- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel A (SNAB) A Level Biology:复习笔记8.2.1 Brain: Structure & Function
Brain: Structure & Function
- The brain, alongside the spinal cord, is part of the central nervous system (CNS)
- The brain is made of billions of interconnected neurones
- Within the brain are different regions that carry out different functions
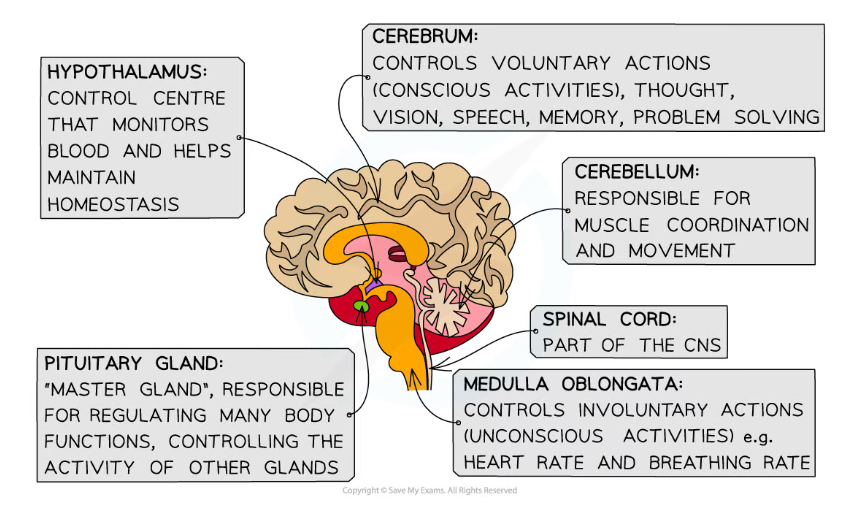
Different regions of the brain carry out different functions
- You need to know the functions of the following brain regions
The cerebrum
- The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain in humans, accounting for about 80% of the total mass of the brain
- It carries out a large variety of functions involved with conscious activities, including:
- Vision
- Hearing
- Speech
- Thinking
- Memory
- The cerebrum is divided into two halves known as the cerebral hemispheres
- The hemispheres are joined together by a band of nerve fibres known as the corpus callosum
- The right hemisphere controls the left side of the body and the left one controls the right side
- The cerebrum has a thin outer layer known as the cerebral cortex or 'grey matter'
- The cerebral cortex consists of the cell bodies of neurones
- It is highly folded, which increases its surface area and allows it to contain a greater number of neurones
- With more neurones in the brain, more neurone connections can be made
- This is important, as the more connections between neurones in the brain, the greater the ability of the brain to carry out more complex behaviours
- Beneath the cerebral cortex or grey matter layer is the 'white matter'
- The white matter consists of the myelinated axons of neurones
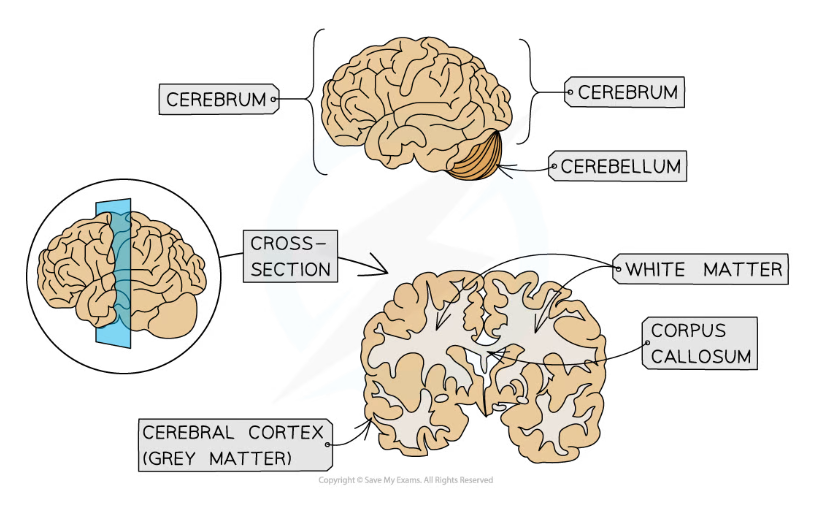
The cerebrum consists of two hemispheres joined by the corpus callosum
The hypothalamus
- The hypothalamus monitors the blood as it flows through the brain and, in response, releases hormones or stimulates the neighbouring pituitary gland to release hormones
- The hypothalamus plays an important role in some homeostatic mechanisms
- Hypothalamus functions include
- Regulating body temperature
- The hypothalamus monitors blood temperature and initiates a homeostatic response if this temperature gets too high or too low
- Osmoregulation
- Cells in the hypothalamus monitor the water balance of the blood and releases the hormone ADH if the blood becomes too concentrated
- ADH increases absorption of water in the kidneys
- Cells in the hypothalamus monitor the water balance of the blood and releases the hormone ADH if the blood becomes too concentrated
- Regulating digestive activity
- The hypothalamus regulates the hormones that control appetite as well as the secretion of digestive enzymes
- Controlling endocrine functions
- The hypothalamus causes the pituitary gland to release hormones that control a variety of processes e.g. metabolism, growth and development, puberty, sexual functions, sleep, and mood
- Regulating body temperature
The cerebellum
- The cerebellum coordinates movement
- This includes balance; a highly complex function that requires coordination between multiple parts, including the eyes, semicircular canals in the ears, and many muscles
The medulla oblongata
- Also known as the medulla
- The medulla contains co-ordination centres that control different functions e.g.
- The cardiac centre controls heart rate
- The respiratory centre controls breathing rate
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









