- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
EDEXCEL IGCSE CHEMISTRY: DOUBLE SCIENCE 复习笔记:3.1.3 Energetics Calculations
EDEXCEL IGCSE CHEMISTRY: DOUBLE SCIENCE 复习笔记:3.1.3 Energetics Calculations
Calculate Heat Energy Change
- In order the calculate heat energy changes you need to know the mass of the substance being heated, the temperature change and the specific heat capacity of the substance
- The specific heat capacity (c) is the energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 g of a substance by 1 K
- The specific heat capacity of water is 4.18 J g-1 K-1
- The energy transferred as heat can be calculated by:
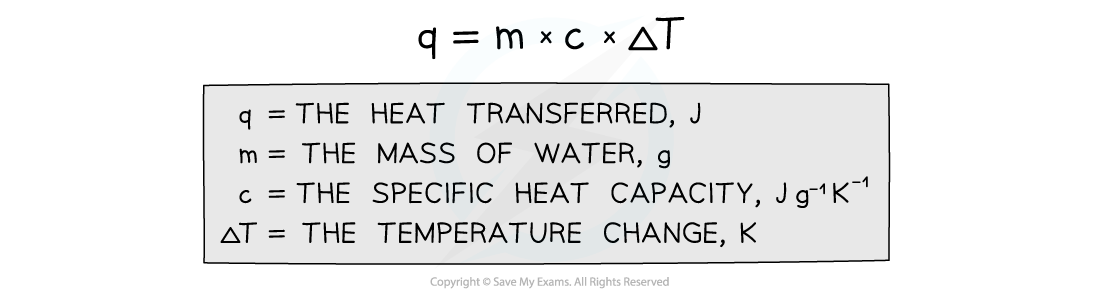
Equation for calculating energy transferred in a calorimeter
- The temperature change in Kelvin is the same as the temperature change in degrees Celsius
Worked Example
Excess iron powder was added to 100.0 cm3 of 0.200 mol dm-3 copper(II)sulfate solution in a calorimeter. The reaction equation was as followsFe (s) + CuSO4 (aq) → FeSO4 (aq) + Cu (s)The maximum temperature rise was 7.5 oC. Determine the heat energy change of the reaction, in kJ
Answer:
The solution is assumed to have the same density as water, so 100.0 cm3 has a mass of 100 g
q = m x c x ΔT
q = 100 g x 4.18 J g-1 K-1 x 7.5 K = – 3135 J = -3.13 kJ
Worked Example
1.023 g of propan-1-ol (M = 60.11 g mol-1) was burned in a spirit burner and used to heat 200 g of water in a copper calorimeter. The temperature of the water rose by 30 oC.Calculate the heat energy change for the combustion of propan-1-ol using this data.
Answer:
Calculate q
q = m x c x ΔT
q = 200 g x 4.18 J g-1 K-1 x 30 K = – 25 080 J = -25 kJ
Calculate Molar Enthalpy Change
- Molar enthalpy change is the heat energy change per mole of substance
- The symbol is ΔH and it has the unit kJ per mole
- If is found by first determining the heat energy change for the reaction, q, and then dividing by the number of moles, n, of the substance
molar enthalpy change = heat change for the reaction ÷ number of moles
ΔH = q ÷ n
Worked Example
The energy from 0.01 mol of propan-1-ol was used to heat up 250 g of water. The temperature of the water rose from 298 K to 310 K (the specific heat capacity of water is 4.18 J g-1 K-1.Calculate the molar enthalpy of combustion.
Answer:
Step 1: q = m x c x ΔT
m (of water) = 250 g
c (of water) = 4.18 J g-1 K-1
ΔT (of water) = 310 – 298 K
= 12 K
Step 2: q = 250 x 4.18 x 12
= 12 540 J
Step 3: This is the energy released by 0.01 mol of propan-1-ol
Total energy ΔH = q ÷ n = 12 540 J ÷ 0.01 mol = 1 254 000 J mol-1
Total energy = – 1254 kJ mol-1
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









