- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel A (SNAB) A Level Biology:复习笔记1.2.5 Monosaccharides
Monosaccharides: Structure
- Carbohydrates are one of the main carbon-based compounds in living organisms
- All molecules in this group contain C, H and O
- Carbon atoms are key to the structure of organic compounds because
- Each carbon atom can form covalent bonds; this makes the compounds very stable
- Covalent bonds are so strong they require a large input of energy to break them
- Carbon atoms can form covalent bonds with oxygen, nitrogen and sulfur
- Carbon atoms can bond to form straight chains, branched chains, or rings
- Each carbon atom can form covalent bonds; this makes the compounds very stable
- Carbon atoms are key to the structure of organic compounds because
- Carbon compounds can form small, single subunits, or monomers, that bond with many repeating subunits to form large molecules, or polymers
- This is a process called polymerisation
- The three types of carbohydrates are monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides
Monosaccharides
- Monosaccharides are the monomers of carbohydrate; they can join together to make carbohydrate polymers
- Monosaccharides are simple carbohydrates
- Monosaccharides are sugars
- There are different types of monosaccharide formed from molecules with varying numbers of carbon (C) atoms, for example
- Triose (3C) eg. glyceraldehyde
- Pentose (5C) eg. ribose
- Hexose (6C) eg. glucose
- Glucose is a well known example of a monosaccharide
- Glucose is a hexose sugar
- The six carbons that make up glucose form a ring structure
- Carbons 1-5 form a ring, while carbon 6 sticks out above the ring
- Glucose comes in two forms; alpha (α) and beta (β)
- The forms of glucose are almost identical; they differ only in the location of the H and OH groups attached to carbon 1
- Alpha glucose has the H above carbon 1 and the OH group below
- Remember = alpha has the H above
- Beta glucose has the H below carbon 1 and the OH group above
- Remember = beta has the H below
- Alpha glucose has the H above carbon 1 and the OH group below
- The forms of glucose are almost identical; they differ only in the location of the H and OH groups attached to carbon 1
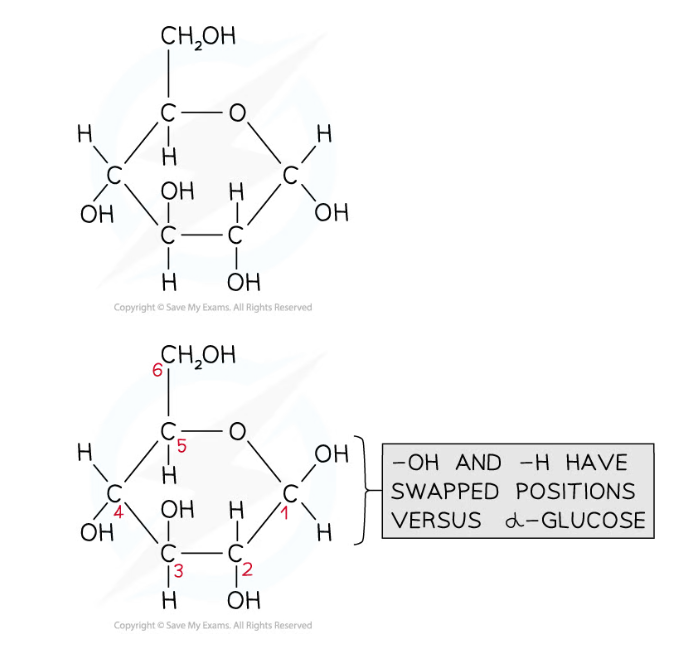
Alpha glucose (top) has the hydrogen above carbon 1 and the OH group below, while beta glucose (bottom) has the hydrogen below carbon 1 and the OH group above
Monosaccharides: Function
- The main function of monosaccharides is to store energy within their bonds
- When the bonds are broken during respiration, energy is released
- The structure of glucose is related to its function as the main energy store for animals and plants
- It is soluble so can be transported easily
- It has many covalent bonds which store energy
- Monosaccharides can combine through condensation reactions to form larger carbohydrates
- Some monosaccharides are used to form long, structural fibers, which can be used as cellular support in some cell types
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









