- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel A (SNAB) A Level Biology:复习笔记4.1.9 Conservation of Biodiversity
Conservation of Biodiversity
- When species go extinct it leads to an overall decrease in biodiversity
- In recent times many species have already gone extinct, while others are endangered
- An endangered species is a species that is being threatened with extinction
- It is therefore important that these species are conserved to prevent them from going extinct
- Conservation of endangered species can be approached in several different ways
- Ideally a species should be kept in their natural habitat, as all the support systems they need to maintain life already exist there
- National parks and marine parks are examples of conservation methods that do this
- When it is not possible to do this endangered species can be captured and placed in captivity for conservation efforts
- Zoos and botanic gardens take part in conservation programmes
- Scientists have also come up with several methods to try and ensure the long-term survival of endangered species through frozen zoos and seed banks
- Conservation of species refers to protecting and managing them for future generations
Seed banks
- A seed bank is a facility that conserves plant diversity by drying and storing seeds in a temperature-controlled environment
- Usually, seeds of the same species are collected from different sites to maintain genetic diversity
- If the plant species goes extinct then the seeds can be used to grow them again
- Seeds can only be stored for so long. After a certain period of time the stored seeds are grown into plants and fresh seeds for storage are taken from those plants
- The Svalbard Global Seed Vault in Norway has almost 1 million species of plant seed. It is located in the Arctic Circle, within ideal environmental conditions
- Many organisations send seeds from crop plants to be stored there for safekeeping
- Some plants have seeds that cannot be frozen such as coffee and cocoa plants
- In order to preserve the genetic diversity of these plants successive generations must be grown or tissue cultures taken
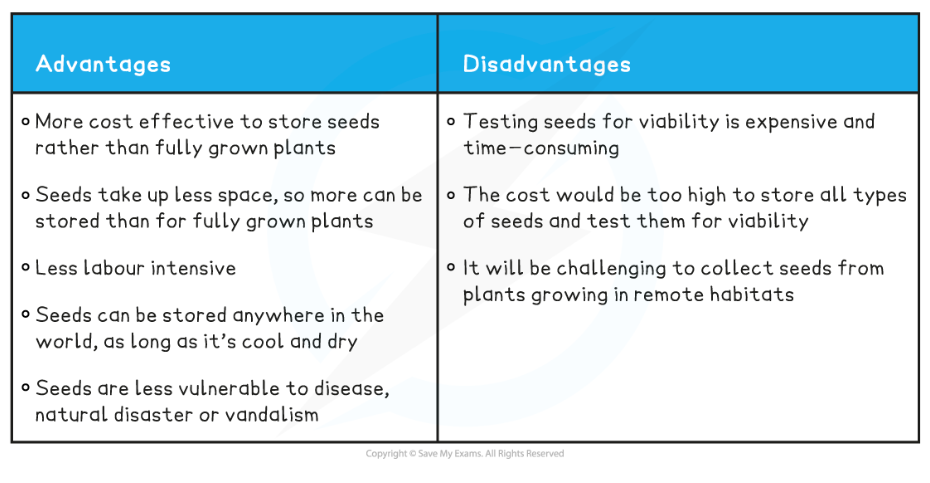
- There are advantages and disadvantages of using seed banks
- Seed banks make valuable contributions to scientific research
- It provides an opportunity to investigate how to successfully grow plants from seeds
- They provide a stock of endangered plants that could be useful to humans (e.g. medicinal plant species, crop plant species) taking pressure off of wild populations
- It is important to note, however, that data gathered from seed banks may not be representative of wild populations due to the small, genetically limited, sample size
- Seed banks also educate people about endangered species and increase interest in conserving these species
- For example, people can be trained to set up local seed banks, which involves the community
Advantages & Disadvantages of Seed Banks Table
Zoos
- Zoos can also contribute to the conservation of endangered animal species
- Captive breeding programmes can breed individuals of a species so their offspring can be released into the wild
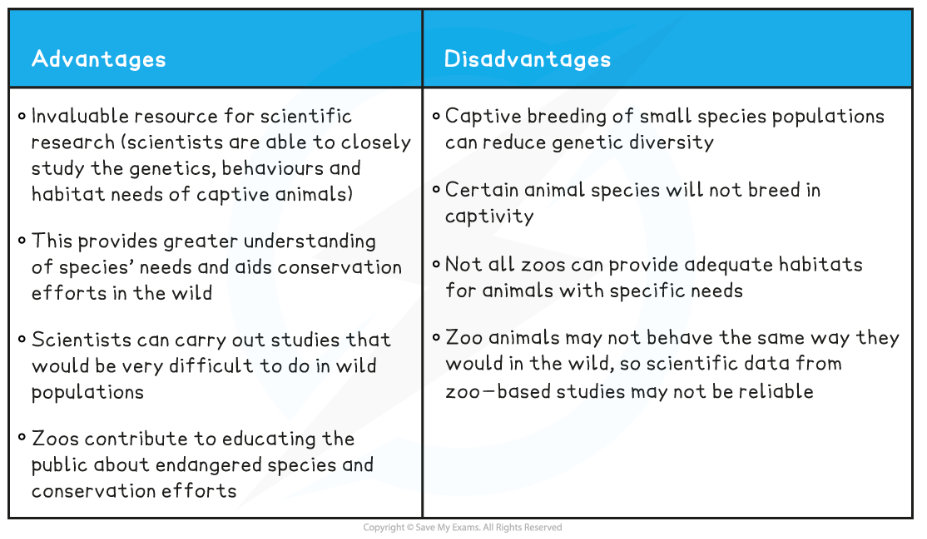
- Zoos are an invaluable resource for scientific research
- Scientists are able to closely study animal’s genetics, behaviours and habitat needs
- There are some problems with zoos and their role in conservation:
- Captive breeding of small species populations can reduce genetic diversity
- Certain animal species will not breed in captivity
- Not all zoos can provide adequate habitats for animals with specific needs
- Many people question the ethics of keeping animals in captivity
- There are stories of both success and failure when it comes to zoos and conservation:
- The oryx is an antelope-like species that was saved from extinction and reintroduced into the wild in Africa thanks to zoos and captive breeding programmes
- Pandas have been in captive breeding programs for over 60 years and not a single panda has been reintroduced into the wild
- Zoos make a valuable contribution to scientific research in a variety of ways:
- They provide information about the specific needs (behavioural, physiological, nutritional) of different animal species, which aids conservation efforts in the wild
- They can carry out studies that would be very difficult to do in wild populations
- Animals in zoos may not behave the same way they would in the wild, so this raises questions about the reliability of the data from some zoo-based studies
- Zoos contribute to educating people about endangered species by bringing them close to these organisms and increasing public enthusiasm for, and public engagement with, conservation efforts
Advantages & Disadvantages of Zoos Table
Reintroduction back into the wild
- Plants and animals from these facilities can be released back into their natural habitat, which holds certain benefits:
- This will help prevent them from going extinct in the wild
- Organisms that rely on these plants and animals for food or habitat may also benefit from their presence
- This contributes toward restoring lost or degraded habitats
- Reintroduction may have some negative effects too:
- These organisms may carry new diseases that will harm other organisms living in that habitat
- Reintroduced animals may lack the ability to find food or communicate effectively with members of their own species
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








