- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel A (SNAB) A Level Biology:复习笔记8.2.7 Action of Drugs on Synapses
Action of Drugs on Synapses
- The chemicals in drugs can have a major impact on the functioning of the brain and nervous system
- Some prescription drugs can have a beneficial effect on those suffering from neurological disorders while recreational drugs can have a damaging or even fatal effect
- Many drugs impact the nervous system by altering the events that occur at a synapse
- Drugs can increase transmission of impulses at a synapse by
- Causing more neurotransmitter to be produced in the synaptic knob
- Causing more neurotransmitter to be released at the presynaptic membrane
- Imitating the effect of a neurotransmitter by binding to and activating receptors on the postsynaptic membrane
- Preventing the breakdown of neurotransmitters by enzymes
- Preventing the reuptake of neurotransmitters by the presynaptic cell
- Drugs can decrease transmission of impulses at a synapse by
- Preventing production of neurotransmitter in the presynaptic knob
- Preventing the release of neurotransmitter at the presynaptic membrane
- Enabling neurotransmitter to gradually leak out of the presynaptic knob so there is little left when an action potential arrives
- The neurotransmitter that leaks out of the cell is destroyed by enzymes
- Binding to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and so preventing neurotransmitters from binding
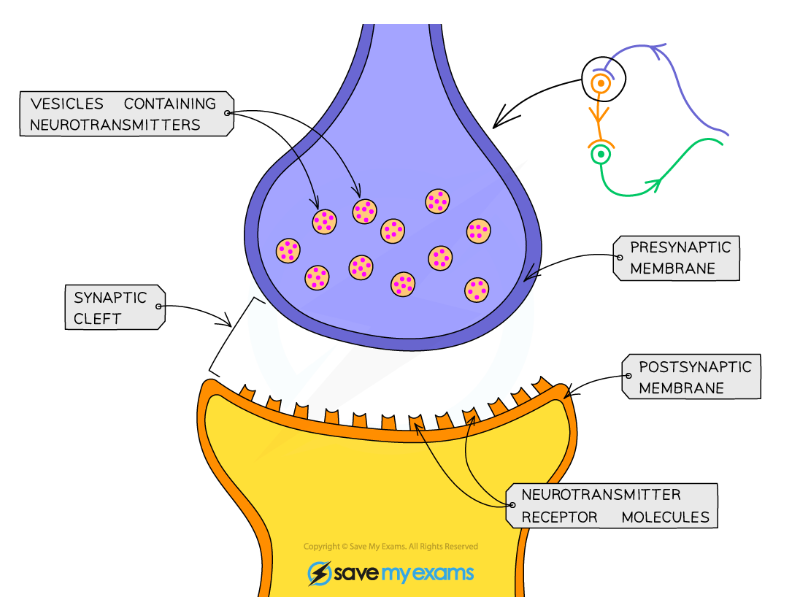
Drugs can influence the transmission of nerve impulses at synapses
MDMA
- MDMA is a recreational drug that is also known as ecstasy
- Its use and sale are criminal offences in most parts of the world
- MDMA effects multiple neurotransmitters, most notably serotonin
- MDMA inhibits the reuptake of serotonin into the presynaptic neurone by binding to the specific proteins that enable serotonin reuptake, located on the presynaptic membrane; this increases the amount of serotonin present in the brain
- Serotonin is usually reabsorbed into the presynaptic neurone to be recycled for future action potentials
- MDMA also triggers the release of further serotonin from presynaptic neurones, further adding to the increase
- MDMA inhibits the reuptake of serotonin into the presynaptic neurone by binding to the specific proteins that enable serotonin reuptake, located on the presynaptic membrane; this increases the amount of serotonin present in the brain
- Serotonin can affect people in many ways including their mood, anxiety and sleep
- When an individual takes MDMA they may feel extreme euphoria and enhanced touch and bodily sensations
L-dopa
- L-dopa is a drug used to treat the symptoms of Parkinson's disease
- It has a very similar structure to dopamine; a neurotransmitter present at lower levels than usual in the brains of those who suffer from Parkinson's disease
- L-dopa is transported from the blood into the brain, where it is converted into dopamine in a reaction catalysed by the enzyme dopa-decarboxylase
- The effect is to increase levels of dopamine in the brain
- Note, dopamine cannot be given directly to those who have Parkinson's disease as it cannot cross the barrier between the blood and the brain
- Increased levels of dopamine mean that more nerve impulses are transmitted in parts of the brain that control movement, giving sufferers better control over their movement and lessening the symptoms of Parkinson's disease
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








