- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel A Level Maths: Mechanics:复习笔记2.3.1 Deriving the suvat Formulae
Deriving the suvat Formulae
What is suvat?
- suvat is an acronym for the five quantities used when modelling motion in a straight-line with constant acceleration
- s – displacement (from the starting point)
- u – initial velocity
- v – final velocity
- a – acceleration
- t – time
- All except time are vector quantities and can be negative
- time is a scalar quantity
What are the suvat (constant acceleration) equations?
- The five equations for motion in a straight line are:
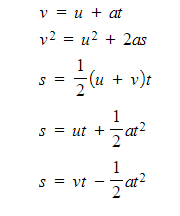
- The equations can only be used when the motion has constant acceleration
- All equations connect four of the five quantities
- Knowing any three allows a fourth to be found
- The equations are provided in the exam
How do I derive the suvat equations?
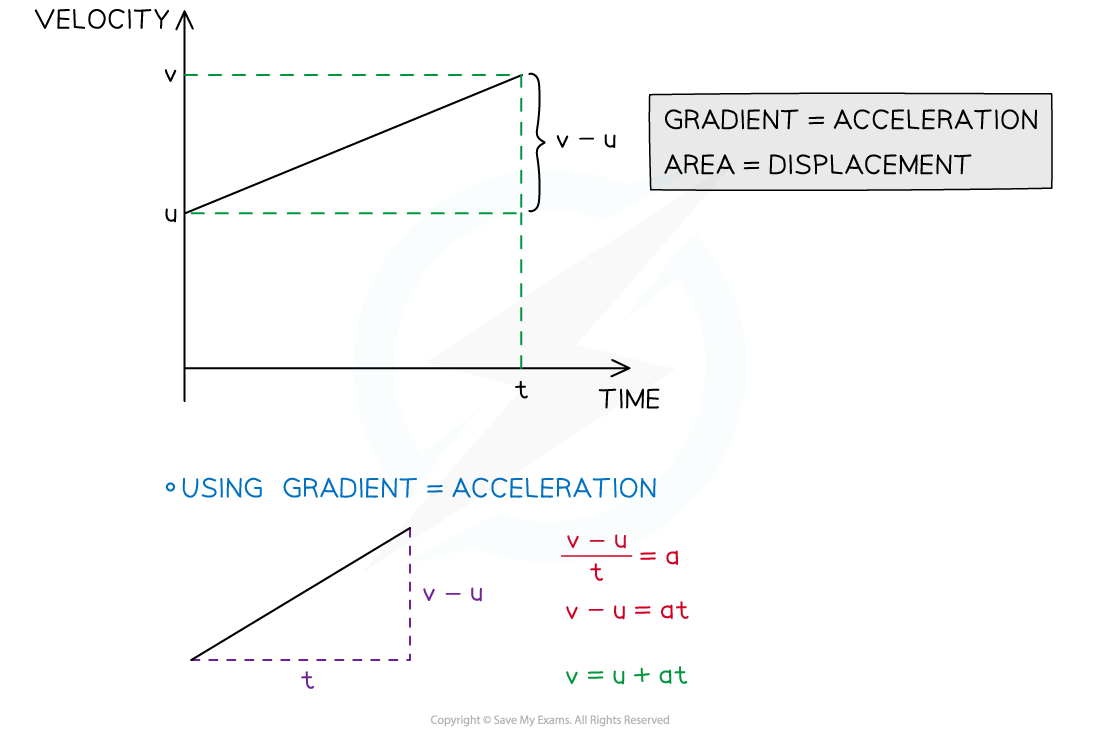
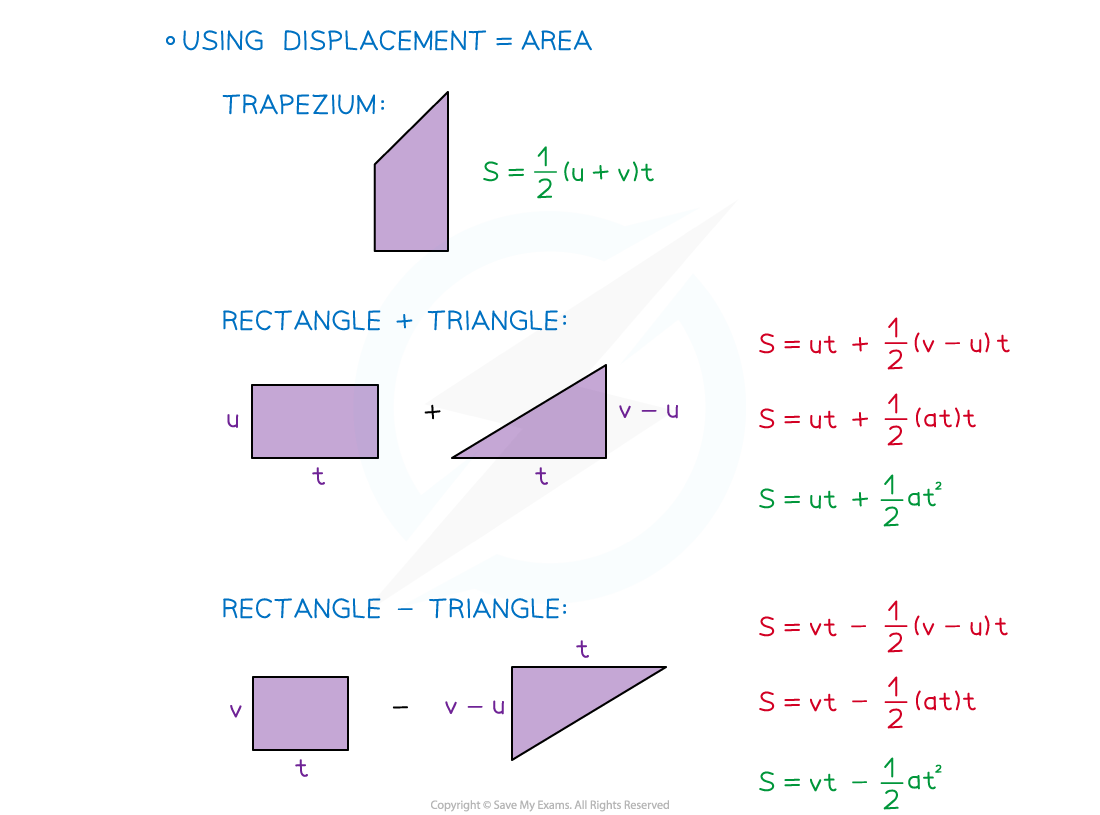
- The four equations that involve time can be derived from a velocity-time graph
- The velocity-time graph will be a straight line as the acceleration is constant
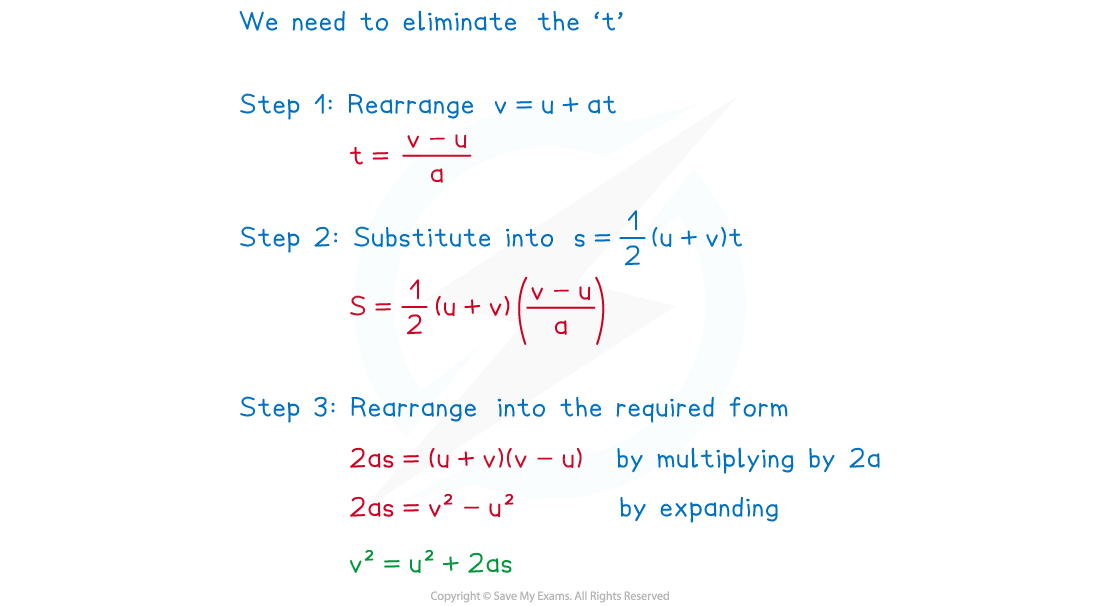
- The fifth equation can be found by choosing any two of the equations and eliminating the t variable (see the worked example)
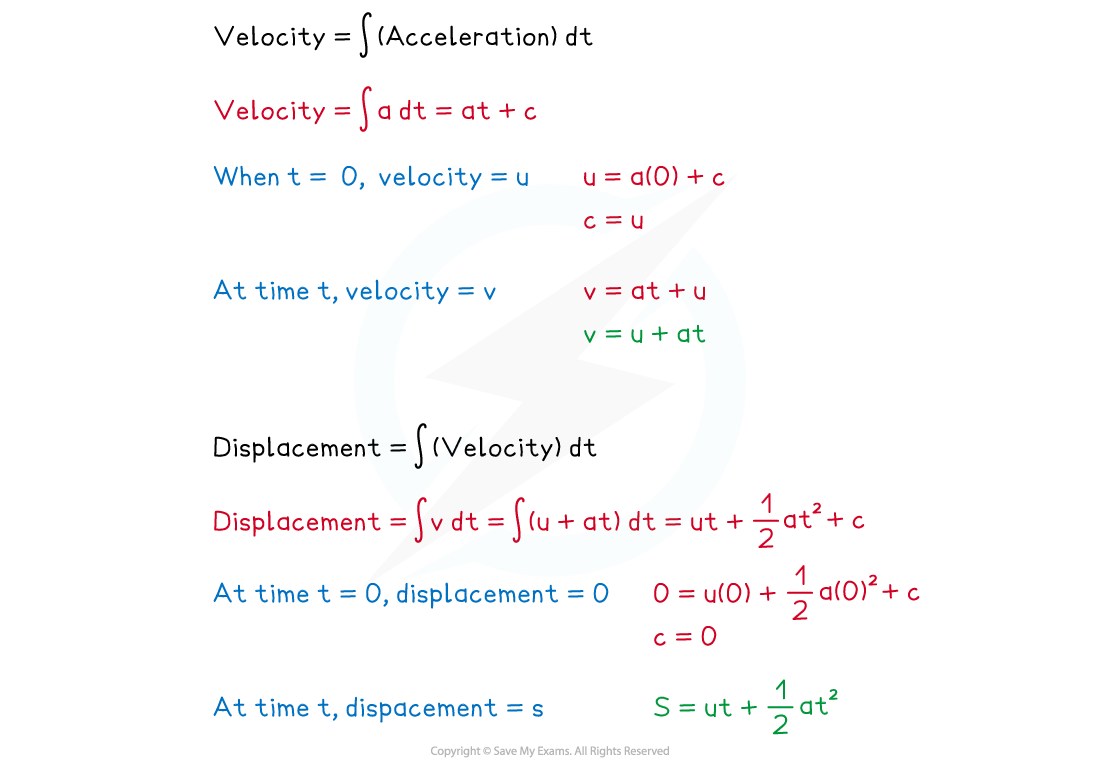
- Two of the equations can also be derived using calculus
- Velocity is found by integrating acceleration
- Displacement is found by integrating velocity
Worked Example
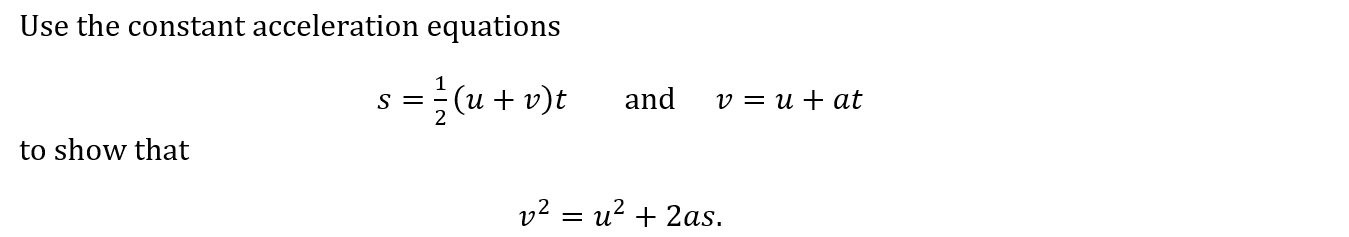
Use the constant acceleration equations
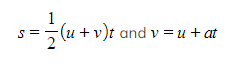
to show that
![]() .
.
Exam Tip
- If you are asked to derive one of the formulae then the question will likely give you a hint as to which method to use. They may provide a velocity-time graph. Make sure you show each step and state any reasons such as the gradient of the graph being the acceleration.
- If the question does not ask you to derive the formulae, then you can use them freely without proof.
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








