- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel A Level Economics A:复习笔记1.2.3 Price, Income & Cross Elasticities of Demand
Price Elasticity of Demand (PED)
- The law of demand states that when there is an increase in price, there will be a fall in quantity demanded
- Economists are interested by how much the quantity demanded will fall
- Price elasticity of demand reveals how responsive the change in quantity demanded is to a change in price
- The responsiveness is different for different types of products
Calculation of PED
- PED can be calculated using the following formula
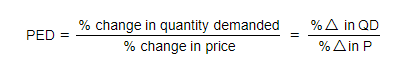
- To calculate a % change, use the following formula
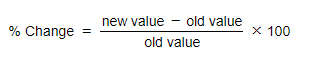
Worked Example
A firm raises the price of its products from £10 to £15. Its sales fall from 100 to 40 units per day. Calculate the PED of its products
Step 1: Calculate the % change in QD
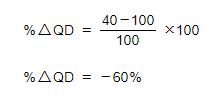
Step 2: Calculate the % change in P
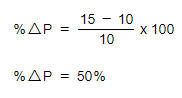
Step 3: Insert the above values in the PED formula
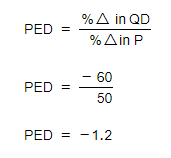
The PED value will always be negative so economists ignore the sign and present the answer as 1.2
Interpreting PED Values
The Size of PED Varies From 0 To Infinity (∞) & Is Classified As Follows
| Value | Name | Explanation |
| 0 | Perfectly Inelastic | The QD is completely unresponsive to a change in P (very theoretical value e.g. heart transplant is extremely inelastic but possibly not perfectly) |
| 0→1 | Relatively Inelastic | The %∆ in QD is less than proportional to the %∆ in P (e.g. addictive products) |
| 1 | Unitary Elasticity | The %∆ in QD is exactly equal to the %∆ in P |
| 1→ ∞ | Relatively Elastic | The %∆ in QD is more than proportional to the %∆ in P (e.g. luxury products) |
| ∞ | Perfectly Elastic | The %∆ in QD will fall to zero with any %∆ in P (highly theoretical elasticity) |
Factors That Influence the PED
- Some products are more responsive to changes in prices than other products
- The factors that determine the responsiveness are called the determinants of PED and include:
- Availability of substitutes: good availability of substitutes results in a higher value of PED (relatively elastic)
- Addictiveness of the product: addictiveness turns products into necessities resulting in a low value of PED (relatively inelastic)
- Price of product as a proportion of income: the lower the proportion of income the price represents, the lower the PED value will be. Consumers are less responsive to price changes on cheap products (relatively inelastic)
- Time period: In the short term, consumers are less responsive to price increases resulting in a low value of PED (relatively inelastic). Over a longer time period consumers may feel the price increase more and will then look for substitutes resulting in a higher value of PED (relatively elastic)
Income Elasticity of Demand (YED)
- Changes in income result in changes to the demand for goods/services
- Economists are interested in how much the quantity demanded will change for different products
- Income elasticity of demand (YED) reveals how responsive the change in quantity demanded is to a change in income
Calculation of YED
- YED can be calculated using the following formula
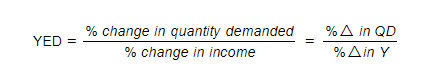
Worked Example
A consumer's income rises from £100 to £125 a week. They originally consumed 12 bagels at the local bakery but this increased to 15 bagels a week. Calculate the YED of the bagels
Step 1: Calculate the % change in QD
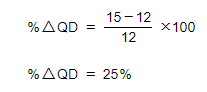
Step 2: Calculate the % change in Y
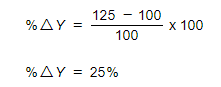
Step 3: Insert the above values in the YED formula
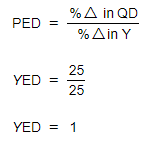
Interpreting YED Values
- The YED value can be positive or negative and the value is important in determining the type of good
The Value of YED Determines the Type of Good and Response to Changes in Income
| Value | Type of Good | Explanation |
| 0→1 | Normal necessity | Demand increases when income increases. Income inelastic which means that it is relatively unresponsive to a change in income |
| >1 | Normal luxury | Demand increases when income increases. Income elastic which means that it is relatively responsive to a change in income |
| <1 | Inferior Good | Demand decreases when income increases |
Factors That Influence YED
- YED is influenced by any factors in an economy which change the wages of workers
- During a recession wages usually fall and demand for inferior goods rises and luxury goods falls
- During a period of economic growth and rising wages, demand for luxury goods increases and demand for inferior goods decreases
- Other influences on income include minimum wage legislation, taxation, increased international trade
Cross Price Elasticity of Demand (XED)
- Changes in the prices of complementary goods and substitutes affect the demand for related products
- Cross price elasticity of demand (XED) reveals how responsive the change in quantity demanded for good A is to a change in price of good B
- The responsiveness is different for different types of products
Calculation of XED
- XED can be calculated using the following formula
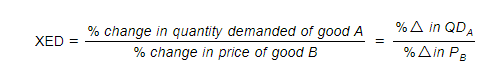
Worked Example
Leading into the release of FIFA 22 Ultimate, EA Sports discounted the price of FIFA 21 from £90 to £60. A game store in Winchester saw an increase in sales of their PlayStation 5 consoles. Prior to the discount they were selling 50 units a week and after the discount this increased to 80 units. Calculate the XED and explain the relationship between the two products
Step 1: Calculate the % change in QDA
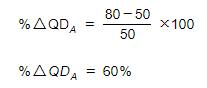
Step 2: Calculate the % change in PB
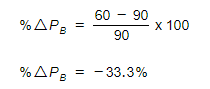
Step 3: Insert the above values in the XED formula

Step 4: Explain the relationship between the two products
The negative sign indicates that these two products are complements and the high value suggests they are strong complements
Interpreting XED Values
Using XED Values to Identify if Goods are Complements, Substitutes, Or Unrelated
| Value | Name | Explanation |
| XED < 0 | Complementary goods | The negative value indicates the two goods are complements The higher the value the stronger the relationship |
| XED > 0 | Substitutes | The positive value indicates the two goods are substitutes The higher the value the stronger the relationship |
| XED = 0 | Unrelated goods | A value of zero indicates that there is no relationship between the two goods. The closer to zero the weaker the relationship is |
Significance of Elasticities to Firms & Governments
- Knowledge of PED is important to firms seeking to maximise their revenue
- If their product is price inelastic in demand, they should raise their prices
- If price elastic in demand, then they should lower their prices
- Knowledge of PED is important to Governments with regard to taxation and subsidies
- If they tax price inelastic in demand products, they can raise tax revenue without harming firms too much
- Consumers are less responsive to price changes so firms will pass on the tax to the consumer
- If they subsidies price elastic in demand products, there can be a greater than proportional increase in demand
- Knowledge of XED is important to firms as they seek to maximise their revenue
- It can help them to adjust pricing strategies for substitute and complementary goods
- It can help them understand the likely impact of competitors' pricing strategies on their sales
- Knowledge of YED is important to firms as they seek to maintain sales and maximise profits through periods of recession or economic growth
- Firms should consider providing more inferior goods in a recessionary environment
- Firms should consider providing more luxury products during periods of economic growth
The Revenue Rule of PED
- The total revenue rule states that in order to maximise revenue, firms should increase the price of products that are inelastic in demand and decrease prices on products that are elastic in demand
Worked Example
A firm raises the price of its products from £10 to £15. Its sales have fallen from 100 to 40 units per day. Explain if they made the correct decision
Step 1: Calculate the initial sales revenue
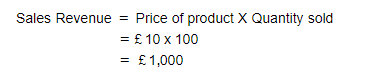
Step 2: Calculate the sales revenue after the price change
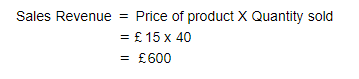
Step 3: Explain the decision
By raising the price, the total revenue has fallen by £400. This indicates that the product is price elastic in demand and the firm should have lowered their price in order to maximise revenue
Exam Tip
A common error students make is to say that when prices increase and the product is inelastic in demand, the quantity demanded does not fall. It does! But it is a less than proportional fall than the increase in price.
So, when Governments tax demerit goods such as cigarettes, the increase in price is greater than the decrease in QD, but QD still falls.
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









