- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel A (SNAB) A Level Biology:复习笔记4.1.5 Natural Selection
Natural Selection can lead to Adaptation & Evolution
- Variation exists within a species population
- Variation refers to the differences between individuals. It can be interspecific (between different species) or intraspecific variation (between individuals of the same species)
- Some of this variation is due to random mutations, which introduce new alleles into a population
- This means that some individuals within the population possess different phenotypes due to genetic variation in the alleles they possess
- Environmental factors affect the chance of survival of an organism; they are said to act as a selection pressure
- Predation, disease and competition are all examples of selection pressures, which make it difficult for all individuals in a population to survive
- Selection pressures increase the chance of individuals with a specific phenotype surviving and reproducing over others
- The advantageous alleles that code for the favourable phenotype will be passed on to offspring
- When selection pressures act over several generations of a species, they have an effect on the frequency of alleles in a population through natural selection
- Natural selection is the process by which individuals with a favourable phenotype are more likely to survive and pass on their alleles to their offspring so that the advantageous alleles increase in frequency over time and generations
- Individuals that do not possess the advantageous alleles will most likely not survive long enough to reproduce, therefore reducing competition for resources
- This will decrease the frequency of these non-advantageous alleles over time in a population
- These changes in allele frequency will ultimately lead to evolution within the population
Evidence for evolution by natural selection
- The theory of evolution by natural selection was first suggested by Charles Darwin
- As evidence mounted in favour of this theory, it became increasingly accepted by scientists
- In science, evidence provides confidence in theories until the point where enough evidence is gathered in order to accept the theory as an accepted scientific explanation
- The peppered moth is an example of how natural selection leads to evolution over time
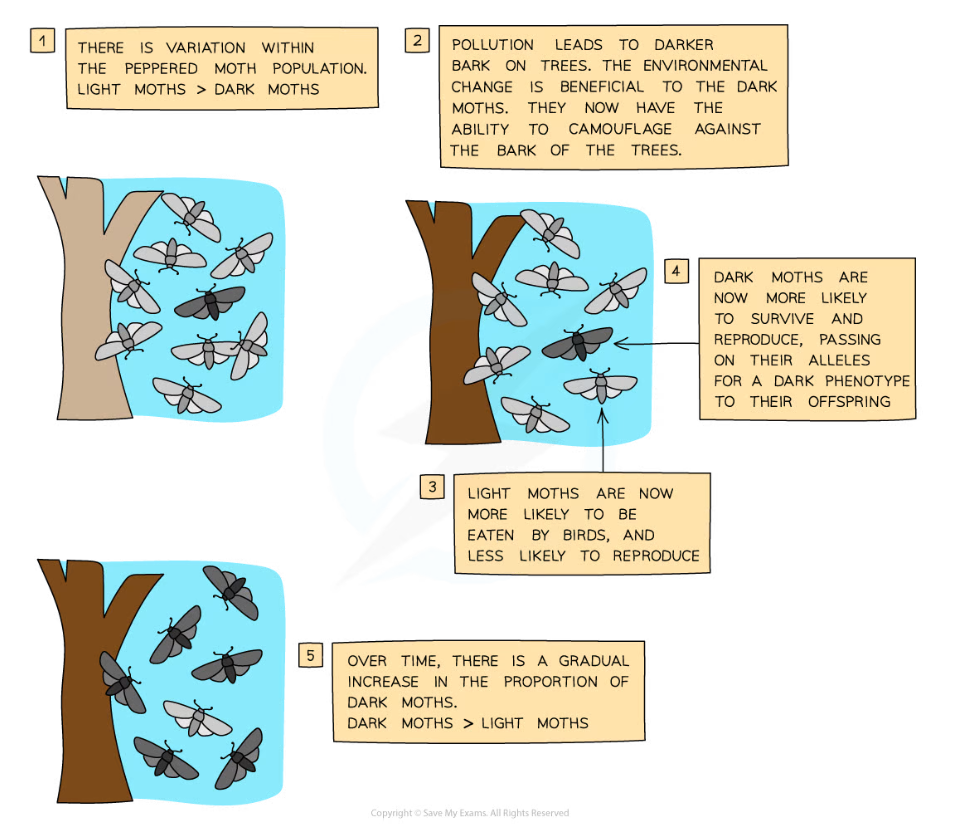
The peppered moth is a well-known example of how natural selection leads to evolution
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








