- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel IGCSE Biology: Double Science 复习笔记 3.2.6 Mutation
Edexcel IGCSE Biology: Double Science 复习笔记 3.2.6 Mutation
Mutations
- Mutations are rare, random changes that occur in the sequence of DNA bases in a gene or a chromosome
- Mutations occur continuously
- As the DNA base sequence determines the sequence of amino acids that make up a protein, mutations in a gene can sometimes lead to a change in the protein that the gene codes for
- Most mutations do not alter the protein or only alter it slightly so that its appearance or function is not changed
- There are different ways that a mutation in the DNA base sequence can occur
Insertions
- A new base is randomly inserted into the DNA sequence
- An insertion mutation changes the amino acid that would have been coded for by the group of three bases in which the mutation occurs
- Remember – every group of three bases in a DNA sequence codes for an amino acid
- An insertion mutation also has a knock-on effect by changing the groups of three bases further on in the DNA sequence
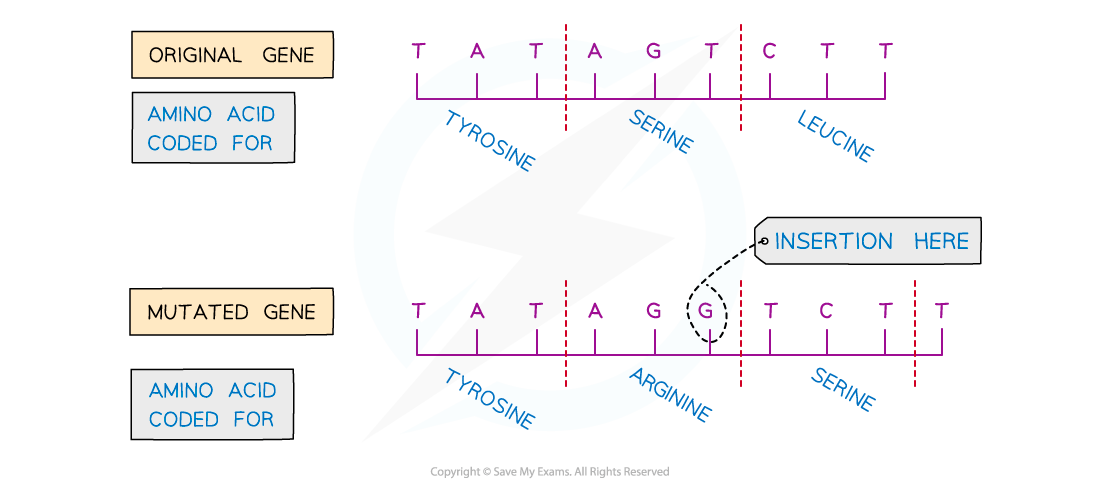
An example of an insertion mutation
Deletions
- A base is randomly deleted from the DNA sequence
- Like an insertion mutation, a deletion mutation changes the amino acid that would have been coded for by the group of three bases in which the mutation occurs
- Like an insertion mutation, a deletion mutation also has a knock-on effect by changing the groups of three bases further on in the DNA sequence
Substitutions
- A base in the DNA sequence is randomly swapped for a different base
- Unlike an insertion or deletion mutation, a substitution mutation will only change the amino acid for the group of three bases in which the mutation occurs; it will not have a knock-on effect
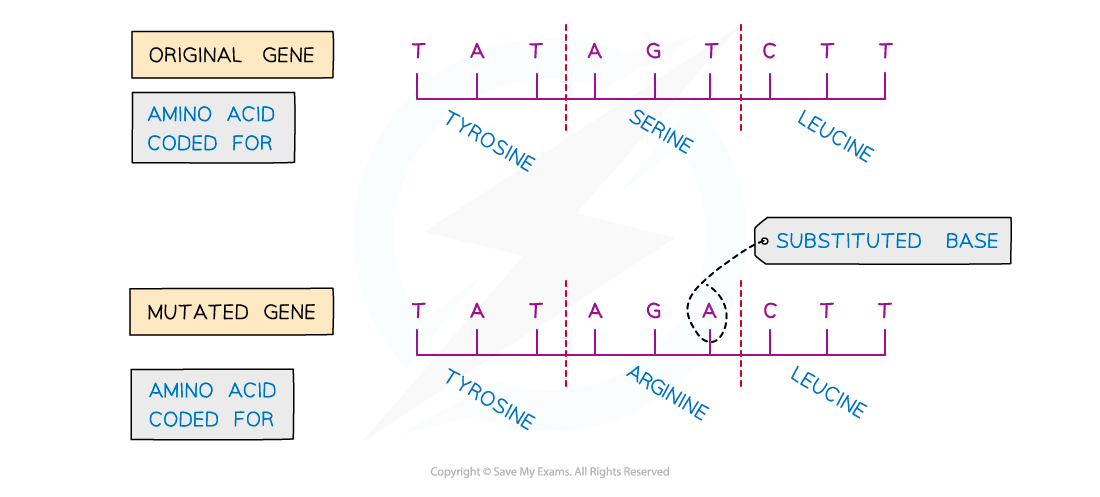
An example of a substitution mutation
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








