- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel A Level Physics:复习笔记10.7 Equations for Cosmology
Redshift Equation
- Recall the Doppler effect is defined as:
The apparent change in wavelength or frequency of the radiation from a source due to its relative motion away from or toward the observer
-
- On Earth, the Doppler effect is most easily observed when something which is both fast moving and emitting a loud sound (such as an ambulance or fast car) moves past an observer, producing a characteristic change in the pitch of the sound that is heard
- In space, the Doppler effect of light can observed when spectra of distant stars and galaxies are observed, this is known as:
- Redshift if the object is moving away from the Earth, or
- Blueshift if the object is moving towards the Earth
- Redshift is defined as:
The fractional increase in wavelength (or decrease in frequency) due to the source and observer receding from each other
- For non-relativistic galaxies, Doppler redshift can be calculated using:
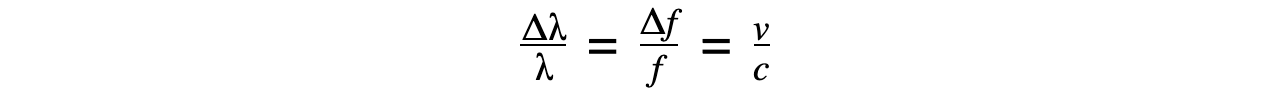
- Where:
- Δλ = shift in wavelength (m)
- λ = wavelength emitted from the source (m)
- Δf = shift in frequency (Hz)
- f = frequency emitted from the source (Hz)
- v = speed of recession (m s-1)
- c = speed of light in a vacuum (m s-1)
Worked Example
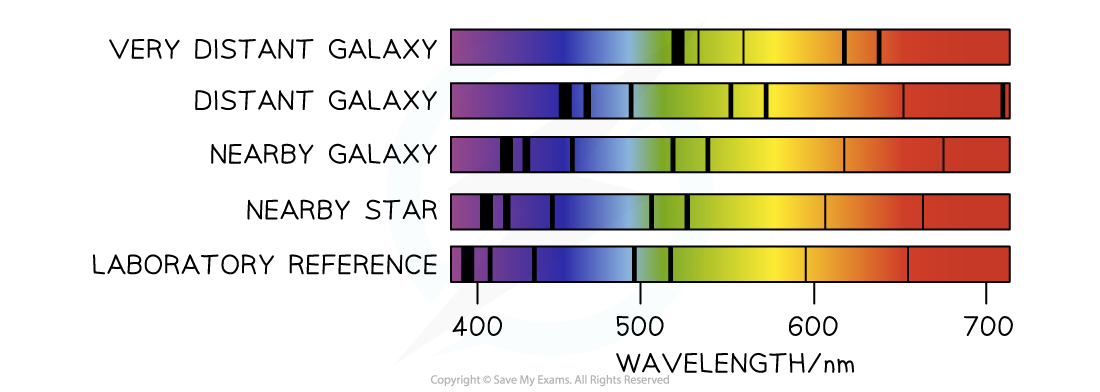
The spectra below show dark absorption lines against a continuous visible spectrum.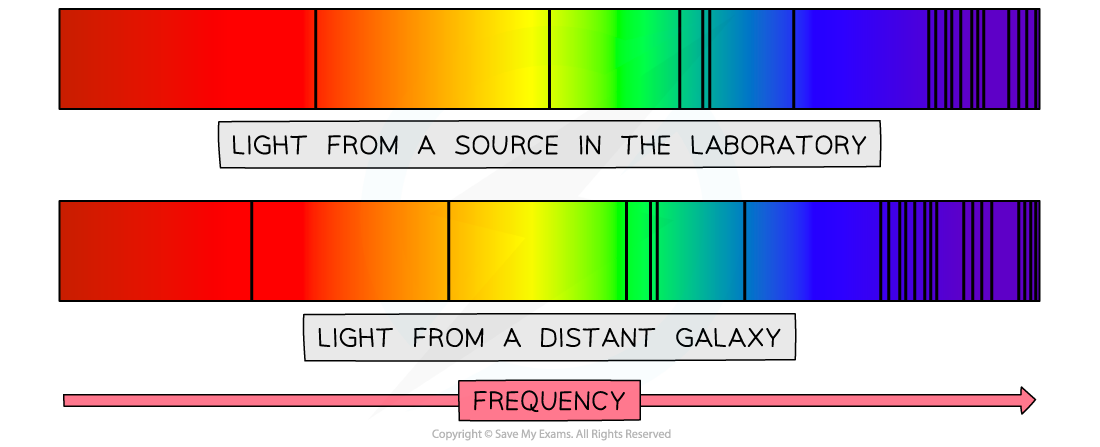
A particle line in the spectrum of light from a source in the laboratory has a frequency of 4.570 × 1014 Hz.
The same line in the spectrum of light from a distant galaxy has a frequency of 4.547 × 1014 Hz.
a) What speed is the distance galaxy moving in relation to the Earth?
b) Is it moving towards or away from the Earth?
Part (a)
Step 1: Write down the known quantities
-
- Emitted frequency, f = 4.570 × 1014 Hz
- Shift in frequency, Δf = (4.547 – 4.570) × 1014 = –2.3 × 1012 Hz
- Speed of light, c = 3.0 × 108 m s–1
Step 2: Write down the Doppler redshift equation
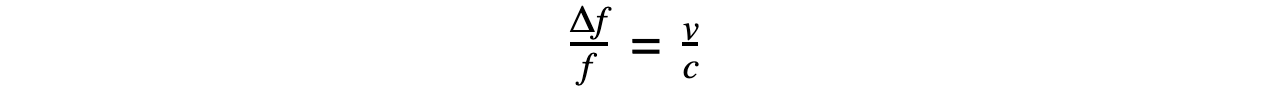
Step 3: Rearrange for speed v, and calculate
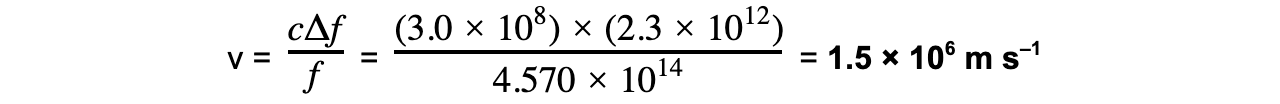
Part (b)
Step 1: Compare the frequencies and answer the question
-
- The observed frequency is less than the emitted frequency (the light from a laboratory source),
- The source is receding (moving away from) from the Earth
Exam Tip
In your exam, be sure to emphasise that redshift means the wavelength of spectral lines increases towards the red end of the spectrum, do not say that the spectral lines become red, as this is incorrect.
The Hubble Equation
- In 1929, the astronomer Edwin Hubble showed that the universe was expanding
- He did this by observing that the absorption line spectra produced from the light of distant galaxies was shifted towards the red end of the spectrum
- This doppler shift in the wavelength of the light is evidence that distant galaxies are moving away from the Earth
- Hubble also observed that light from more distant galaxies was shifted further towards the red end of the spectrum compared to closer galaxies
- From this observation he concluded that galaxies or stars which are further away from the Earth are moving faster than galaxies which are closer
- Hubble’s law states:
The recessional velocity, v, of a galaxy is proportional to its distance from Earth
- Hubble’s law can be expressed as an equation:
v ≈ H0d
- Where:
- v = recessional velocity of an object, the velocity of an object moving away from an observer (km s-1)
- H0 = Hubble constant, this will be provided in your examination along with the correct units (km s-1 Mpc-1)
- d = distance between the object and the Earth (Mpc)
- Alternatively, if the velocity of the receding object was measured in km s–1 and the distance from the earth to the object was measured in km, then then unit for the Hubble constant would be s–1
- Hubble’s law shows:
- The further away a star is from the Earth, the faster it is moving away from us
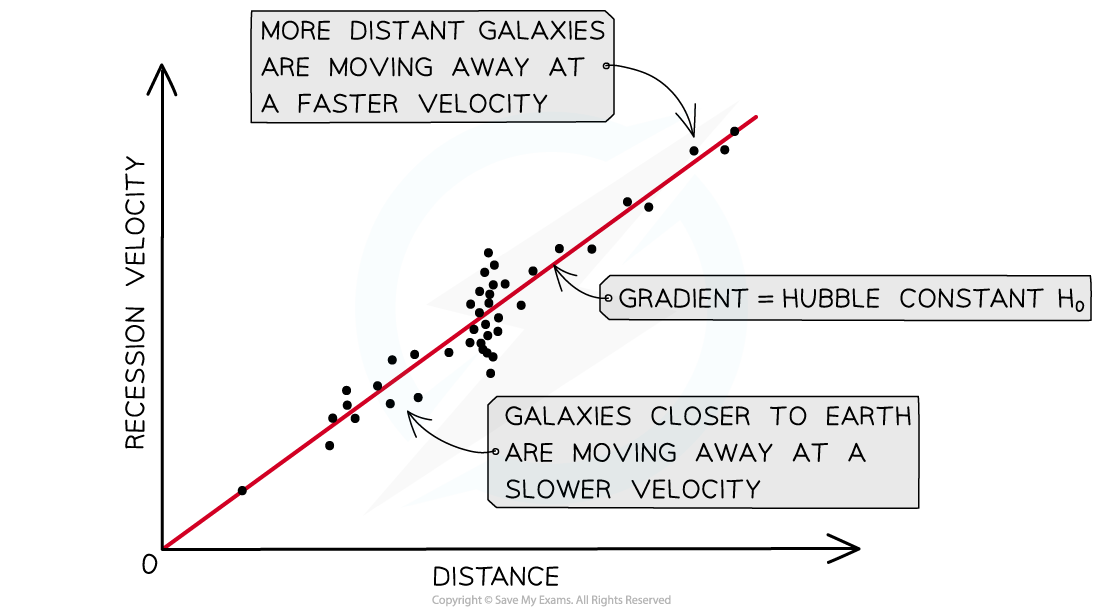
A key aspect of Hubble’s law is that the furthest galaxies appear to move away the fastest
Worked Example
A distant galaxy is 20 light-years away from Earth.
Use Hubble’s Law to determine the velocity of the galaxy as it moves away from Earth.
The Hubble constant is currently agreed to be 2.2 x 10-18 s-1.
Step 1: List the known quantities:
-
- d = 20 light years
- Ho = 2.2 x 10-18 s-1
Step 2: Convert 20 light-years to m:
-
- From the data booklet: 1 ly ≈ 9.5 x 1015 m
- So, 20 ly = 20 x (9.5 x 1015) = 1.9 x 1017 m
Step 3: Substitute values into Hubble's Law:
-
- From the data booklet: v ≈ H0d
- So, v ≈ (2.2 x 10-18 ) x (1.9 x 1017) = 0.418 m s-1
Step 4: Confirm your answer:
-
- The velocity of the galaxy as it moves away from Earth 0.42 m s-1
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









