- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel A Level Further Maths: Core Pure:复习笔记8.1.3 Modelling using First Order Differential Equations
Modelling using First Order Differential Equations
Why are differential equations used to model real-world situations?
- A differential equation is an equation that contains one or more derivatives
- Derivatives deal with rates of change, and with the way that variables change with respect to one another
- Therefore differential equations are a natural way to model real-world situations involving change
- Most frequently in real-world situations we are interested in how things change over time, so the derivatives used will usually be with respect to time t
How do I set up a differential equation to model a situation?
- An exam question may require you to create a differential equation from information provided
- The question will provide a context from which the differential equation is to be created
- Most often this will involve the rate of change of a variable being proportional to some function of the variable
-
- For example, the rate of change of a population of bacteria, P, at a particular time may be proportional to the size of the population at that time
-
- The expression ‘rate of’ (‘rate of change of…’, ‘rate of growth of…’, etc.) in a modelling question is a strong hint that a differential equation is needed, involving derivatives with respect to time t
-
- So with the bacteria example above, the equation will involve the derivative
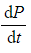
- So with the bacteria example above, the equation will involve the derivative
-
- Recall the basic equation of proportionality
- If y is proportional to x, then y = kx for some constant of proportionality k
- So for the bacteria example above the differential equation needed would be
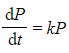
- So for the bacteria example above the differential equation needed would be
- The precise value of k will generally not be known at the start, but will need to be found as part of the process of solving the differential equation
- It can often be useful to assume that k > 0 when setting up your equation
- In this case, -k will be used in the differential equation in situations where the rate of change is expected to be negative
- So in the bacteria example, if it were known that the population of bacteria was decreasing, then the equation could instead be written
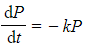
- If y is proportional to x, then y = kx for some constant of proportionality k
- Often scenarios will involves multiple things than affect the rate
- If something causes the variable to increase then that term will be added to the rate of change
- Such as water flowing into a space
- If something causes the variable to decrease then that term will be subtracted from the rate of change
- Such as water flowing out of space
- If something causes the variable to increase then that term will be added to the rate of change
Worked Example
a) In a particular pond, the rate of change of the area covered by algae, A, at any time t is directly proportional to the square root of the area covered by algae at that time. Write down a differential equation to model this situation.

b) Newton’s Law of Cooling states that the rate of change of the temperature of an object, T, at any time t is proportional to the difference between the temperature of the object and the ambient temperature of its surroundings, Ta , at that time. Assuming that the object starts off warmer than its surroundings, write down the differential equation implied by Newton’s Law of Cooling.
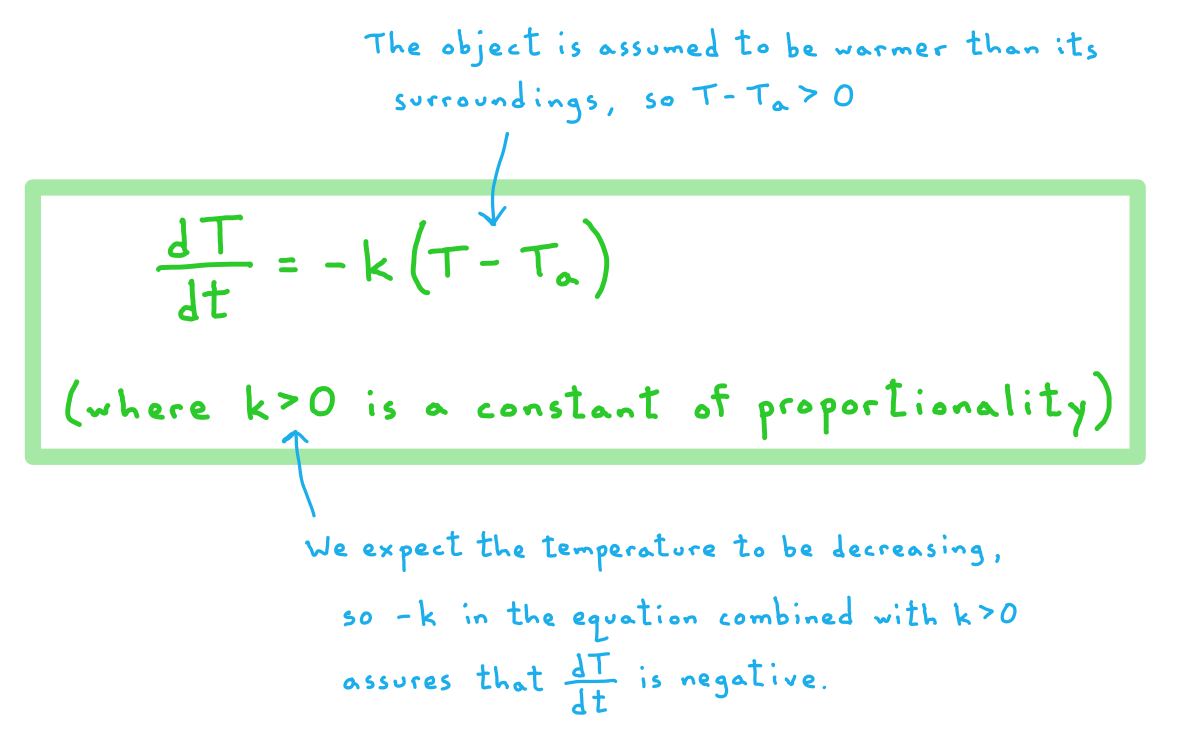
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









