- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel A Level Physics:复习笔记5.14 Critical Angle
Critical Angle
- As the angle of incidence is increased, the angle of refraction also increases until it gets to 90°
- When the angle of refraction is exactly 90° the light is refracted along the boundary
- At this point, the angle of incidence is known as the critical angle C
- This angle can be found using the formula:
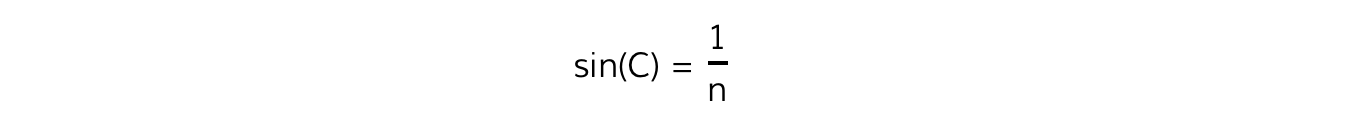
- This can easily be derived from Snell’s law where:
- θ1 = C
- θ2 = 90°
- n1 = n
- n2 = 1 (air)
Worked Example
A glass cube is held in contact with a liquid and a light ray is directed at the vertical face of the cube. The angle of incidence at the vertical face is 39° and the angle of refraction is 25° as shown in the diagram. The light ray is totally internally reflected at X.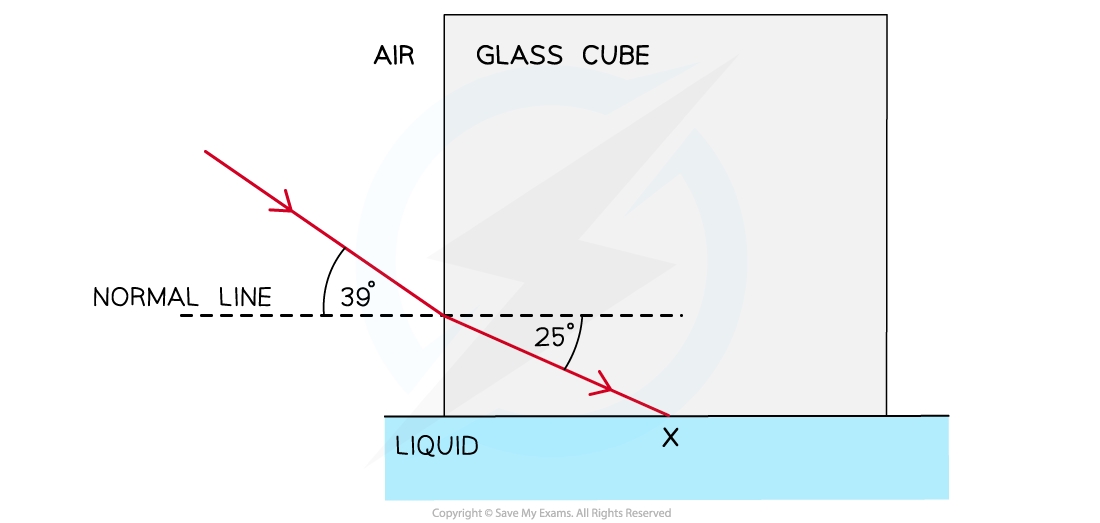 Complete the diagram to show the path of the ray beyond X to the air and calculate the critical angle for the glass-liquid boundary.
Complete the diagram to show the path of the ray beyond X to the air and calculate the critical angle for the glass-liquid boundary.
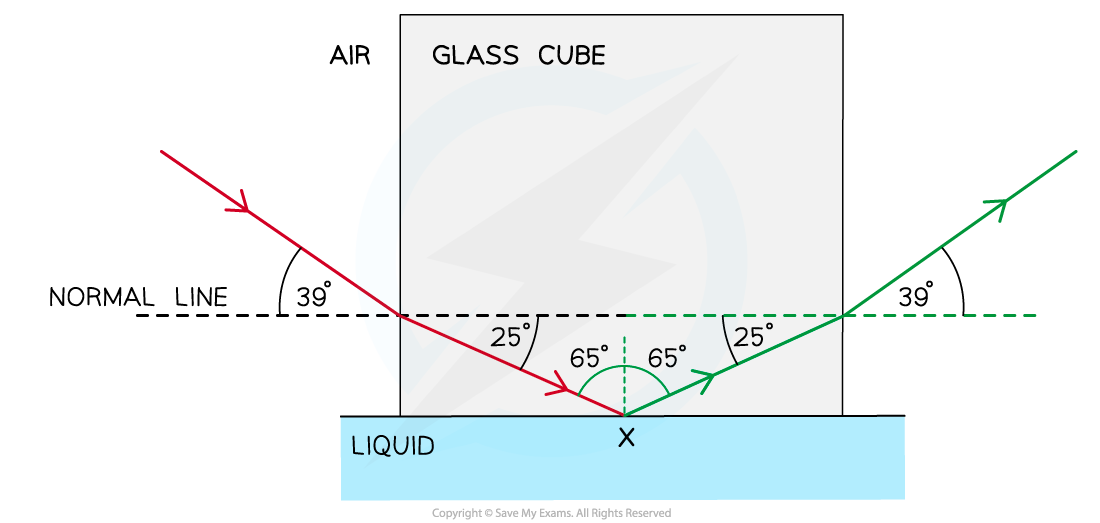
Step 1: Draw the reflected angle at the glass-liquid boundary
-
- When a light ray is reflected, the angle of incidence = angle of reflection
- Therefore, the angle of incidence (and reflection) is 90° – 25° = 65°
Step 2: Draw the refracted angle at the glass-air boundary
-
- At the glass-air boundary, the light ray refracts away from the normal
- Due to the reflection, the light rays are symmetrical to the other side
Step 3: Calculate the critical angle
-
- The question states the ray is “totally internally reflected for the first time” meaning that this is the lowest angle at which TIR occurs
- Therefore, 65° is the critical angle
Exam Tip
Always draw ray diagrams with a ruler, and make sure you're comfortable calculating unknown angles. The main rules to remember are:
- Angles in a right angle add up to 90°
- Angles on a straight line add up to 180°
- Angles in any triangle add up to 180°
For angles in parallel lines, such as alternate and opposite angles, take a look at the OCR GCSE maths revision notes '7.1.1 Angles in Parallel Lines'
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









