- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel A Level Economics A:复习笔记1.2.5 Elasticity of Supply
Price Elasticity of Supply (PES)
- The law of supply states that when there is an increase in price (ceteris paribus), producers will increase the quantity supplied and vice versa
- Economists are interested by how much the quantity supplied will increase
- Price elasticity of supply (PES) reveals how responsive the change in quantity supplied is to a change in price
- The responsiveness is different for different types of products
Calculation of PES
- PES can be calculated using the following formula
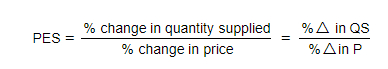
- To calculate a % change, use the following formula
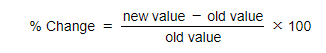
Worked Example
In recent months, the price of avocados has increased from £0.90 to £1.45. Bewdley Farm Shop in the Severn valley have sought to maximise their profits by increasing the quantity supplied to market. They have been able to increase sales from 110 units a week to 120 units a week. Calculate the PES of avocados and explain one reason for the value
Step 1: Calculate the % change in QS
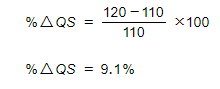
Step 2: Calculate the % change in P
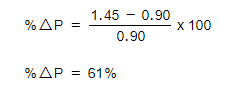
Step 3: Insert the above values in the PES formula

Step 4: Explain one reason for the value
The PES value of 0.15 indicates that avocados are very price inelastic in supply. Even with a significant increase in price, suppliers are unable to supply more likely due to the time it takes to grow additional avocados
Exam Tip
When doing elasticity calculations make sure that your final answer is not expressed as a percentage. This is a common error and loses marks.
Interpreting PES Values
The Values of PES Vary From 0 To Infinity (∞) & They Are Classified As Follows
| Value | Name | Explanation |
| 0 | Perfectly Inelastic | The QS is completely unresponsive to a change in P (e.g. fixed number of seats in a theatre) |
| 0→1 | Relatively Inelastic | The %∆ in QS is less than proportional to the %∆ in P (e.g agricultural products) |
| 1→ ∞ | Relatively Elastic | The %∆ in QS is more than proportional to the %∆ in P (e.g t-shirts) |
| ∞ | Perfectly Elastic | The %∆ in QS will fall to zero with any %∆ in P. However, supply is unlimited at a particular price. This is a very theoretical scenario but is evident when examining international trade diagrams |
Factors That Influence the PES
- Some products are more responsive to changes in prices than other products
- The factors that determine the responsiveness are called the determinants of PES and include:
- Mobility of the factors of production: if producers can quickly switch their resources between products, then the PES will be more elastic. For example, if prices of hiking boots increase and shoe manufacturers can switch resources from producing trainers to boots, then boots will be price elastic in supply
- Availability of raw materials: if raw materials are scarce then PES will be low (inelastic). If they are abundant, PES will be higher (elastic)
- Ability to store goods: if products can be easily stored then PES will be higher (elastic) as producers can quickly increase supply (for example, tinned food products). An inability to store products results in lower PES (inelastic)
- Spare capacity: if prices increase for a product and there is capacity to produce more in the factories that make those products, then supply will be elastic. If there is no spare capacity to increase production, then supply will be inelastic
- Time period: In the short run, producers may find it harder to respond to an increase in prices as it takes time to produce the product (e.g., avocados). However, in the long run they can change any of their factors of production so as to produce more
Exam Tip
Many students confuse PES with PED and inadvertently answer questions using knowledge from PED. When faced with PES questions, tell yourself to think like a producer (and not a consumer!) and it will help you to stay focused on providing the correct answer.
Distinction Between Short-run & Long-run
- The resources used in production are called factors of production
- All four factors of production are required to produce any good/service
- Land: non man made resources used in production (e.g. coal)
- Capital: man made resources used in production (e.g. MRI machine or fertiliser)
- Labour: people involved in the production process
- Entrepreneurship: the individual(s) involved in organising the other factors of production
- Economists differentiate between the short-run and the long-run periods of production and these definitions relate to the factors of production. It is not a physical period of time
- Short-run is any period of time in which at least one factor of production is fixed and this is a limiting factor. For example, Lego may be able to vary all factors of production in the short-run, except for the number of factories (capital) that they have
- Long-run is any period of time in which all the factors of production are variable (it is also called the planning stage). Producers are able to vary all of their resources so as to respond to changing market conditions. For example, Lego could build a new factory so as to take advantage of higher prices or greater demand
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









