- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel A Level Physics:复习笔记6.6 Energy-Momentum Relation
Deriving the Energy-Momentum Relation
- The equation for calculating the kinetic energy Ek of a particle m moving at velocity v is given by:
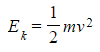
- The formula for the momentum p of the same particle is:
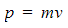
- Combining these gives an equation that links kinetic energy to momentum, called the energy-momentum relation
- Firstly, substituting the equation for velocity
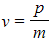 into the equation for kinetic energy gives:
into the equation for kinetic energy gives:
- Firstly, substituting the equation for velocity
-
- Multiplying brackets out and simplifying gives:
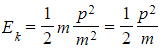
- Therefore the energy-momentum is presented as:
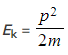
- Where:
- Ek = kinetic energy (J)
- p = momentum (kg m s-1)
- m = mass (kg)
Exam Tip
This is a common derivation, so make sure you're comfortable with deriving this from scratch! Think carefully about the algebra on each step.
Using the Energy-Momentum Relation
- The energy-momentum relation is particularly useful for:
- Calculations involving the kinetic energy of subatomic particles travelling at non-relativistic speeds (i.e. much slower than the speed of light)
- Projectiles and collisions involving large masses
Worked Example
Calculate the kinetic energy, in MeV, of an alpha particle which has a momentum of 1.1 × 10–19 kg m s–1.
Use the following data:
- Mass of a proton = 1.67 × 10–27 kg
- Mass of a neutron = 1.67 × 10–27 kg
Step 1: Write the energy-momentum relation
-
- The energy-momentum relation is given by
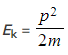
- The energy-momentum relation is given by
Step 2: Determine the mass of an alpha particle
-
- An alpha particle is comprised of two protons and two neutrons
- Therefore, the mass of an alpha particle mα = 2mp + 2mn, where mp and mn is the mass of a proton and neutron respectively
- So mα = 2(1.67 × 10–27) + 2(1.67 × 10–27) = 6.68 × 10–27 kg
Step 3: Substitute the momentum and the mass of the alpha particle into the energy-momentum relation
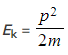
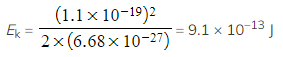
Step 4: Convert the value of kinetic energy from J to MeV
1 MeV = 1.6 × 10–13 J
-
- Therefore:

Exam Tip
Calculations with the energy-momentum equation often require changing units, especially between eV and J due to it commonly being used for particles. Remember that 1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J. Therefore
eV → J = × (1.60 × 10-19)
J → eV = ÷ (1.60 × 10-19)
The prefix 'mega' (M) means × 106 therefore, 1 MeV = (1.60 × 10-19) × 106 = 1.60 × 10-13
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1