- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel A (SNAB) A Level Biology:复习笔记8.1.2 Neurones: Structure & Function
Neurones: Structure & Function
- Neurones are specialised cells of the nervous system which carry electrical impulses around the body
- A bundle of neurones is known as a nerve
- There are different types of neurones, but the following features are found in all types
- A long fibre known as an axon
- A cell body that contains the nucleus and other cellular structures
- The end of the axon, known as the axon terminal, has many nerve endings
- The nerve endings at the axon terminals allow neurones to connect to and receive impulses from other neurones, forming a network for easy communication
- Some neurones are myelinated, meaning that their axon is insulated by a fatty layer known as the myelin sheath
- The myelin sheath is made up of specialised cells known as Schwann cells which wrap themselves around the axon
- There are uninsulated gaps between the Schwann cells known as the nodes of Ranvier
- Electrical impulses in myelinated cells do not travel down the whole axon, but jump from one node to the next, speeding up impulse transmission
- In non-myelinated neurones the axon is not insulated by Schwann cells
- The impulse travels more slowly as it moves through the entire length of the axon
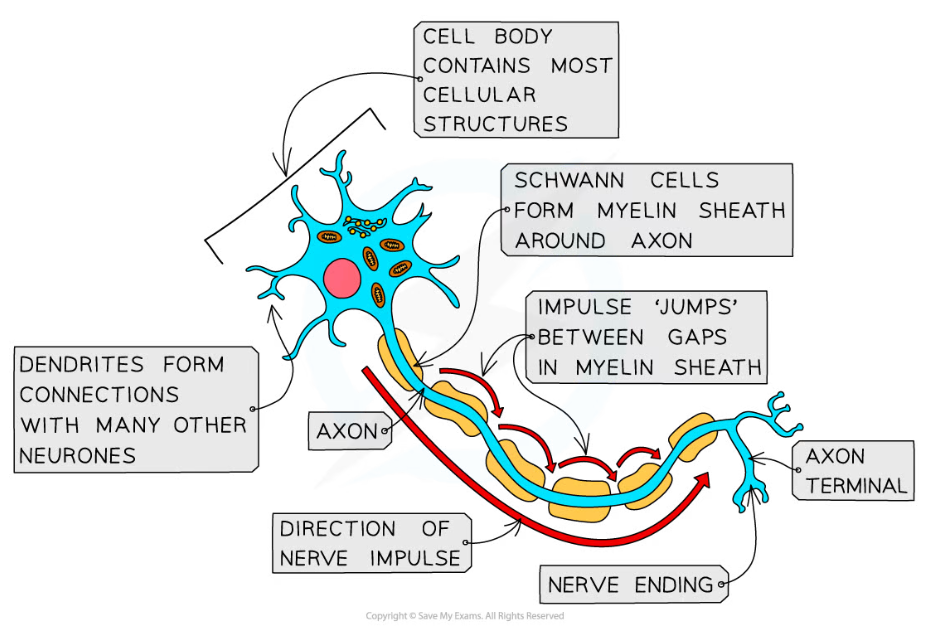
Neurones have a long axon, a cell body, and an axon terminal, and some neurones are myelinated
- There are three main types of neurones
- Sensory neurones carry impulses from receptors to the brain and spinal cord in the CNS
- Relay neurones are found entirely within the CNS and connect sensory and motor neurones
- Motor neurones carry impulses from the CNS to effector muscles or glands
- Each type of neurone has a slightly different structure
- Motor neurones
- A large cell body at one end that lies within the spinal cord or brain
- Many highly-branched dendrites extending from the cell body, providing many connections with the axon terminals of other neurones
- Relay neurones
- Short neurones with axons and highly branched dendrites
- Sensory neurones
- A cell body that branches off in the middle of the axon and has no dendrites
- The axon terminal is attached to a receptor cell
- The section of neurone that links the axon terminal with the cell body is known as a dendron
- The section of neurone that connects the cell body with the CNS is the axon
- Motor neurones
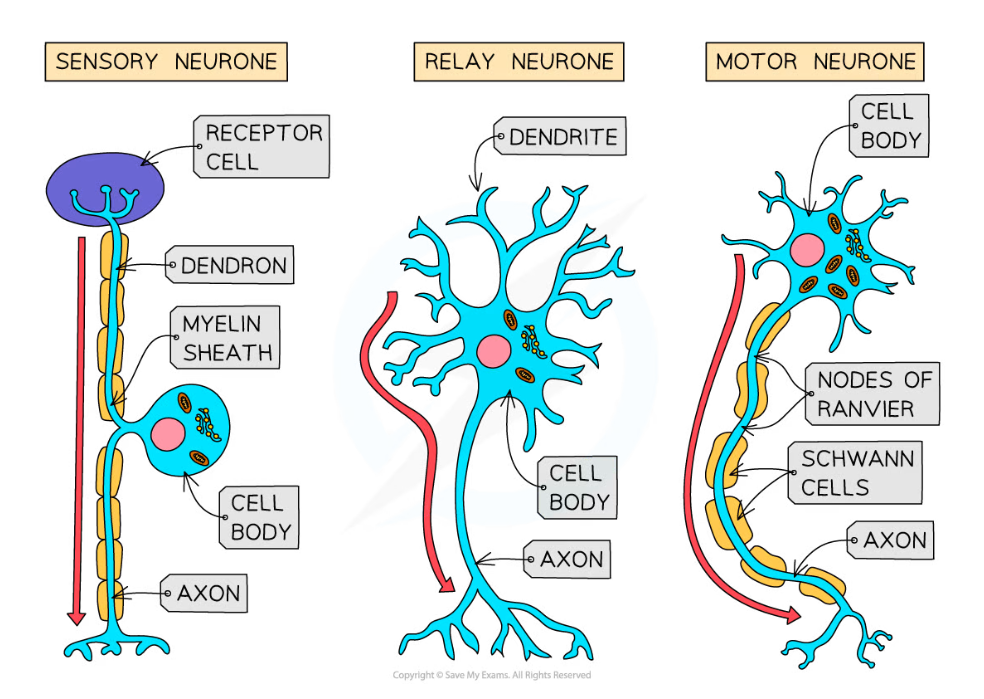
Different types of neurone differ in both structure and function
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








