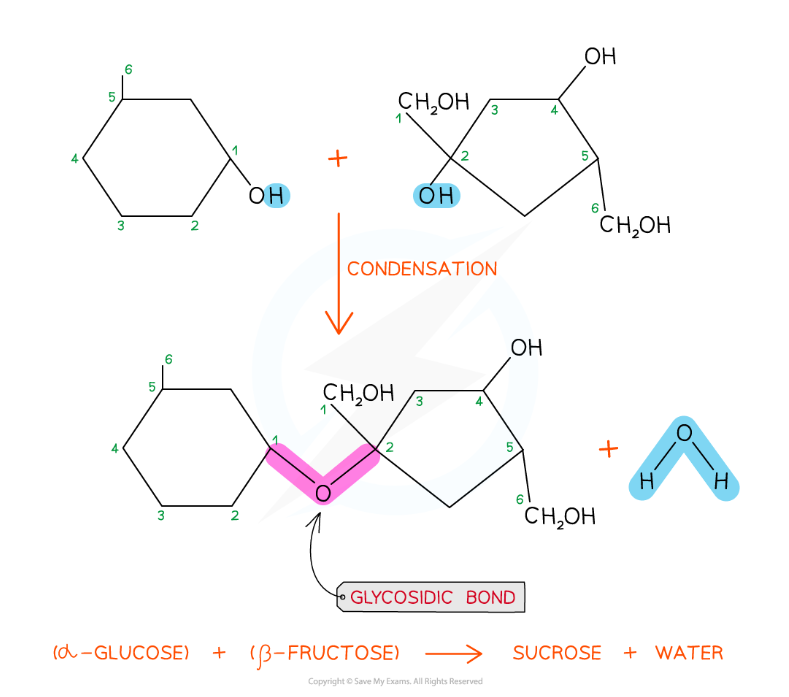
The formation of a glycosidic bond by condensation between α-glucose and β-fructose to form a disaccharide (sucrose)
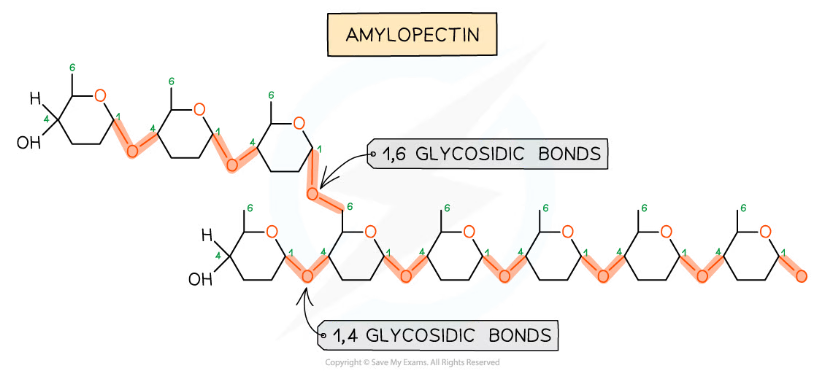
The formation of glycosidic bonds to create a polysaccharide (amylopectin)
Types of Glycosidic Bonds Table
Breaking the glycosidic bond
- The glycosidic bond is broken when water is added in a hydrolysis (meaning ‘hydro’ - with water and ‘lyse’ - to break) reaction
- Disaccharides and polysaccharides are broken down in hydrolysis reactions
- Hydrolytic reactions are catalysed by enzymes, these are different to those present in condensation reactions
- Examples of hydrolytic reactions include the digestion of food in the alimentary tract and the breakdown of stored carbohydrates in muscle and liver cells for use in cellular respiration
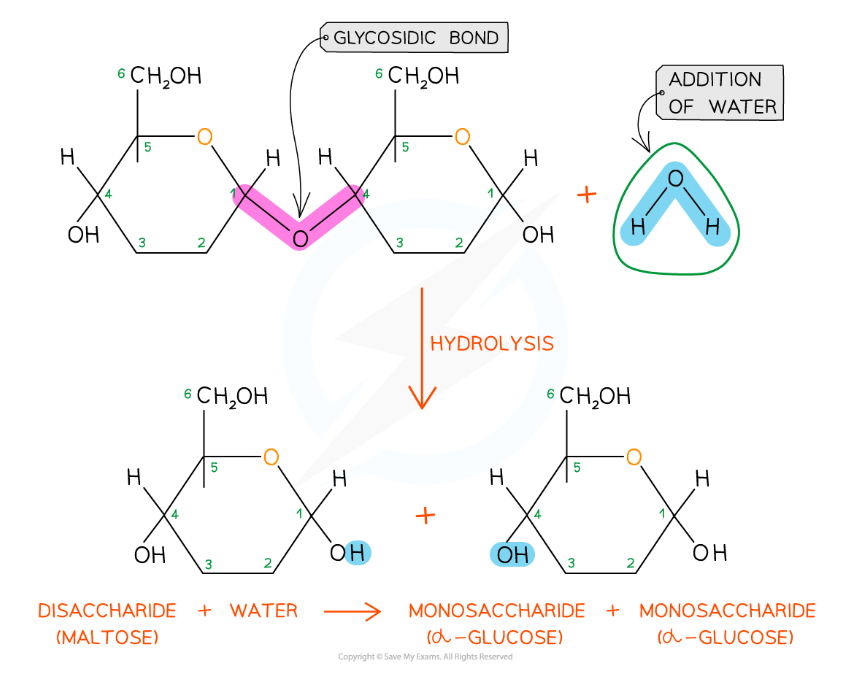
Glycosidic bonds are broken by the addition of water in a hydrolysis reaction
- Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar which gives a negative result in a Benedict’s test. When sucrose is heated with hydrochloric acid this provides the water that hydrolyses the glycosidic bond resulting in two monosaccharides that will produce a positive Benedict's test
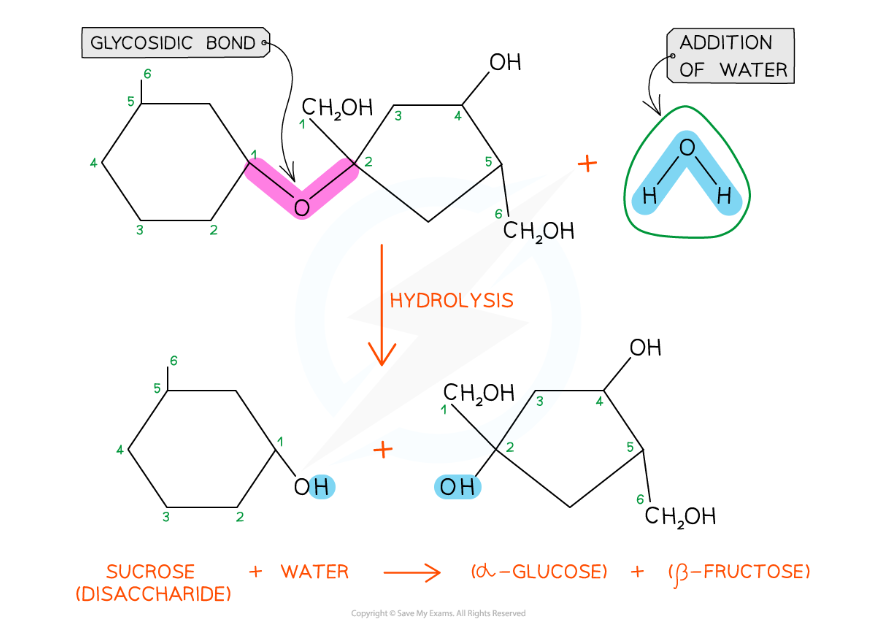
A molecule of glucose and a molecule of fructose are formed when one molecule of sucrose is hydrolysed; the addition of water to the glycosidic bond breaks it
Common disaccharides
- Monosaccharides can join together via condensation reactions to form disaccharides
- A condensation reaction is one in which two molecules join together via the formation of a new chemical bond, with a molecule of water being released in the process
- The new chemical bond that forms between two monosaccharides is known as a glycosidic bond
- To calculate the chemical formula of a disaccharide, you add all the carbons, hydrogens and oxygens in both monomers then subtract 2x H and 1x O (for the water molecule lost)
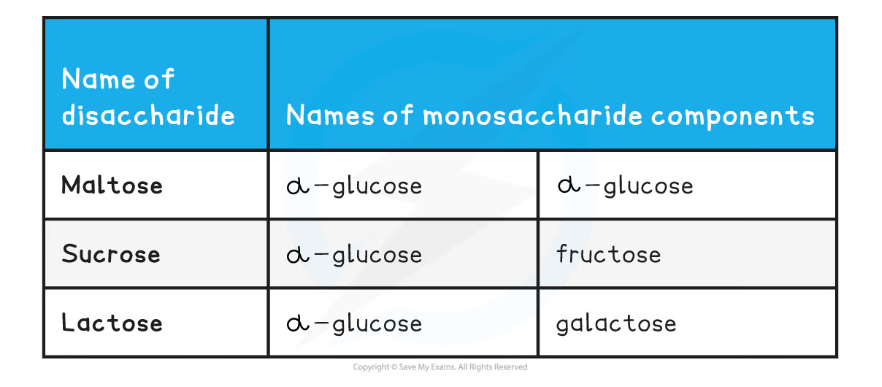
- Common examples of disaccharides include:
- Maltose (the sugar formed in the production and breakdown of starch)
- Sucrose (the main sugar produced in plants)
- Lactose (a sugar found only in milk)
- All three of the common examples above have the formula C12H22O11
Common Disaccharides and their Monosaccharide Monomers Table
The disaccharide maltose is formed from two α-glucose monomers (sub-units)
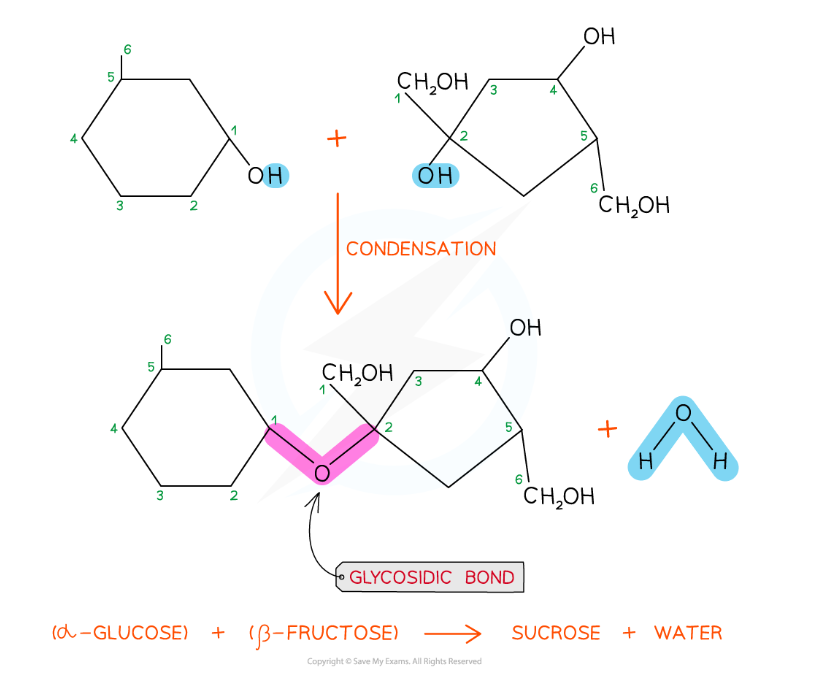
The disaccharide sucrose is formed from α-glucose and fructose monomers (sub-units)
Exam Tip
Make sure you can identify where the glycosidic bond is in a carbohydrate.Remember that disaccharides hydrolyse to two monosaccharides whereas polysaccharides must undergo many hydrolytic reactions until they form monosaccharides.Like glucose, galactose and fructose are monosaccharides and actually have the same molecular formula as glucose. However, the atoms that make up these three monosaccharides are arranged in different ways, meaning they each have slightly different molecular structures, giving them slightly different properties.
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









