- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel A Level Economics A:复习笔记3.5.3 Wage Determination in Competitive & Non-competitive Markets
Diagrammatic Analysis of the Labour Market
- Labour market equilibrium occurs where the demand for labour (DL) is equal to the supply of labour (SL)
- The DL is the demand by firms for workers
- The SL is the supply of labour by workers
- Individual firms are price takers in the labour market as they have to accept the wage rate that workers are being paid in the industry
- If they offer a lower wage, they will likely struggle to recruit workers
- If they offer a higher wage there will be a large number of workers applying to work there
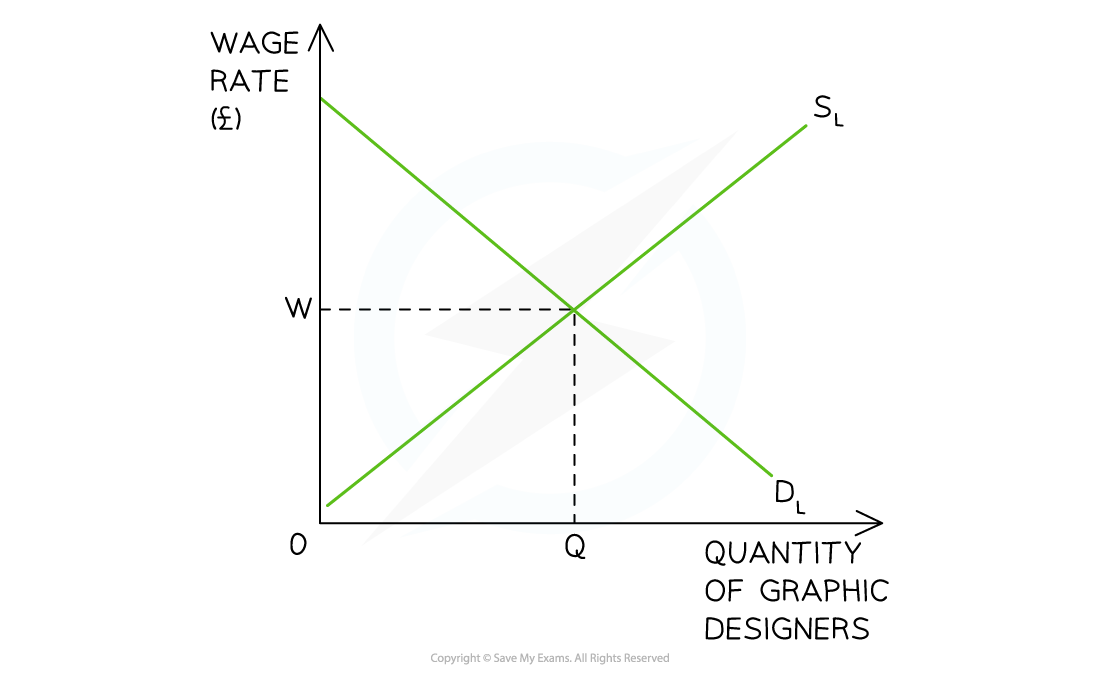
In the labour market for graphic designers, the equilibrium wage rate is W and the equilibrium quantity is Q. At this point the DL = SL
Diagram Analysis
- The market for graphic designers is in equilibrium where DL = SL
- The equilibrium wage is W and the quantity of labour is Q
- There is no excess supply of labour
- There is no excess demand for labour
Current Labour Market Issues
- The labour market is extremely important as jobs provide income to households, which directly impacts the standard of living in an economy
- Changes to conditions in the labour market can be traumatic as they may result in changes to wage rates, working conditions and/or the benefits associated with a particular job
- These changes can possibly decrease the standard of living for many people
Current Labour Market Issues in the UK
| Skills shortages | Youth unemployment | Changes to retirement ages |
|
|
|
| School leaving age | Zero-hour contracts | Temporary/flexible working |
|
|
|
Government Intervention in the Labour Market
Maximum & Minimum Wages
- The UK Government usually intervenes in the labour market in order to improve equity & avoid the exploitation of workers
- A maximum wage is a government imposed price ceiling below the market price & is rarely used
- There has been some discussion recently to set maximum wages for CEOs as their wages in early 2022 were 86x the average wage of full-time employees
- If CEOs were paid less then the average pay per worker may increase
- A minimum wage is a legally imposed wage level that employers must pay their workers
- It is set above the market rate
- The minimum wage/hour varies based on age
- A maximum wage is a government imposed price ceiling below the market price & is rarely used

A national minimum wage (NMW1) is imposed above the market wage rate (We) at W1
Diagram Analysis
- The market equilibrium wage & quantity for truck drivers in the UK is seen at WeQe
- The UK government imposes a national minimum wage (NMW) at W1
- Incentivised by higher wages, the supply of labour increases from Qe to Qs
- Facing higher production costs, the demand for labour by firms decreases from Qe to Qd
- This means that at a wage rate of W1 there is excess supply of labour & the potential for real wage unemployment equal to QdQs
Exam Tip
When evaluating national minimum wages, do not assume that they will automatically increase unemployment. Many studies have shown that unemployment does not increase - and in some instances employment increases. This is likely due to the fact that workers are receiving higher wages and choose to consume more. This increases aggregate demand (AD) in the economy which in turn increases the demand for labour by firms - thus eradicating any potential real wage unemployment.
Public Sector Wage Setting
- The UK government is the largest employer in the nation
- In April 2022 there were 5.74 million public sector workers out of a total of 29.6 million employed workers (19.39%)
- In many industries, the UK Government is the dominant employer & so is able to exercise monopsony power in setting the wage rates
- There are several implications of this public sector wage setting
- If the government increases the NMW, they are significantly increasing their own wage bill
- The private sector often uses public sector wages as a benchmark for their own wage calculations
- If public sector wages increase & private sector ones do not, it can create tension between workers in the different sectors
- Increases to public sector pay often have to be paid for by increases in tax rates for the entire working population
- In June 2022, public sector workers were striking due to issues with the pay increases offered by the Government
- Worker's wages were frozen from 2010 to 2015 after the 2008 global financial crisis
- This was followed by rampant inflation & wage increases well below the level of inflation
Policies To Tackle Labour Market Immobility
- There are many individual policies that the UK Government employs in order to reduce labour market immobility & together they help reduce the labour market failures
Examples Of Policies Used To Tackle Labour Market Immobility
| Policy | Explanation |
| Improved education/training | Education improves skills & a wider skill base allows workers to move more easily between jobs which are not 100% identical |
| Targeting skills shortages | Identifying markets with specific skills shortages & training workers in those skills provides some opportunity for workers to switch between occupations |
| Subsidising employers | A per hire subsidy from the government provides an incentive for employers to take on workers without the necessary skills (& train them) - or workers from a specific demographic (e.g. disabled workers) & this improves occupational mobility |
| Relocation subsidies | Providing relocation subsidies to workers reduces both geographical & occupational immobility |
| Reducing information asymmetry | Setting up job centres and improving the flow of information between employers & the unemployed helps workers to quickly identify new opportunities |
| Reducing discrimination | Reducing discrimination in hiring practices will help some workers improve occupational mobility |
Significance of the PED & PES for Labour
The elasticity of demand for labour
- This refers to how responsive a firms demand for labour is to a change in the price of labour (wage rate)
- If the demand for labour is elastic, then an increase in the wage rate will result in a more than proportional decrease in the quantity of labour demanded by firms
- If the demand for labour is inelastic, then an increase in the wage rate will result in a less than proportional decrease in the quantity demanded of labour demanded by firms
- If demand is elastic firms will be very responsive to changes in wage rates, rapidly hiring workers when wages fall and firing workers when wages rise
- If demand is inelastic firms will have a much smaller response to rising or falling wages
Factors That Influence PED of Labour
|
The proportion of labour costs to total costs
The higher these are then the more elastic the demand for labour will be; the lower these are then the more inelastic the demand for labour will be |
Ease & cost of factor substitution
If substituting capital for labour is easy & the cost is comparable to the increase in wages, the demand for labour will be more elastic - and vice versa |
|
PED of the final product
If the product being produced is price inelastic in demand, then the demand for labour is likely to be more inelastic i.e if wages rise, firms will pass on the increased costs of production to the final consumers |
Time period
In the short-run, demand for labour is likely to be more price inelastic i.e an increase in wages will have a less than proportional decrease in the quantity demanded. However, in the medium to long-term firms can research alternative methods of production & the demand for labour becomes more price elastic |
The elasticity of supply of labour
- This refers to how responsive the supply of labour is to a change in the price of labour (wage rate)
- If the supply of labour is elastic, then an increase in the wage rate will result in a more than proportional increase in the quantity of labour supplied
- If the supply of labour is inelastic, then an increase in the wage rate will result in a less than proportional increase in the quantity of labour supplied
- In low skilled occupations the quantity of labour supplied is very responsive to a change in wage rates i.e. supply of labour is elastic
- Occupations which require a longer & higher level of training tend to have an inelastic supply of labour i.e even if wage rates increased significantly, there would be a less than proportional increase in the supply of labour in the short run
转载自savemyexams


最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








