- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
OCR A Level Biology:复习笔记2.1.7 Organelles & the Production of Proteins
Organelles & the Production of Proteins
- In cells, many organelles are involved in the production and secretion of proteins
- Organelles are specialised parts of a cell that carry out a particular function
- Some organelles are membrane-bound
- The organelles involved in protein synthesis include:
- Nucleus
- Ribosomes
- Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
- Golgi apparatus
- Cell surface membrane
- The nucleus stores the DNA (that codes for the production of proteins) and also contains the nucleolus, which manufactures ribosomes (required for protein synthesis)
- The DNA from the nucleus is copied into a molecule of mRNA via a process known as transcription
- The mRNA strand leaves the nucleus through a nuclear pore and attaches to a ribosome on the rough endoplasmic reticulum
- The ribosome 'reads' the genetic instructions contained within the mRNA and uses this code to synthesise a protein via a process known as translation
- This protein then passes into the lumen (the inside space) of the rough endoplasmic reticulum to be folded and processed
- Cells that produce a large amount of proteins (e.g. enzyme or hormone-producing cells) have an extensive rough endoplasmic reticulum
- The processed proteins are then transported to the Golgi apparatus (also known as the Golgi body or Golgi complex) in vesicles, which fuse with the Golgi apparatus, releasing the proteins
- The Golgi apparatus modifies the proteins, preparing them for secretion
- Proteins that go through the Golgi apparatus are usually exported (e.g. hormones such as insulin), put into lysosomes (such as hydrolytic enzymes) or delivered to other membrane-bound organelles
- The modified proteins then leave the Golgi apparatus in vesicles
- Finally, these vesicles (containing the final proteins) fuse with the cell surface membrane, releasing the proteins
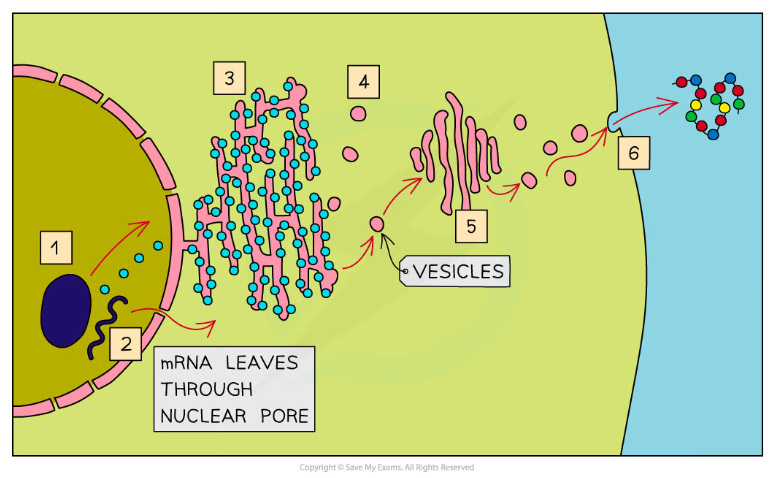
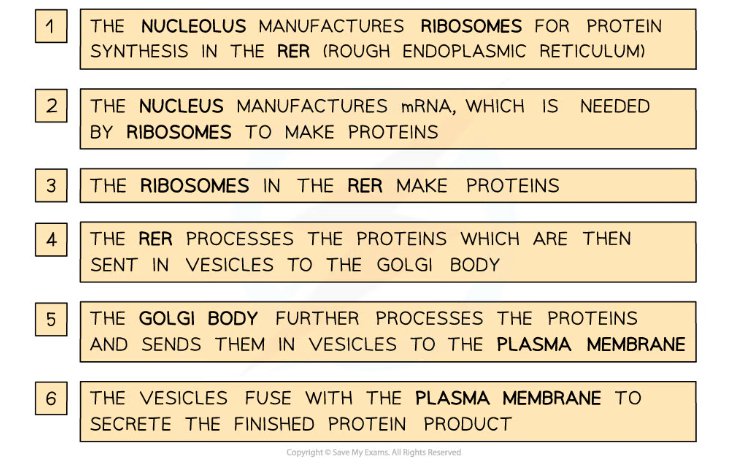
Many organelles are involved in the production and secretion of proteins
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









