- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel A Level Physics:复习笔记11.8 Core Practical 15: Investigating Gamma Radiation Absorption
Core Practical 15: Investigating Gamma Radiation Absorption
Aim of the Experiment
- To investigate the absorption of gamma rays by different thicknesses of lead
Variables:
- Independent variable = Thickness of lead
- Dependent variable = Count rate
- Control variables:
- Radioactive source
- Distance of GM tube to source
- Location / background radiation
Equipment List
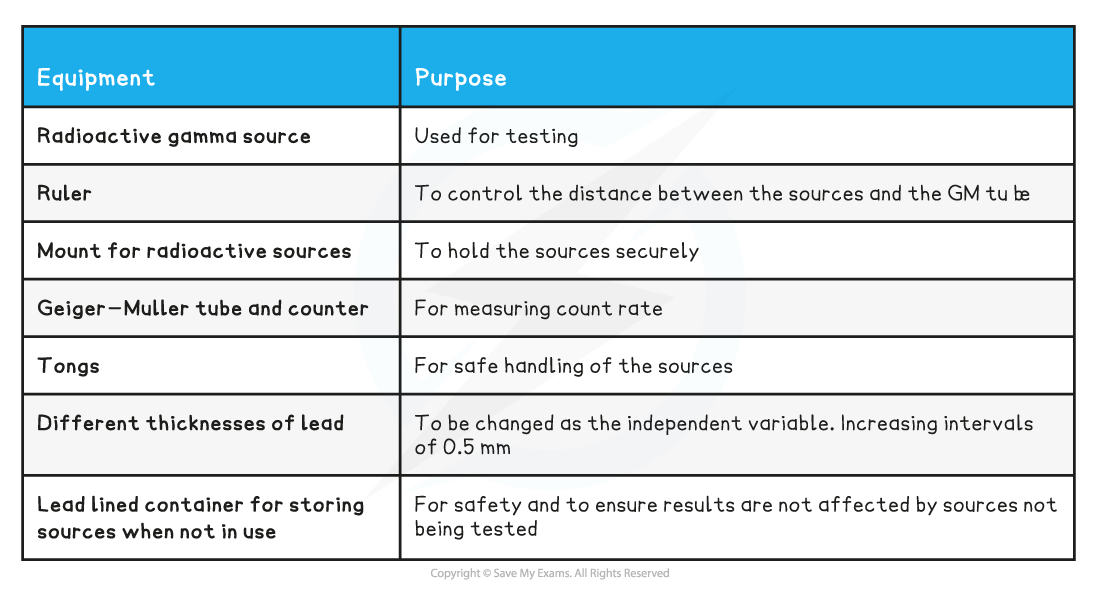
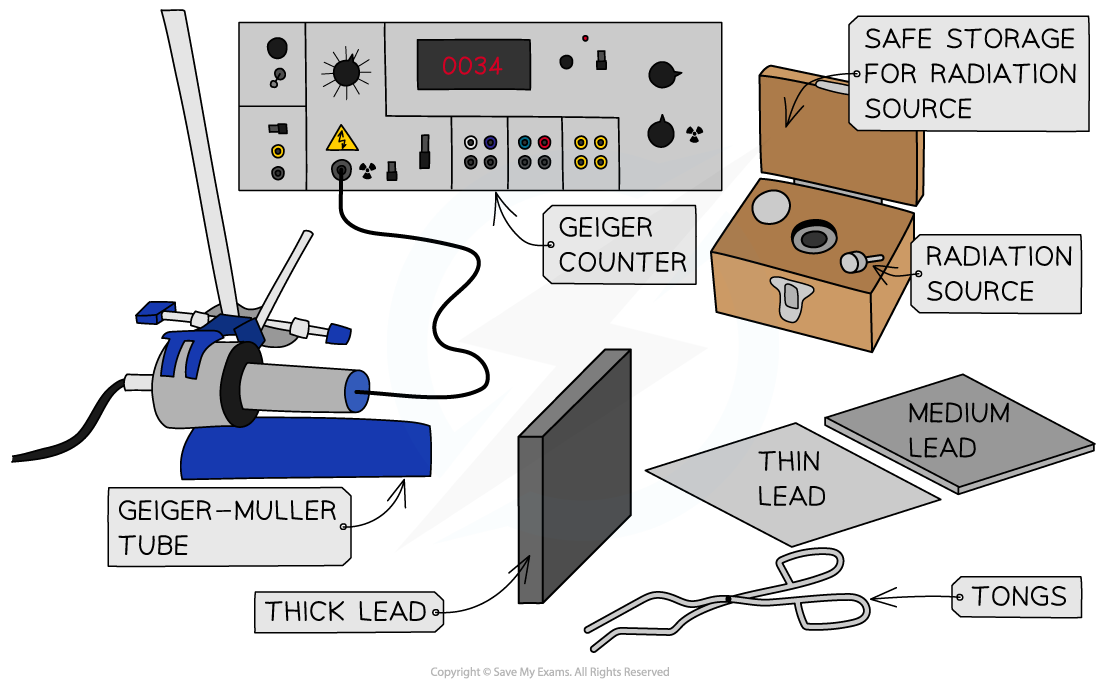
- Resolution of measuring equipment:
- Ruler = 1 mm
- Geiger-Müller tube = 0.01 μS/hr
Method
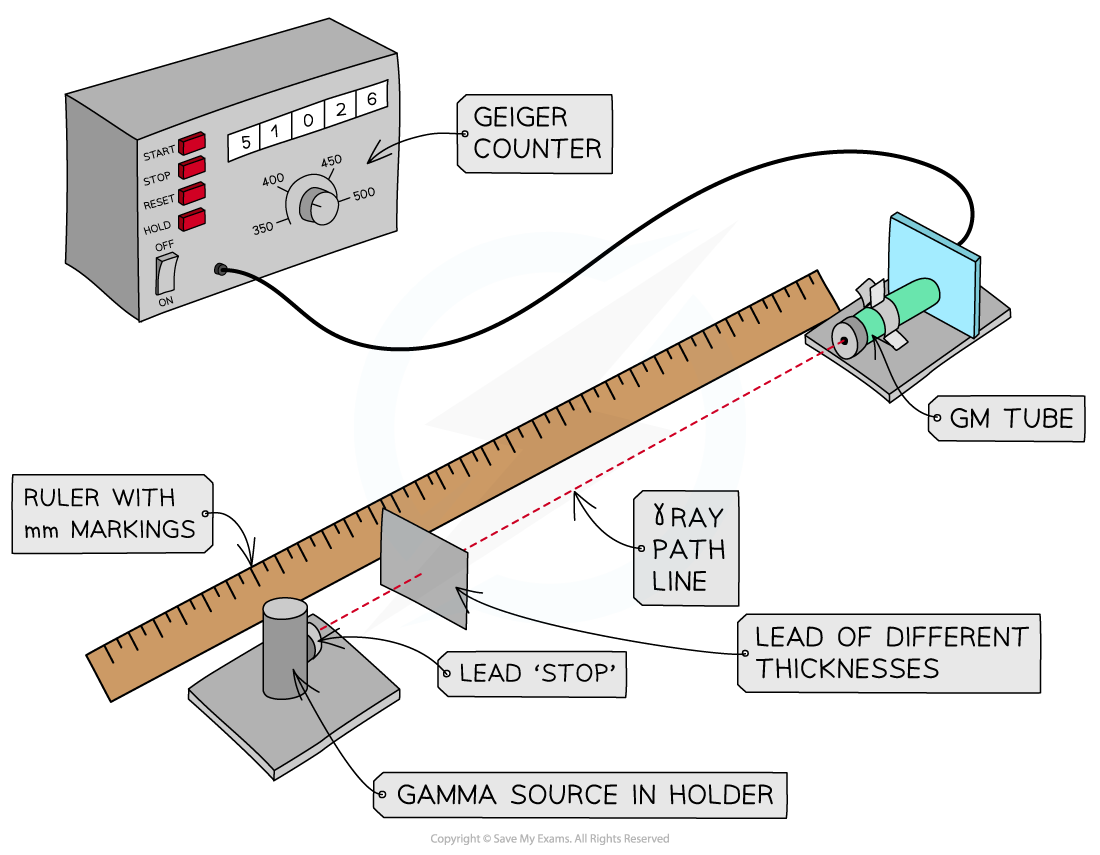
- Connect the Geiger-Müller tube to the counter and, without any sources present, measure background radiation over a five-minute period
- Record this value
- Calculate the average background rate per minute
- Measure the thickness of the lead absorbers using Vernier calipers at three points on each sheet.
- For each sheet record the average thickness
- Place the radioactive source a fixed distance of 10 cm away from the tube
- Record the count rate over one minute
- Repeat steps 3 and 4 a further two times, recording the count rate each time
- Place the thinnest absorber directly in front of the gamma ray source
- Repeat steps 3-5
- Replace the sheet with another thickness and continue taking three readings per thickness
Analysis of Results
- If the count over that interval falls to background levels (allow for a little random variation), then the radiation has all been absorbed
- You will be able to determine the thickness of the lead required to absorb gamma radiation
Evaluating the Experiment
Systematic Errors:
- Make sure that the source is stored well away from the counter during the experiment
- Conduct all runs of the experiment in the same location to avoid changes in background radiation levels
Random Errors:
- The accuracy of such an experiment is improved with using a reliable source of radiation with a long half-life and an activity well above the natural background level
Safety Considerations
- When not using a source, keep it in a lead-lined container
- When in use, try and keep a good distance (a metre or so) between yourself and the source
- When handling the source, do so using tweezers (or tongs) and point the source away from you
- Wash your hands and remove your outer layer of clothing after handling a radioactive source
Exam Tip
When answering questions about the core practicals you could try to remember the acronym SCREAMS:
- S: Which variable will you keep the same
- C: which variable should you change
- R: what will you do to make your experiment reliable
- E: what special equipment and equations are required
- A: how will you analyse your results
- M: which variable will you measure
- S: what safety precautions will you take?
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








