- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel A Level Physics:复习笔记4.5 Hooke's Law
Hooke's Law
- When a force F is added to the bottom of a vertical metal wire of length L, the wire stretches
- A material obeys Hooke’s Law if:
The extension of the material is directly proportional to the applied force (load) up to the limit of proportionality
- This linear relationship is represented by the Hooke’s law equation:
ΔF = kΔx
- Where:
- F = applied force (N)
- k = spring constant (N m–1)
- Δx = extension (m)
- The spring constant is a property of the material being stretched and measures the stiffness of a material
- The larger the spring constant, the stiffer the material
- Hooke's Law applies to both extensions and compressions:
- The extension of an object is determined by how much it has increased in length
- The compression of an object is determined by how much it has decreased in length
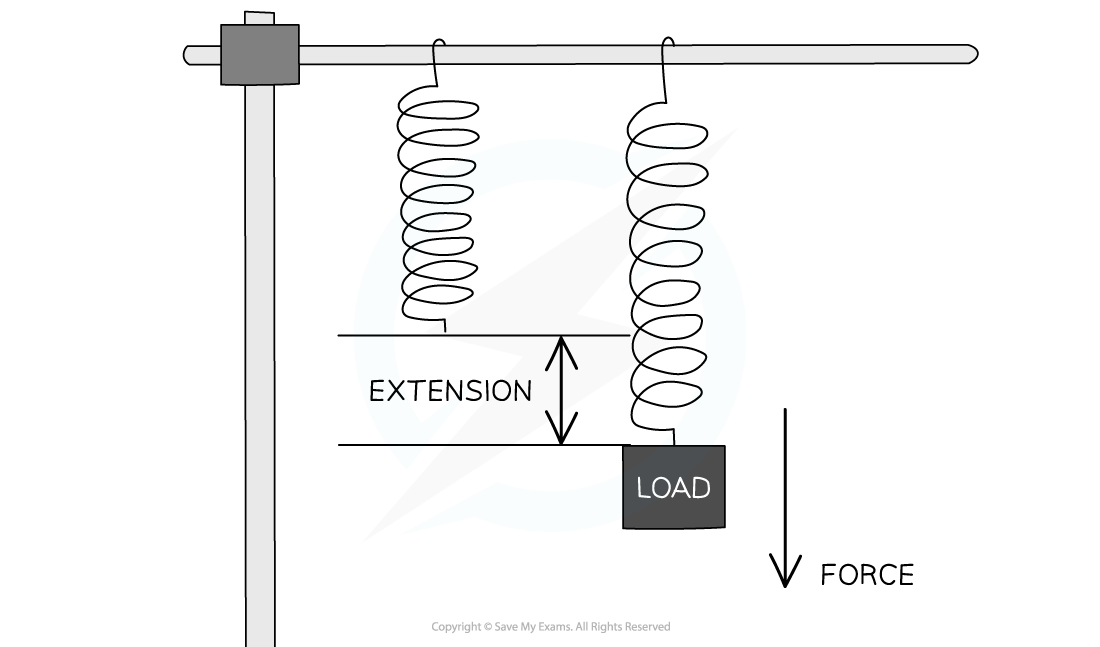
Stretching a spring with a load produces a force that leads to an extension
Force–Extension Graphs
- The way a material responds to a given force can be shown on a force-extension graph
- A material may obey Hooke's Law up to a point
- This is shown on its force-extension graph by a straight line through the origin
- As more force is added, the graph may start to curve slightly
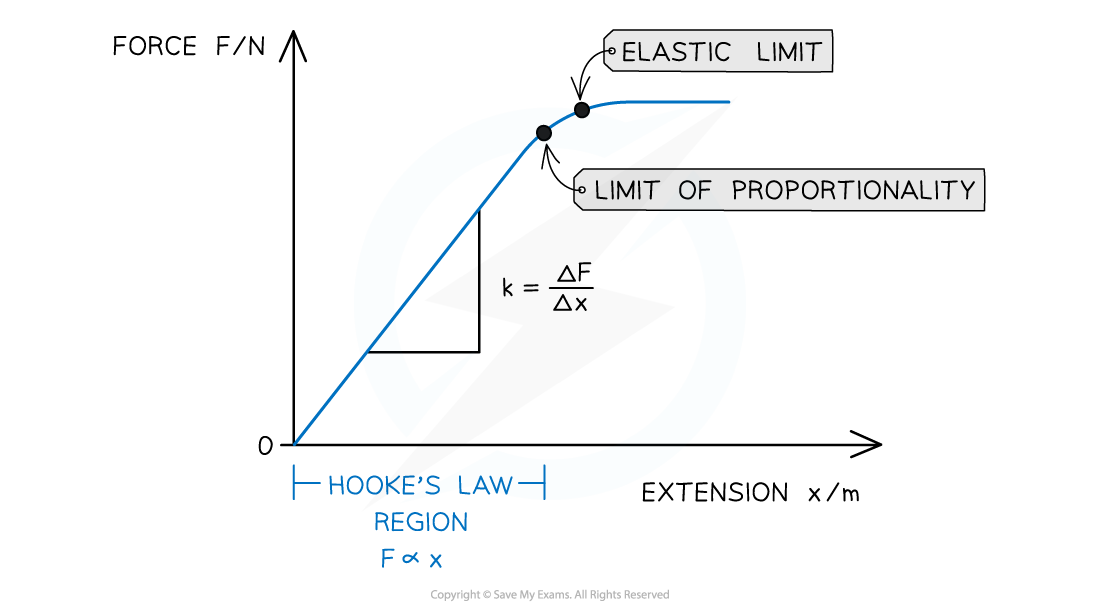
The Hooke's Law region of a force-extension graph is a straight line. The spring constant is the gradient of that region
- The key features of the graph are:
- The limit of proportionality: The point beyond which Hooke's law is no longer true when stretching a material i.e. the extension is no longer proportional to the applied force
- The point is identified on the graph where the line starts to curve (flattens out)
- Elastic limit: The maximum amount a material can be stretched and still return to its original length (above which the material will no longer be elastic). This point is always after the limit of proportionality
- The gradient of this graph is equal to the spring constant k
- The limit of proportionality: The point beyond which Hooke's law is no longer true when stretching a material i.e. the extension is no longer proportional to the applied force
Worked Example
A spring was stretched with increasing load.
The graph of the results is shown below.
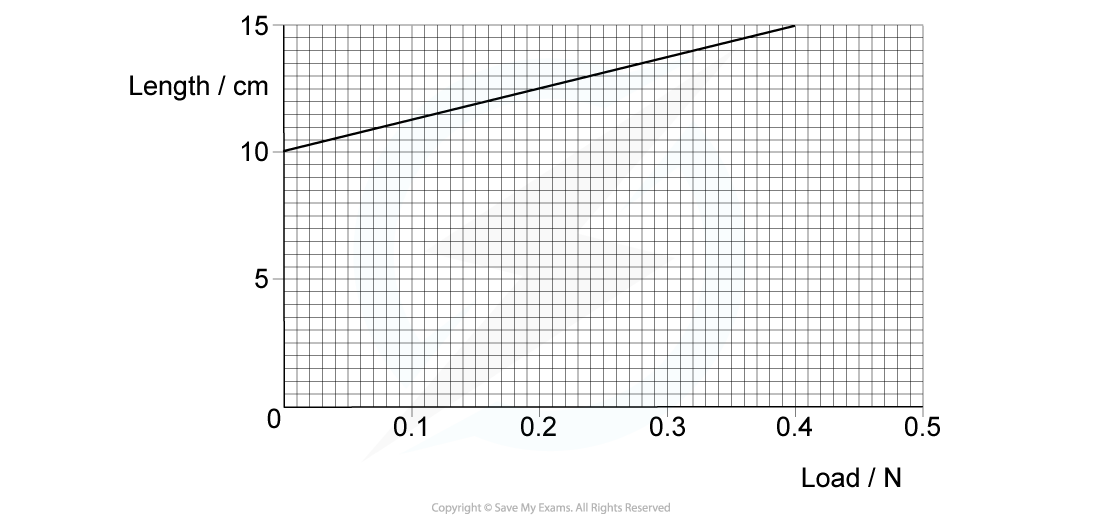
What is the spring constant?
Step 1: Rearrange Hooke's Law to make the spring constant the subject
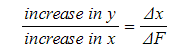 Step 2: Compare the gradient to the equation in Step 1
Step 2: Compare the gradient to the equation in Step 1
-
- This graph is length - extension, so the gradient gives:
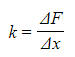
-
- Therefore k is the reciprocal of the gradient
Step 3: Find the gradient
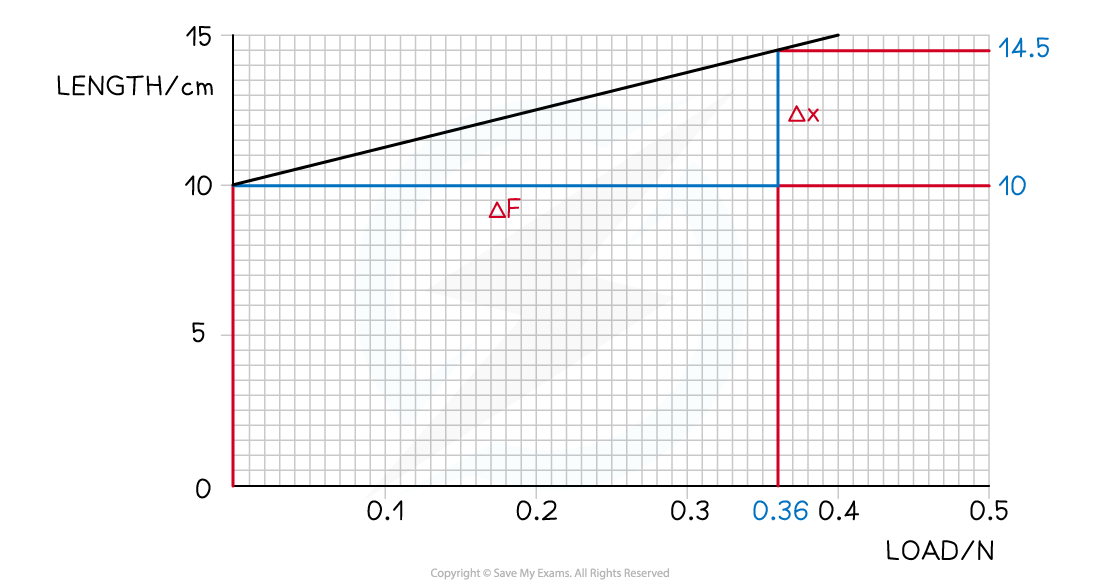
Step 4: Calculate gradient

Step 5: Calculate the spring constant by finding the reciprocal of the gradient
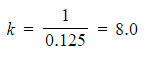
Step 6: Write the answer, including units
-
- Spring constant, k = 8.0 N m−1
Exam Tip
Always double check the axes before finding the spring constant as the gradient of a force-extension graph. Exam questions often swap the force (or load) onto the x-axis and extension (or length) on the y-axis.
In this case, the gradient is not the spring constant, it is 1 ÷ gradient instead.
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









