- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel A Level Physics:复习笔记8.8 Annihilation of Matter & Antimatter
Annihilation of Matter & Antimatter
Annihilation
- When a particle meets its antiparticle partner, the two will annihilate
- Annihilation is:
When a particle meets its equivalent anti–particle they both are destroyed and their mass is converted into energy in the form of two gamma ray photons
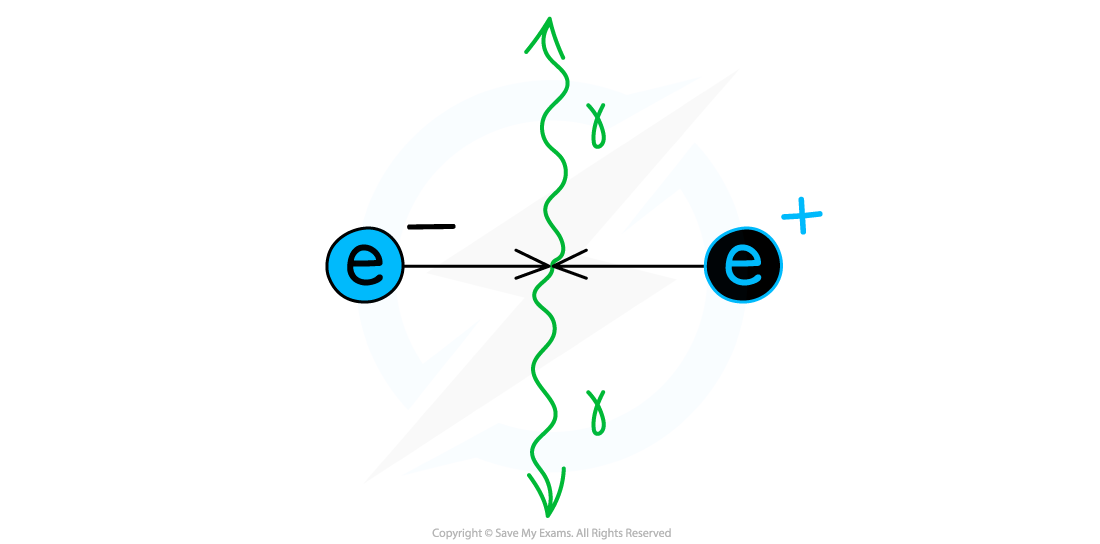
When an electron and positron collide, their mass is converted into energy in the form of two photons emitted in opposite directions
Pair Production
- Pair production is the opposite of annihilation
- Pair production is:
When a photon interacts with a nucleus or atom and the energy of the photon is used to create a particle–antiparticle pair
- The presence of a nearby neutron is essential in pair production so that the process conserves both energy and momentum
- A single photon alone cannot produce a particle–anti-particle pair or the conservation laws would be broken
- Pair creation is a case of energy being converted into matter
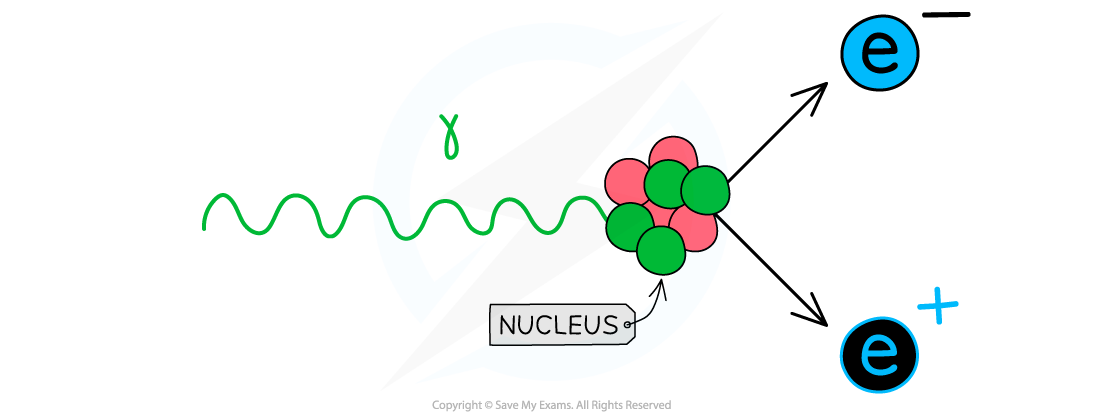
When a photon with enough energy interacts with a nucleus it can produce an electron-positron pair
- This means the energy of the photon must be above a certain value to provide the total rest mass energy of the particle–antiparticle pair
- Einstein's famous mass-energy relation showed that energy can be converted into mass, and vice versa
- It is given by:
ΔE = c2 Δm
- Where:
- Δm = rest mass of the particle (kg)
- c = speed of light (m s–1)
- ΔE = rest mass energy of the particle (J)
- Therefore, in order to create a particle & anti-particle pair, the energy carried by a single photon must be at least twice the rest-mass energy required, i.e.
2ΔE = 2(c2 Δm)
- This also means if a particle meets its anti-particle and annihilates, the energy carried away by each of the two photons Ephoton is given by:
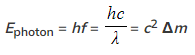
Worked Example
Calculate the maximum wavelength of one of the photons produced when a proton and antiproton annihilate each other.

Exam Tip
Since the Planck constant is in Joules (J s) remember to always convert the rest mass-energy from MeV to J.
Remember that the equation E = hf is only relevant for photons, not for all particles!
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









