- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel A Level Physics:复习笔记11.3 Binding Energy per Nucleon Graph
Binding Energy per Nucleon Graph
- When comparing the stability of different nuclei, it is useful to look at the binding energy per nucleon
- The binding energy per nucleon is defined as:
The binding energy of a nucleus divided by the number of nucleons in the nucleus
- A higher binding energy per nucleon indicates a higher stability since it requires more energy to pull the nucleus apart
- Iron (A = 56) has the highest binding energy per nucleon, which makes it the most stable of all the elements
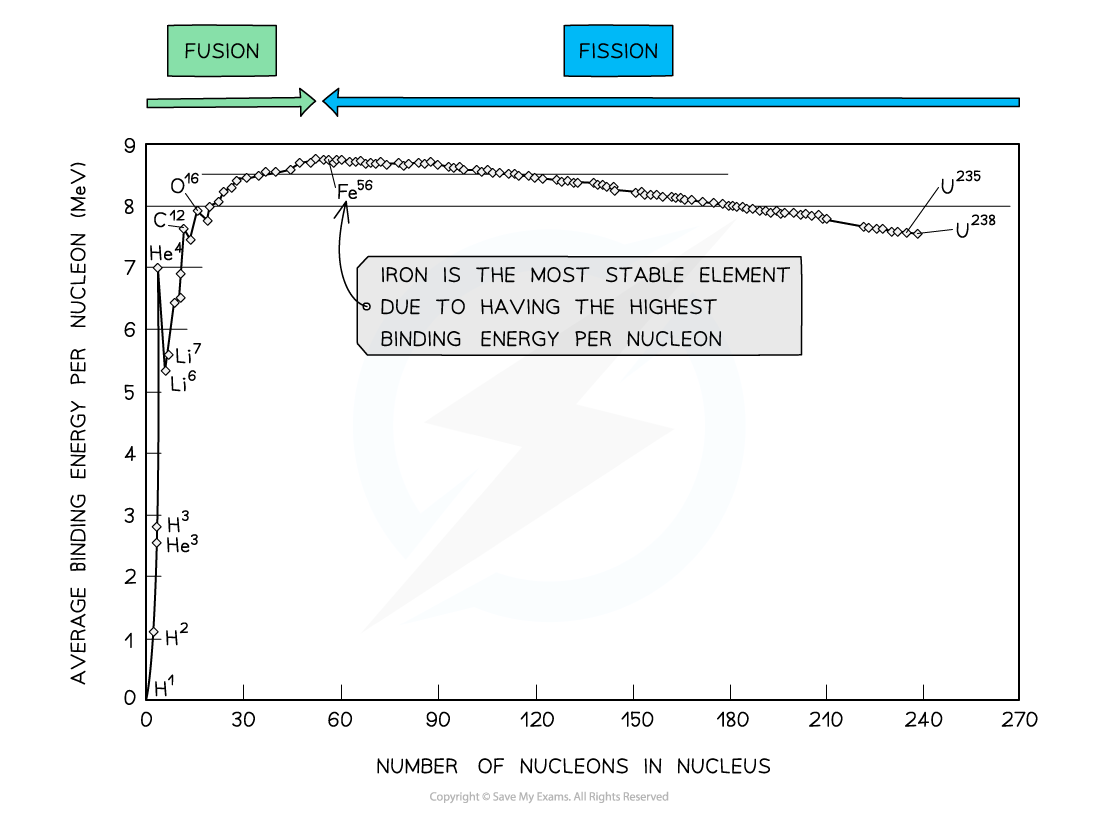
By plotting a graph of binding energy per nucleon against nucleon number, the stability of elements can be inferred
Key Features of the Graph
- At low values of A:
- Nuclei tend to have a lower binding energy per nucleon, hence, they are generally less stable
- This means the lightest elements have weaker electrostatic forces and are the most likely to undergo fusion
- Helium (4He), carbon (12C) and oxygen (16O) do not fit the trend
- Helium-4 is a particularly stable nucleus hence it has a high binding energy per nucleon
- Carbon-12 and oxygen-16 can be considered to be three and four helium nuclei, respectively, bound together
- At high values of A:
- The general binding energy per nucleon is high and gradually decreases with A
- This means the heaviest elements are the most unstable and likely to undergo fission
Worked Example
Determine the binding energy per nucleon of Iron-56 (![]() ) in MeV
) in MeV
Mass of a neutron = 1.675 × 10−27 kg
Mass of a proton = 1.673 × 10−27 kg
Mass of a ![]() nucleus = 9.228 × 10−26 kg
nucleus = 9.228 × 10−26 kg
Step 1: Calculate the mass defect
Number of protons, Z = 26
Number of neutrons, A – Z = 56 – 26 = 30
Mass defect, Δm = Zmp + (A – Z)mn – mtotal
Δm = (26 × 1.673 × 10-27) + (30 × 1.675 × 10-27) – (9.288 × 10-26)
Δm = 8.680 × 10-28 kg
Step 2: Calculate the binding energy of the nucleus
Binding energy, ΔE = Δmc2
E = (8.680 × 10-28) × (3.00 × 108)2 = 7.812 × 10-11 J
Step 3: Calculate the binding energy per nucleon
Binding energy per nucleon = ![]()
![]()
Step 4: Convert to MeV
J → eV: divide by 1.6 × 10-19
eV → MeV: divide by 106
binding energy per nucleon = ![]()
Exam Tip
Checklist on what to include (and what not to include) in an exam question asking you to draw a graph of binding energy per nucleon against nucleon number:
- You will be expected to draw the best fit curve AND a cross to show the anomaly that is Helium
- Do not begin your curve at A = 0, this is not a nucleus!
- Make sure to correctly label both axes AND units for binding energy per nucleon
- You will be expected to include numbers on the axes, mainly at the peak to show the position of iron (56Fe)
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








