- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
OCR A Level Biology:复习笔记1.1.7 Drawing Conclusions
Drawing Conclusions
- Evaluating experimental results and drawing conclusions from them are two very important skills
- Evaluation of results is a different skill from evaluation of the experimental procedure used to obtain those results
- Conclusions can only be drawn from the results once they have been properly evaluated
- For example, during the planning of an experiment, potential limitations of the experimental procedure will have been identified
- Before drawing conclusions, the impact that these limitations could theoretically have had (or may actually have had) on the data collected should be evaluated
- If this evaluation shows these potential impacts to be negligible, a conclusion can more likely be drawn from the results
- If it is decided that the limitations could have had a significant impact on the data, then it is much harder to draw a conclusion and it should be recognised that any conclusions drawn have a greater chance of being incorrect
The importance of precision and accuracy in drawing conclusions
- The precision and accuracy of experimental apparatus used and measurements taken has an important impact on any conclusions made from the results of an experiment
- The precision of a measurement: this is how close the measured values are to each other; if measurements are repeated several times, then they can be described as precise when the values are very similar to, or the same as, each other
- The precision of a measurement is reflected in the values recorded - measurements to a greater number of decimal places are said to be more precise than those to a whole number
- Accuracy: this is how close a measured value is to the true value; the accuracy can be increased by repeating measurements and finding a mean average
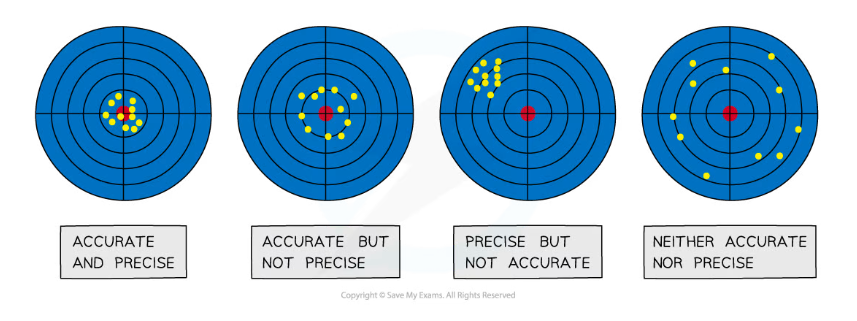
The difference between precise and accurate results
- Most items of apparatus will have a margin of error that can be used in percentage error calculations
- This percentage error will then give an idea of the magnitude of any error and therefore how much of an impact it may have had on the results
- If the percentage error is too high, any conclusions drawn may be rejected or further testing may be required by making improvements to the apparatus used or to the experimental procedure in order to reduce the percentage error
Anomalies
- Experimental errors (also known as operator errors or 'one off' errors) will affect the results of an experiment and can produce anomalies
- These anomalies should be identified during the evaluation of results and before drawing conclusions
- Anomalies can be identified by looking for results or data points on a graph that don't fit with the trend or with other replicates carried out during the experiment
- These anomalous results will show a larger difference from the mean than the rest of the results (a result is often taken to be anomalous if it differs from the mean result by more than 10%)
- The results or 'data' collected from an experiment can be made more reliable if the experiment is repeated several times and anomalies are removed
- This, in turn, allows more valid conclusions to be drawn
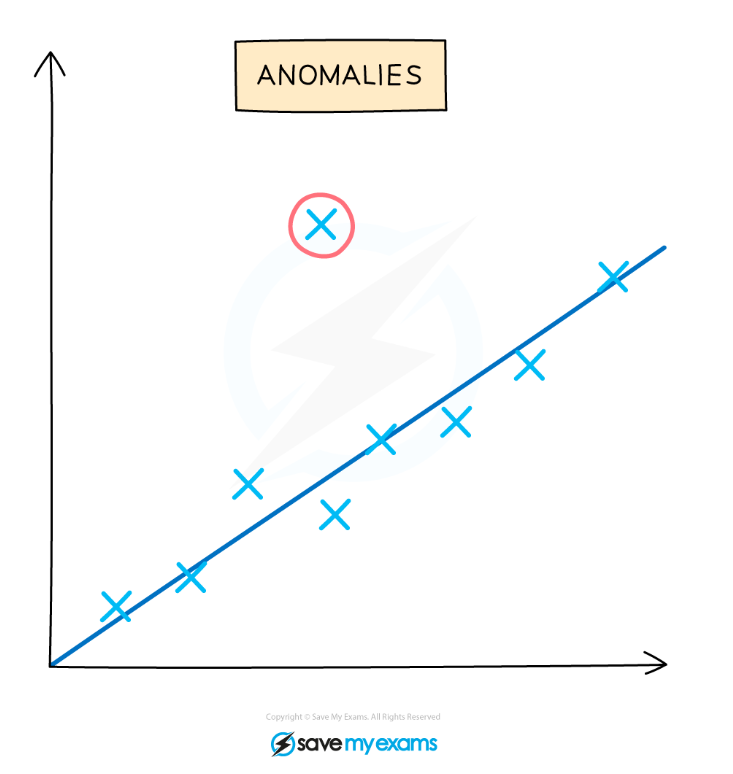
Identifying an anomalous result from a graph
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









