- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel A Level Chemistry:复习笔记7.6.4 Organic Techniques - Preparation
Distillation & Refluxing
Simple distillation
- Simple distillation is a common practical completed in organic chemistry
- It is used as there are times that a reaction does not go to completion or there are other chemicals produced as well as the desired product
- Simple distillation allows you to separate compounds by their boiling point
- Chemicals with the lowest boiling point will distill first
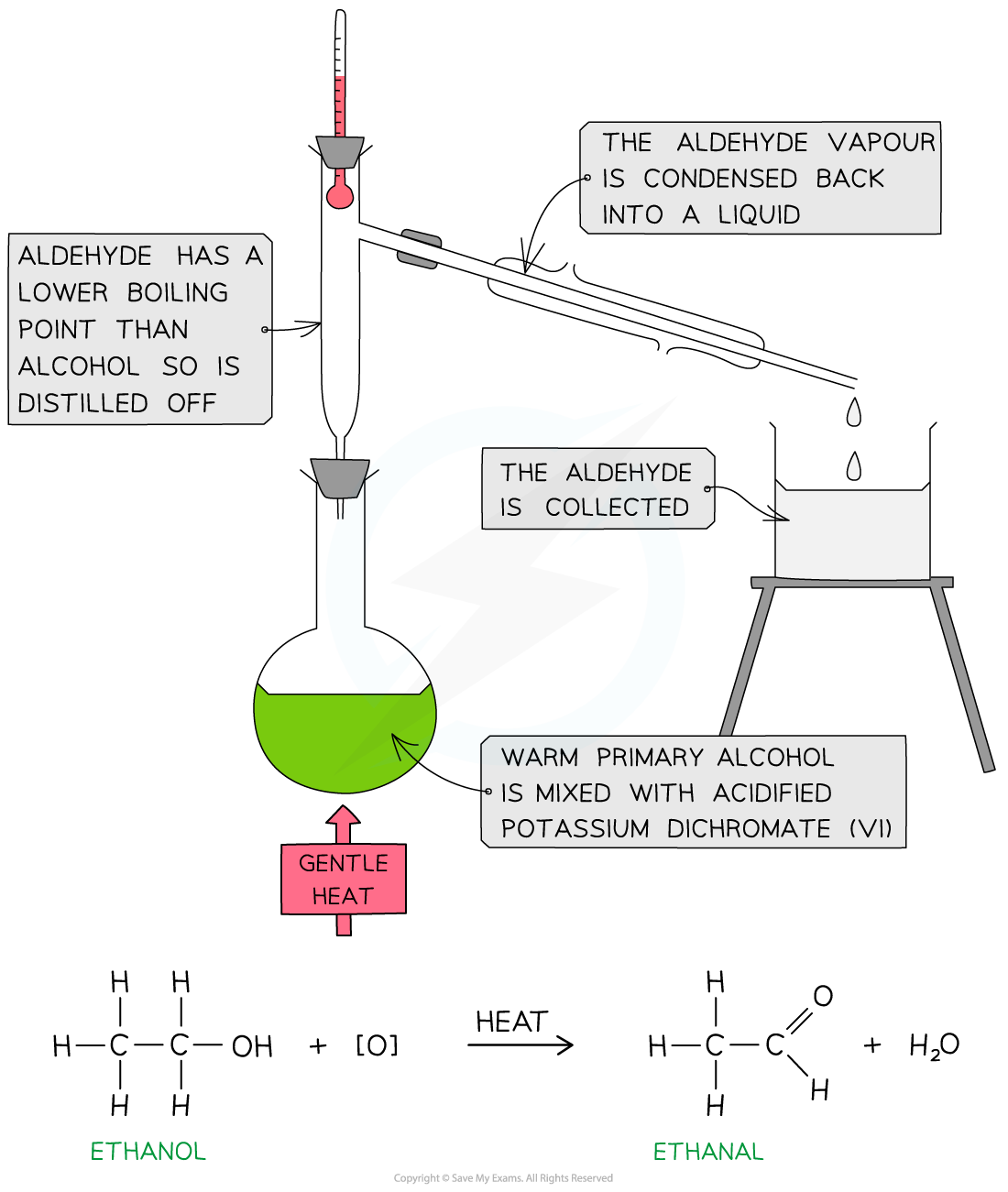
- One of the most common simple distillation practicals is the oxidation of primary and secondary alcohol to aldehydes and ketones
The simple distillation process
- To produce an aldehyde from a primary alcohol, a reaction mixture containing the primary alcohol and acidified potassium dichromate solution is placed into a pear-shaped or round bottomed flask
- Anti-bumping granules are added to promote smooth boiling
- Quickfit apparatus is then set up, including a still head and condenser connected to the side
- The joints of the Quickfit apparatus are often have a thin layer of silicon grease smeared over them to give a better seal as well as to make it easier to disassemble the equipment afterwards
- A Quickfit thermometer can be used, with the thermometer bulb sitting where the vapours will pass into the condenser
- A steady and constant stream of water passes through the condenser in a 'water jacket' - it enters at the bottom of the condenser and the drainage pipe removes the water from the top of the condenser
Heating under Distillation Apparatus
- The reaction mixture is heated until it boils using a heating mantle
- Electric heating mantles are used for this because the temperature can be controlled, and because you are using chemicals which are flammable
- The distillate which forms in the condenser drips directly into a receiving vessel
- The distillate which should be collected, is that which is given off at +/- 2 oC of the boiling point of the desired product
- Some distillate may be given off below this temperature - this needs to be discarded and a clean vessel used to collect the desired product
- Stop collecting the distillate if the temperature rises above +/- 2oC of the boiling point of the desired product
- The aldehyde product has a lower boiling point than the alcohol (since it has lost the H-bonding) so it can be distilled off as soon as it forms
Steam distillation
- Steam distillation is used to separate an insoluble liquid from an aqueous solution
- Steam is bubbled through a reaction mixture containing the aqueous solution and the insoluble liquid that forms a separate layer
- As the steam bubbles through the reaction mixture it mixes the layers so they form part of the evaporating liquid
- Advantages of steam distillation are:
- The insoluble liquid distils at a temperature below its usual boiling point
- It reduces the chances of thermal decomposition of the insoluble liquid
Heating under reflux
- Organic reactions often occur slowly at room temperature
- Therefore, organic reactions can be completed by heating under reflux to produce an organic liquid
- This allows the mixture to react as fully as possible without the loss of any reactants, products or solvent
- In distillation, you are trying to separate a chemical or product from a mixture
- When heating under reflux, you aim to keep all the chemicals inside the reaction vessel
The Heating under Reflux Process:
- Example reactions where heating under reflux could be used include:
- The production of a carboxylic acid from a primary alcohol using acidified potassium dichromate
- The production of an ester from an alcohol and acid in the presence of an acid catalyst
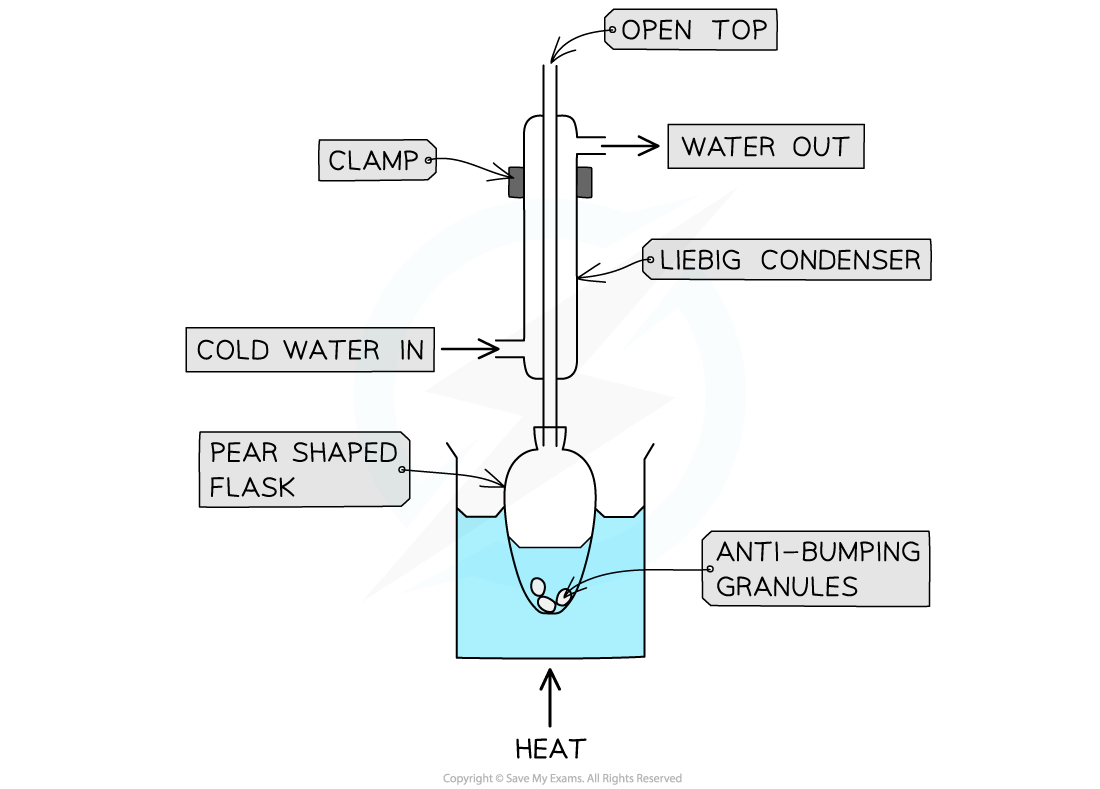
- The reaction mixture is placed into a pear-shaped or round bottomed flask
- Anti-bumping granules are, again, added to promote smooth boiling
- The flask is placed in a heating mantle or it can be immersed in a water bath for heating
- Quickfit apparatus is then set up with the condenser clamped vertically in place
- The joints of the Quickfit apparatus are commonly greased as with distillation
- A steady and constant stream of water passes through the condenser in a 'water jacket' - it enters at the bottom of the condenser and the drainage pipe removes the water from the top of the condenser
- The water is heated and the reaction mixture allowed to boil
- The heated is stopped and the mixture allowed to cool back to room temperature
The preparation of ethyl ethanoate involves heating under reflux for about 15 minutes
Exam Tip
- These practicals give you the opportunity to discuss:
- The use of an electric heating mantles and water baths rather than a Bunsen burner
- The choice and setup of laboratory apparatus
- Health and safety considerations including the careful handling of different liquids, including those which are corrosive, irritant, flammable and toxic
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









