- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel IGCSE Biology: Double Science 复习笔记 2.7.1 Human Gas Exchange System
Edexcel IGCSE Biology: Double Science 复习笔记 2.7.1 Human Gas Exchange System
Structure of the Breathing System
- The lungs are the gas exchange surface in humans
- All gas exchange surfaces have features in common which allow the maximum amount of gases to be exchanged across the surface in the smallest amount of time
- They include:
- Large surface area to allow faster diffusion of gases across the surface
- Thin walls to ensure diffusion distances remain short
- Good ventilation with air so that diffusion gradients can be maintained
- Good blood supply to maintain a high concentration gradient so diffusion occurs faster
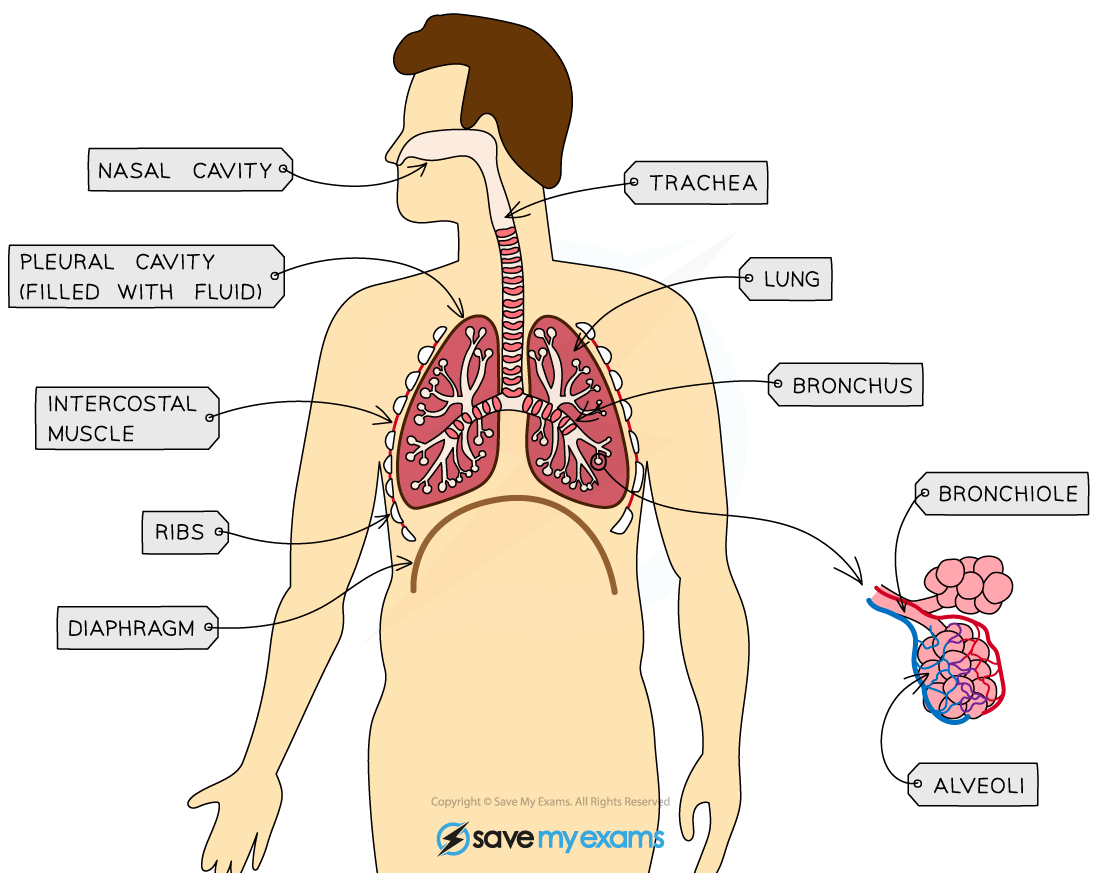
Structures in the human breathing system
Breathing Structures Table


Cilia and mucus
- The passages down to the lungs are lined with ciliated epithelial cells
- Cilia cells have tiny hairs on the end of them that beat and push mucus up the passages towards the nose and throat where it can be removed
- The mucus is made by special mucus-producing cells called goblet cells because they are shaped like a goblet, or cup
- The mucus traps particles, pathogens like bacteria or viruses, and dust and prevents them from getting into the lungs and damaging the cells there
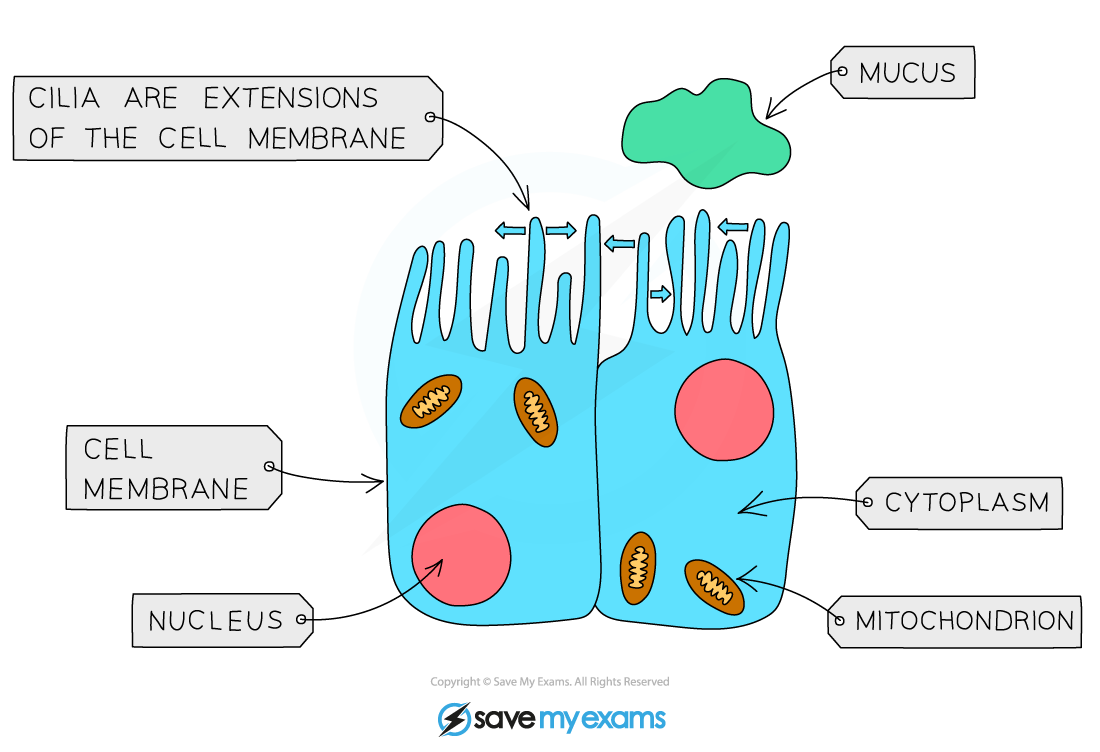
Mucus traps particles, dust and pathogens and cilia beat and push it up and away from the lungs
Exam Tip
You may notice that several of the features of alveoli that make them suited to their function are the same as those that make villi suited to their function or root hair cells suited to their function – the reason for this is because all of these structures are involved in transporting substances across their surfaces – by diffusion, active transport, osmosis or a combination.So if you learn the features for one, you also know many of the features of the others!
Alveoli
- The alveoli are highly specialised for gas exchange
- There are many rounded alveolar sacs which give a very large surface area to volume ratio
- Alveoli (and the capillaries around them) have thin, single layers of cells to minimise diffusion distance
- Ventilation maintains high levels of oxygen and low levels of carbon dioxide in the alveolar air space
- A good blood supply ensures constant supply of blood high in carbon dioxide and low in oxygen
- A layer of moisture on the surface of the alveoli helps diffusion as gases dissolve
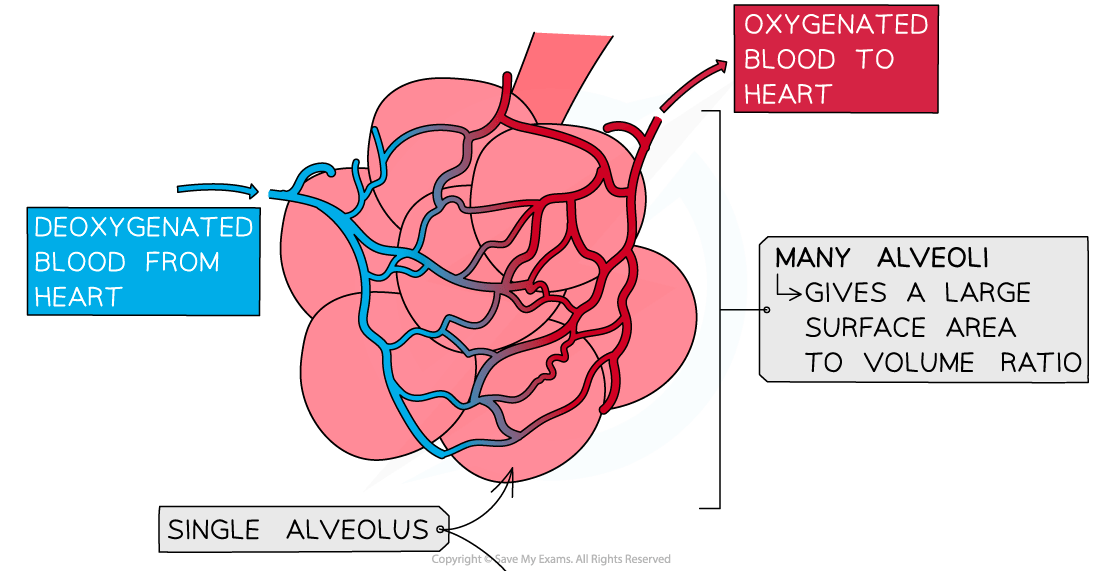
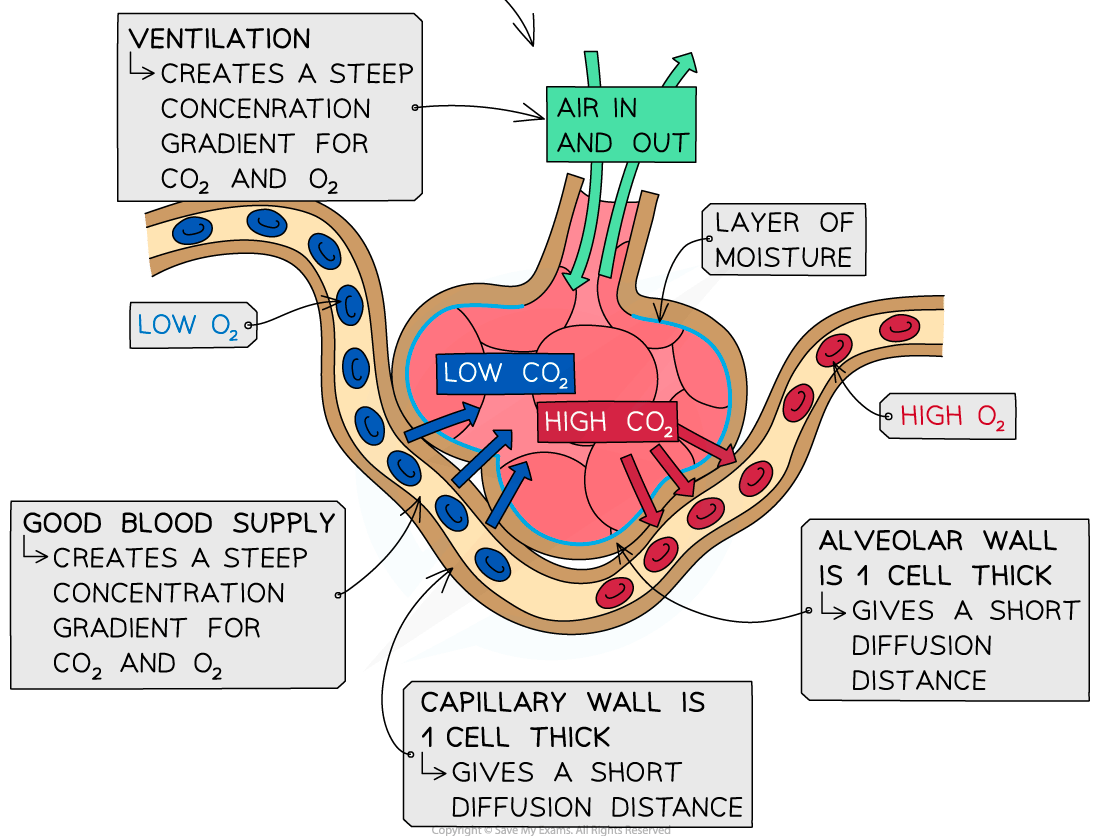
Alveoli are specifically adapted to maximise gas exchange
Intercostal Muscles & Diaphragm
- Muscles are only able to pull on bones, not push on them
- This means that there must be two sets of intercostal muscles to work antagonistically to facilitate breathing
- External intercostal muscles, pull the rib cage up
- Internal intercostal muscles pull the ribcage down
- The diaphragm is a thin sheet of muscle that separates the chest cavity from the abdomen
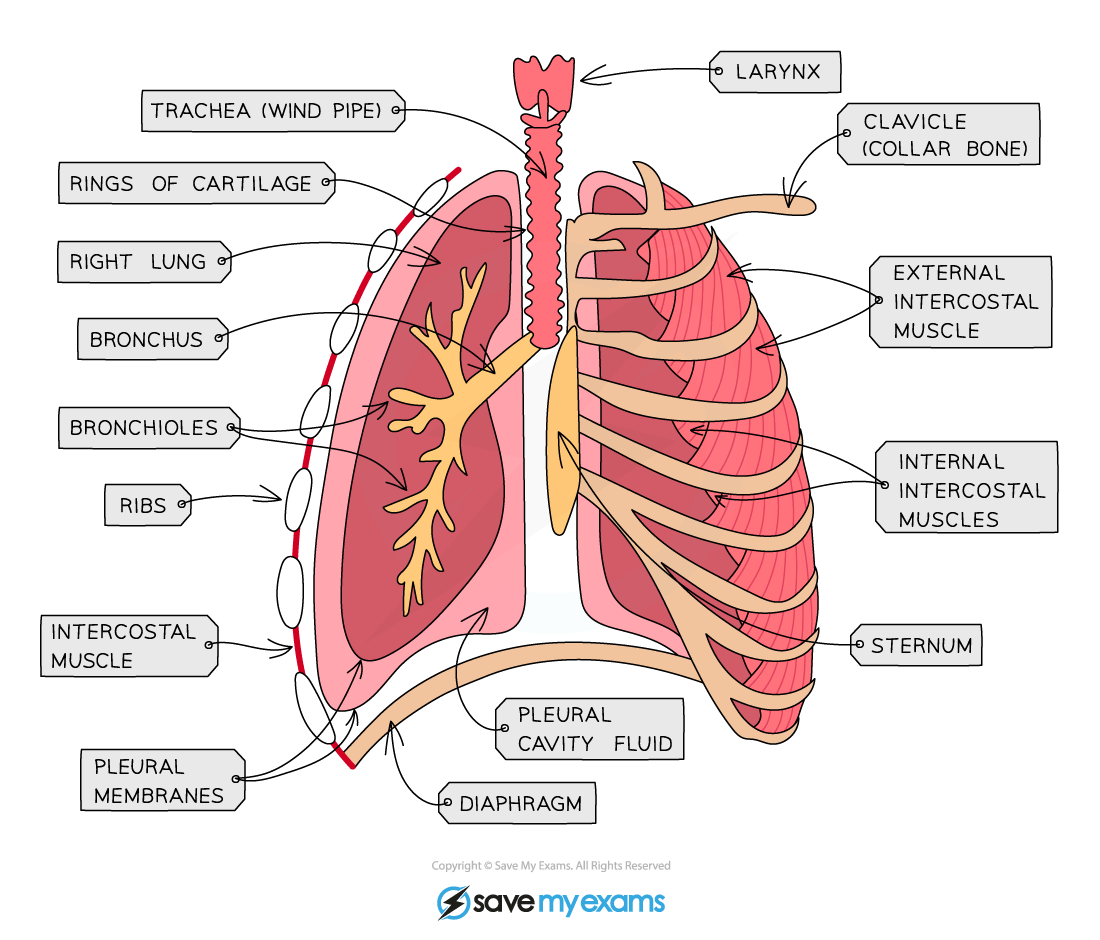
There are 2 sets of intercostal muscles: the external, on the outside of the rib cage, and the internal, on the inside of the rib cage
Ventilation
- During inhalation
- The diaphragm contracts and flattens
- The external set of intercostal muscles contract to pull the ribs up and out:
- This increases the volume of the chest cavity (thorax)
- Leading to a decrease in air pressure inside the lungs relative to outside the body
- Air is drawn in
- During exhalation
- The diaphragm relaxes it moves upwards back into its domed shape
- The external set of intercostal muscles relax so the ribs drop down and in
- This decreases the volume of the chest cavity (thorax)
- Leading to an increase in air pressure inside the lungs relative to outside the body
- Air is forced out
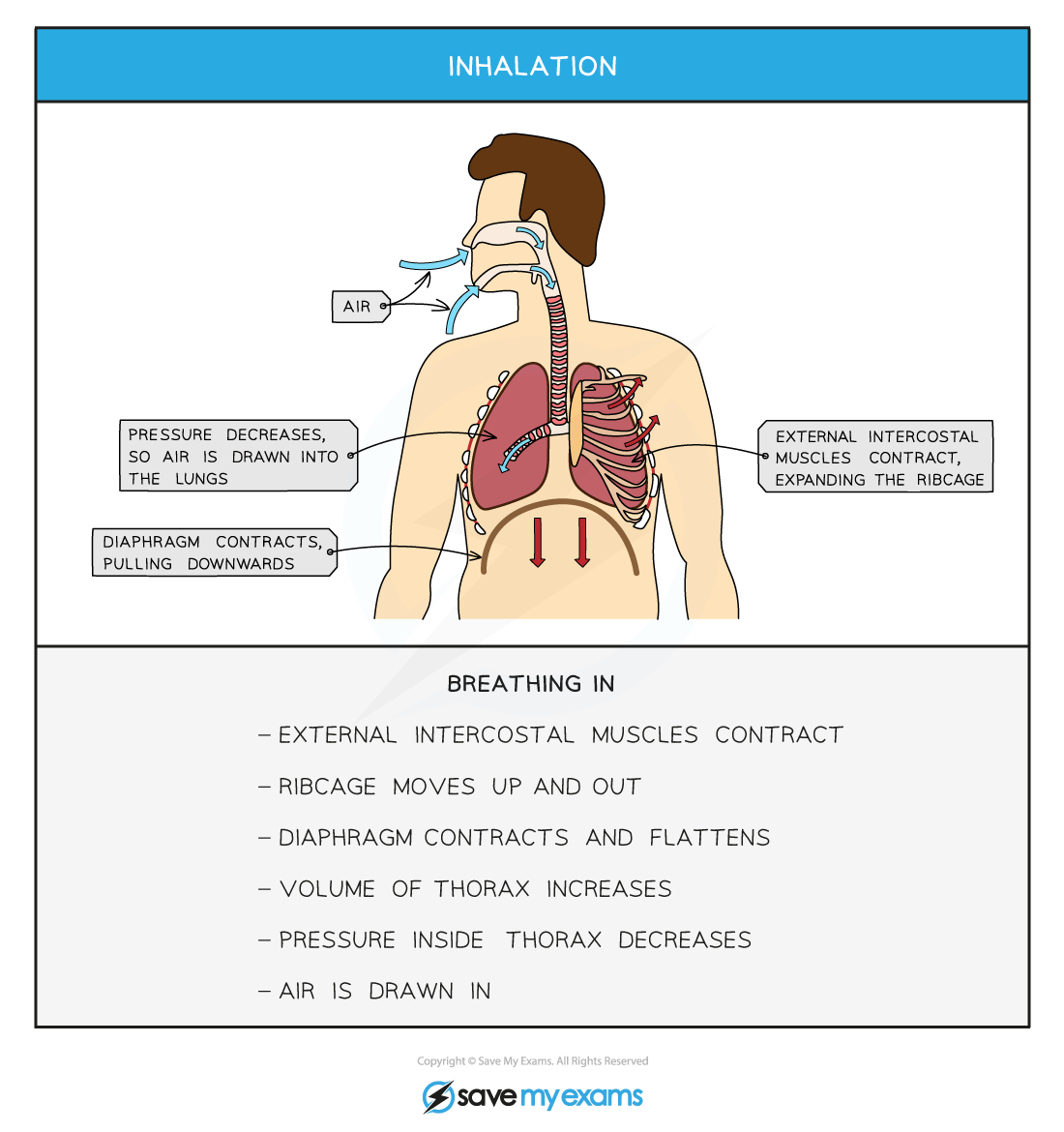
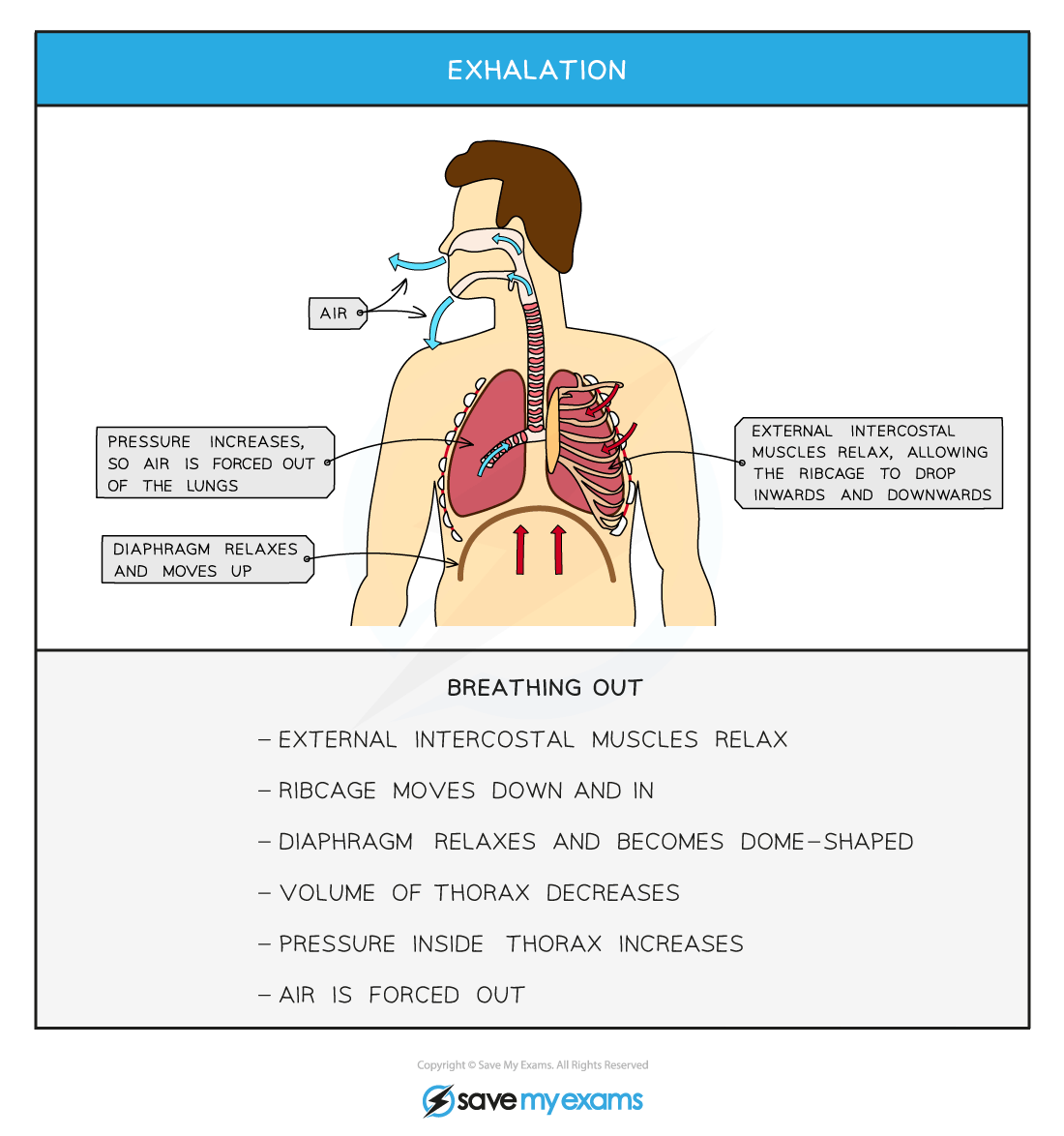
Changes in the thorax during ventilation
Forced Exhalation
- The external and internal intercostal muscles work as antagonistic pairs (meaning they work in different directions to each other)
- When we need to increase the rate of gas exchange (for example during strenuous activity) the internal intercostal muscles will also work to pull the ribs down and in to decrease the volume of the thorax more, forcing air out more forcefully and quickly – this is called forced exhalation
- There is a greater need to rid the body of increased levels of carbon dioxide produced during strenuous activity
- This allows a greater volume of gases to be exchanged
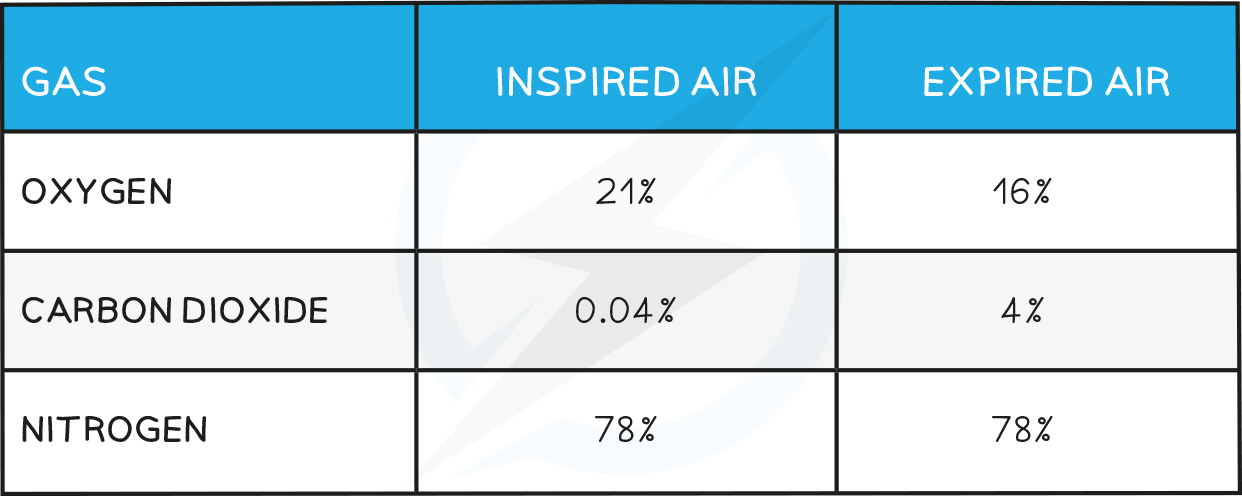
The differences between inspired air and expired air during ventilation
Exam Tip
You may see the terms inhalation OR inspiration (breathing in), and exhalation OR expiration (breathing out). Both sets of terms mean exactly the same thing, so don’t let them confuse you!This sequence of events is a common exam question and you should be able to explain in detail what is happening to the external and internal intercostal muscles, the rib cage, the diaphragm, the volume and the pressure-volume of the lungs when breathing in and out.Remember, if you learn one, the other is almost exactly the opposite.
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









