- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel A Level Economics A:复习笔记3.3.2 Costs
The Relationships Between Different Types of Costs
- Fixed costs are costs that do not change as the level of output changes
- These have to be paid whether output is zero or 5000
- e.g. building rent, management salaries, insurance, bank loan repayments etc.
- These have to be paid whether output is zero or 5000
- Variable costs are costs that vary directly with output
- These increase as output increases & vice versa
- E.g. raw material costs, wages of workers directly involved in production
- These increase as output increases & vice versa
- Marginal cost is the cost of producing an additional unit of output
Cost Calculations
Based on the above definitions, we can calculate several different types of costs
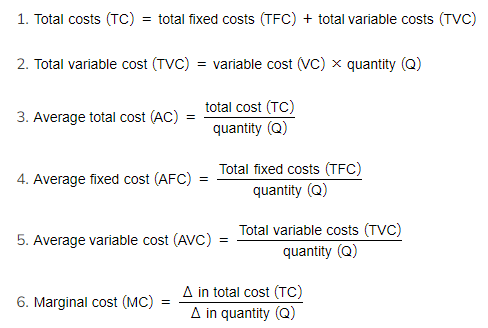
Cost Calculations Using the Above Formulas
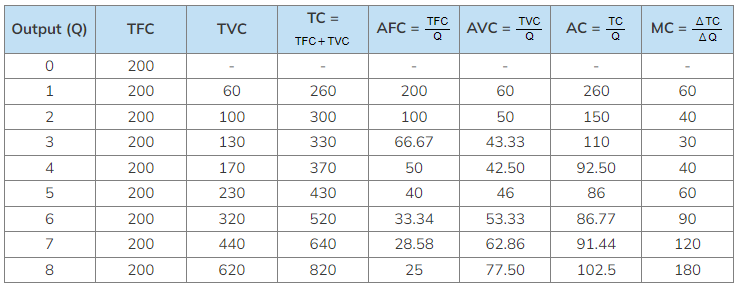
Short-run Cost Curves
Concepts That Help to Provide Understanding of How the Cost Curves Are Derived
| Concept | Explanation |
|
Short-run |
That period of time in which at least one factor of production is fixed. E.g. it is difficult to change machinery or the number of factories in the short run, but that can be achieved in the long run. The variable factor that is usually added to production is labour as it is easy to hire new workers |
| Long-run | That period of time in which all of the factors of productions are variable. This is also called the planning stage as firms can plan for increased capacity and production |
| Marginal product of labour (MP) | The change in output that results from adding an additional unit of labour |
| Law of diminishing marginal productivity | In the short run, as more of a variable factor (e.g. labour) is added to fixed factors (e.g. capital), there will initially be an increase in productivity. However, a point will be reached where adding additional units begins to decrease productivity due to the relationship between labour and capital |
- In the short-run, the shapes of the cost curves (AC, AVC & MC) are determined by the law of diminishing marginal productivity
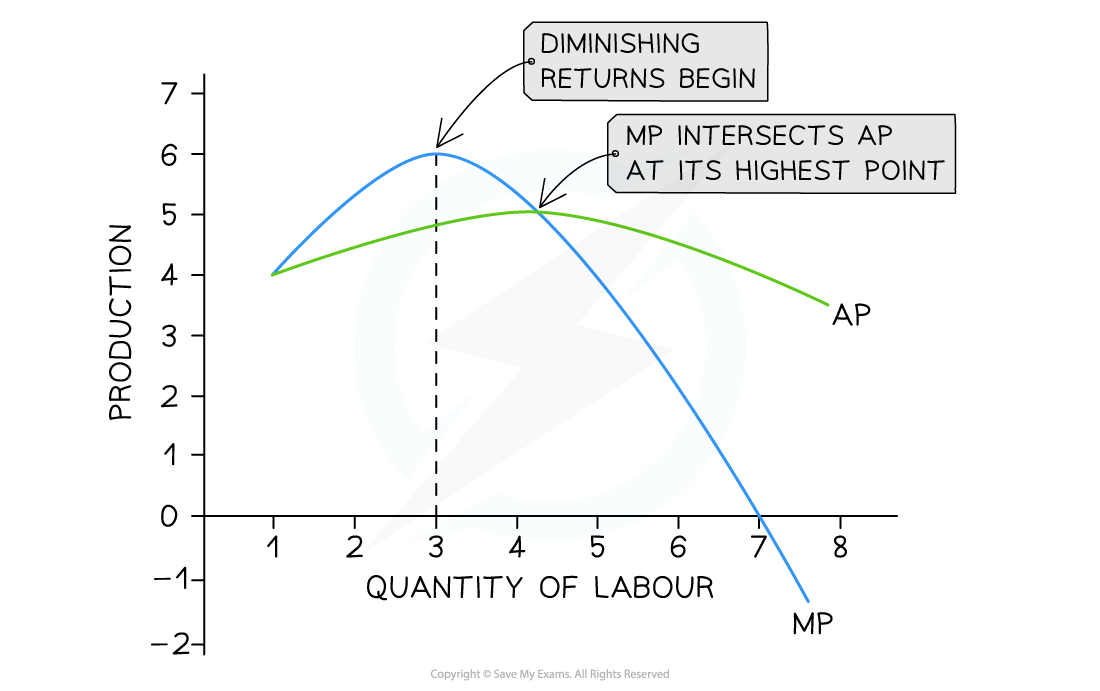
In the short run, marginal product (MP) increases with the addition of three workers before diminishing returns for each additional worker begin
Diagram Analysis
- A small food van selling burgers (product) at a music festival increases productivity up to the addition of a third worker
- After that, workers get in each other's way & there is not enough grill space (capital) & MP no longer increases
- If more workers are hired, then the MP of each additional worker begins to fall
- Adding additional workers up to the 7th worker will keep increasing the total product
- With the hiring of the 7th worker, the MP turns negative which will decrease the total product
Connection Between Diminishing Marginal Returns & The Cost Curves
- As the marginal product increases, marginal costs decrease
- There is an inverse relationship
- Increasing returns = decreasing costs
- Decreasing returns = increasing costs
- There is an inverse relationship
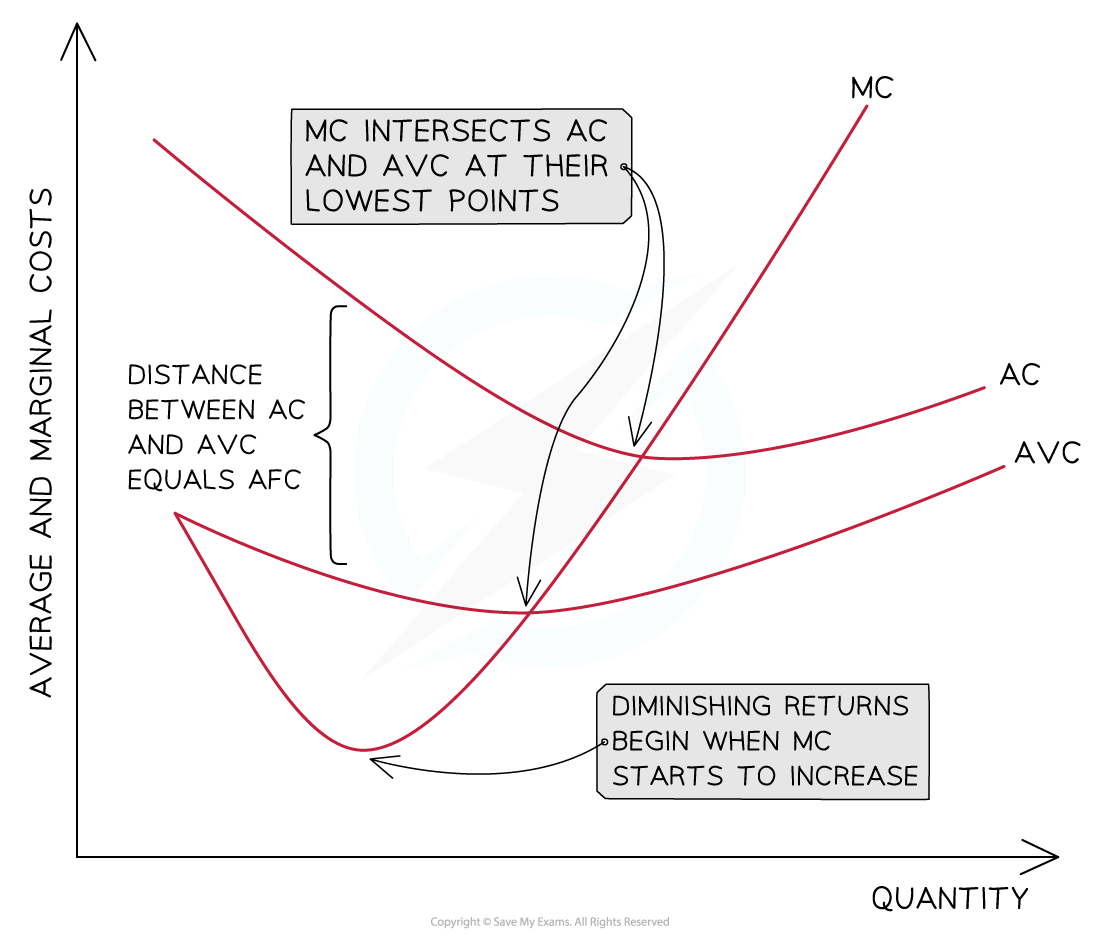
Diagram Analysis
- The distance between the AVC & AC = the AFC
- AVC converges towards AC as the AFC continuously decreases with an increase in output
- AVC decreases as additional workers are added & each worker produces additional product
- Marginal costs (MC) decrease initially as additional workers are added & the marginal product is increasing
- Diminishing returns begin when the MC starts to increase
- MC will cross the AVC and AC curves at their lowest point
- As long as the cost of producing the next unit (MC) is lower than the average, it will pull down the average
- When the cost of producing the next unit (MC) is higher than the average, it will pull up the average
Short-run and Long-run Average Costs Curves
- Day to day operations of a firm occur in the short-run
- In the long-run, they are able to plan to increase the scale of production
- E.g by increasing the size of the factory
- Larger scale = more output & the firm moves onto a new SRAC curve in which the average unit costs are lower
- In the long-run, a growing firm is likely to keep repeating this process,
- Each time a more efficient SRAC is generated
- The long-run average cost curve (LRAC) is the line of best fit between the lowest points of the short-run ATC curves
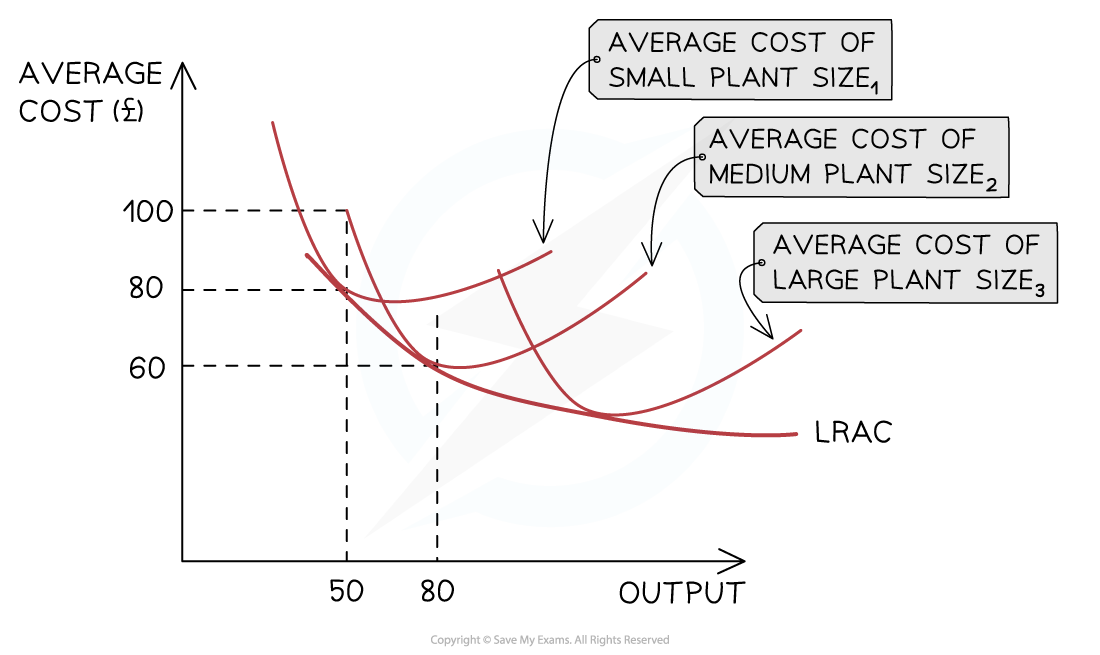
The LRAC curve is generated by the addition of successive SRAC as the firm expands its scale of production
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









