- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel A Level Chemistry:复习笔记7.3.4 Acyl Chlorides & Esters
Hydrolysis of Esters
Hydrolysis of Esters - Acid
- The reverse of the esterification reaction is called hydrolysis
- Ester hydrolysis is a useful reaction for creating biodegradable plastics
- Esters can be hydrolysed to reform the carboxylic acid and alcohol or salts of carboxylic acids by using either dilute acid (e.g. sulfuric acid) or alkali (e.g. sodium hydroxide) and heat
- When an ester is heated under reflux with acid an equilibrium mixture is established, meaning that the hydrolysis reaction is not complete
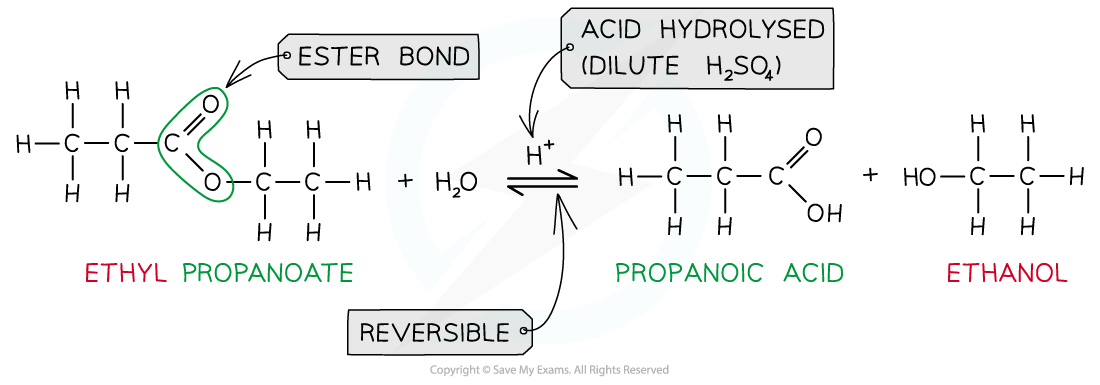
Ester hydrolysis by dilute acid is a reversible reaction forming carboxylic acid and alcohol
Hydrolysis of Esters - Alkaline
- However, heating the ester under reflux with dilute alkali (e.g. sodium hydroxide) is an irreversible reaction as the ester is fully hydrolysed and the reaction goes to completion
- The carboxylic acid produced reacts with excess alkali to form a carboxylate salt and alcohol
- The sodium carboxylate salt requires further acidification to turn into a carboxylic acid
- The sodium carboxylate (-COO-) ion needs to get protonated by an acid (such as HCl) to form the carboxylic acid (-COOH)
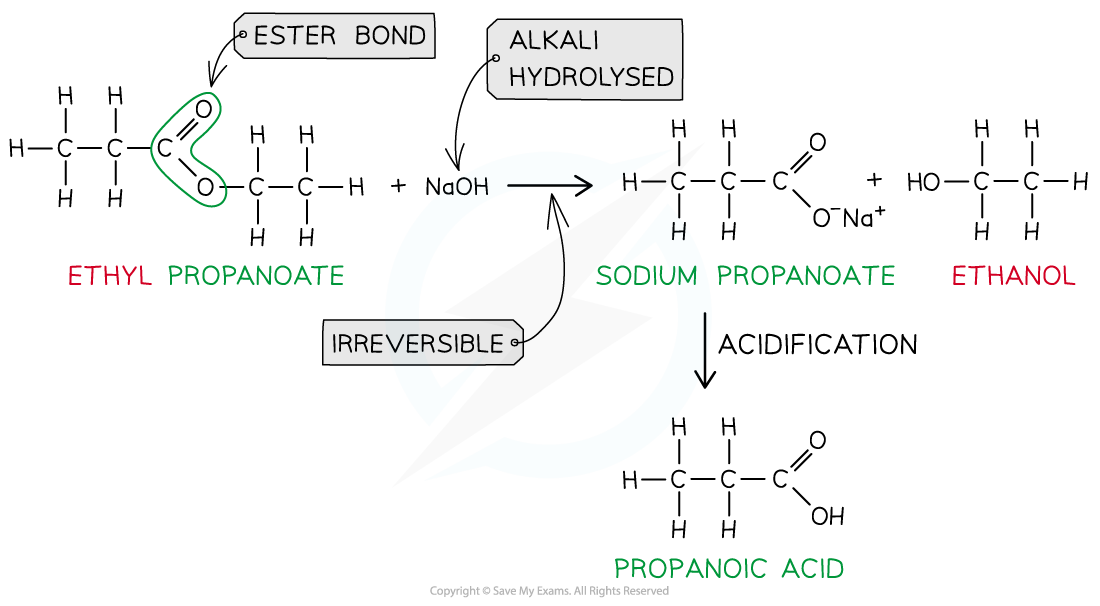
Ester hydrolysis by dilute alkali is an irreversible reaction forming a sodium carboxylate salt and alcohol
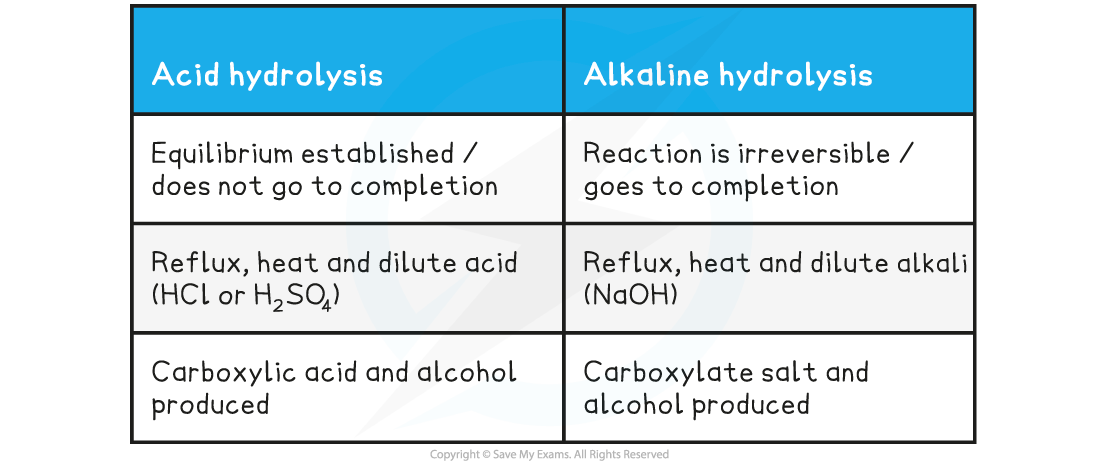
Table showing Differences in Hydrolysis of Esters
Worked Example
Name the products and write equations for the following hydrolysis reaction:
- Ethyl ethanoate with hot dilute sulfuric acid solution
- Methyl propanoate by hot sodium hydroxide solution
Answer:
Answer 1: Ethanoic acid and ethanol
CH3COOCH2CH3 + H2O ⇌ CH3COOH + CH3CH2OH
Answer 2: Sodium propanoate and methanol
CH3CH2COOCH3 + NaOH → CH3CH2COONa + CH3OH
Acyl Chlorides & Esters
Acyl groups
- Acyl groups can be built into many molecules using acyl chlorides or acid anhydrides (known as acylating agents)
- Acyl chlorides are derivatives of carboxylic acids by substitution of the -OH group by a chlorine atom
- Acyl chlorides are named by identifying the parent hydrocarbon chain and adding the suffix -oyl chloride
- They can also be named by removing the -oic acid from the carboxylic acid and adding -oyl chloride
- Acid anhydrides are also derivatives of carboxylic acids formed by substitution of the -OH group by an alkanoate
- Acid anhydrides are named by identifying the parent hydrocarbon chain and adding the suffix -oic anhydride
- They can also be named by removing the -oic acid from the carboxylic acid and adding -oic anyhydride
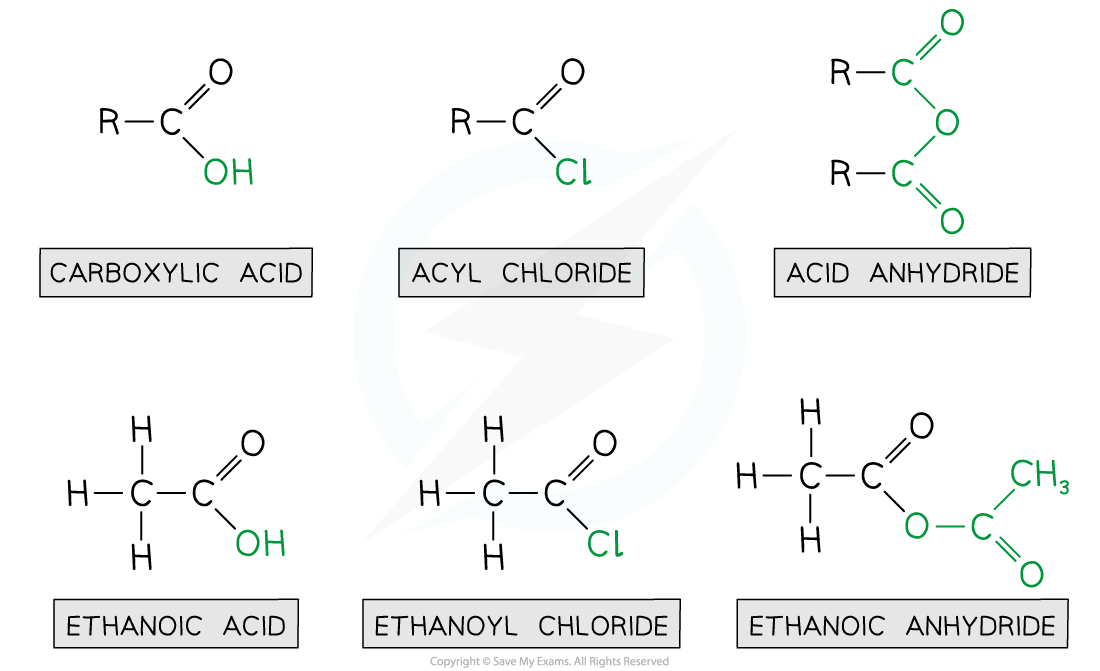
Ethanoic acid derivatives
Worked Example
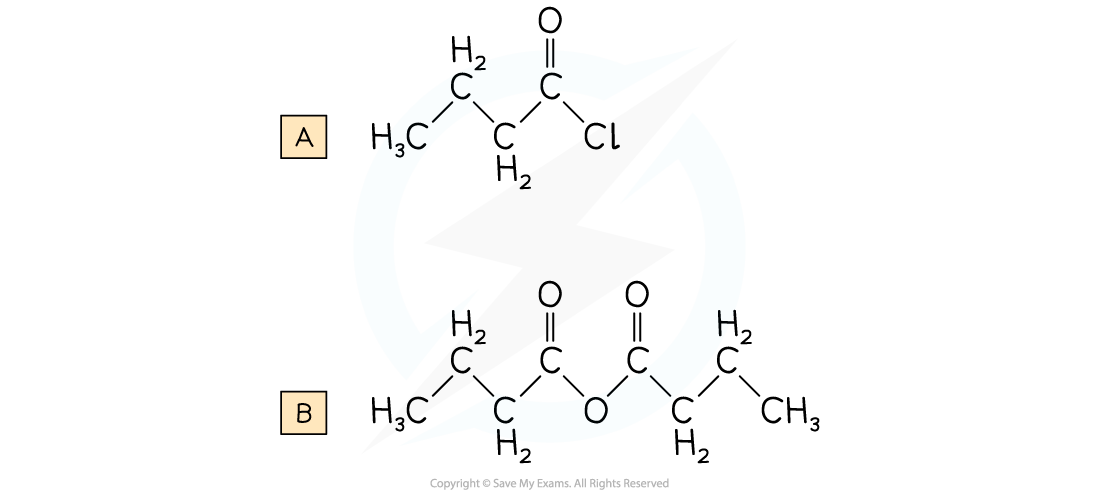
Draw the displayed formula for the following:
A. Butanoyl chloride
B. Butanoic anhydride
Answer:
- Acyl chlorides are reactive organic compounds that undergo many reactions such as nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions
- In nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions, the nucleophilic addition of a small molecule across the C=O bond takes place followed by elimination of a small molecule
- Examples of these nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions include:
- Hydrolysis
- Reaction with alcohols to form esters
- Reaction with ammonia and primary amines to form amides
Hydrolysis
- The hydrolysis of acyl chlorides results in the formation of a carboxylic acid and HCl molecule
- This is a nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction
- A water molecule adds across the C=O bond
- A hydrochloric acid (HCl) molecule is eliminated
- An example is the hydrolysis of propanoyl chloride to form propanoic acid and HCl

Acyl chlorides are hydrolysed to carboxylic acids
Formation of esters
- Acyl chlorides can react with alcohols to form esters
- The esterification of acyl chlorides is also a nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction
- The alcohol adds across the C=O bond
- A HCl molecule is eliminated

Acyl chlorides undergo esterification with alcohols to form esters
Formation of amides
- Acyl chlorides can form amides with primary amines and concentrated ammonia
- The nitrogen atom in ammonia and primary amine has a lone pair of electrons which can be used to attack the carbonyl carbon atom in the acyl chlorides
- The product is an amide (when reacted with ammonia) or N-substituted amide (when reacted with primary amines)
- This is also an example of a nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction as
- The amine or ammonia molecule adds across the C=O bond
- A HCl molecule is eliminated
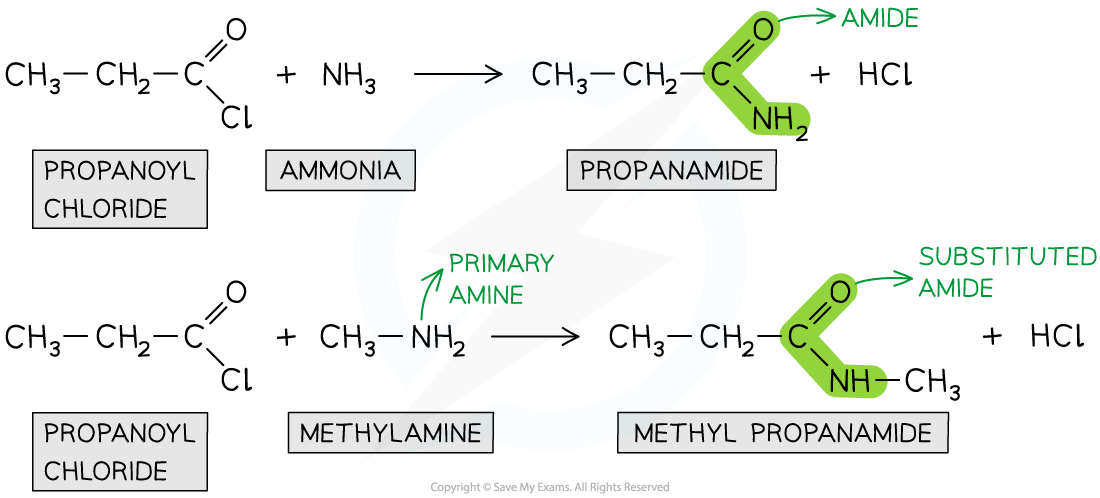
Acyl chlorides undergo reactions with ammonia and primary amines to form amides
Condensation Polymerisation
- Addition polymerisation has been covered in reactions of alkenes
- They are made using monomers that have C=C double bonds joined together to form polymers such as polyethene
- Condensation polymerisation is another type of reaction whereby a polymer is produced by repeated condensation reactions between monomers
- Natural condensation polymers are all formed by elimination of water
- Although the process of condensation polymerisation involves the elimination of a small molecule
- Condensation polymers can be identified because the monomers are linked by ester or amide bonds
Polyester
- Is formed by the reaction between dicarboxylic acid monomers and diol monomers
- Polyester is produced by linking these monomers with ester bonds / links
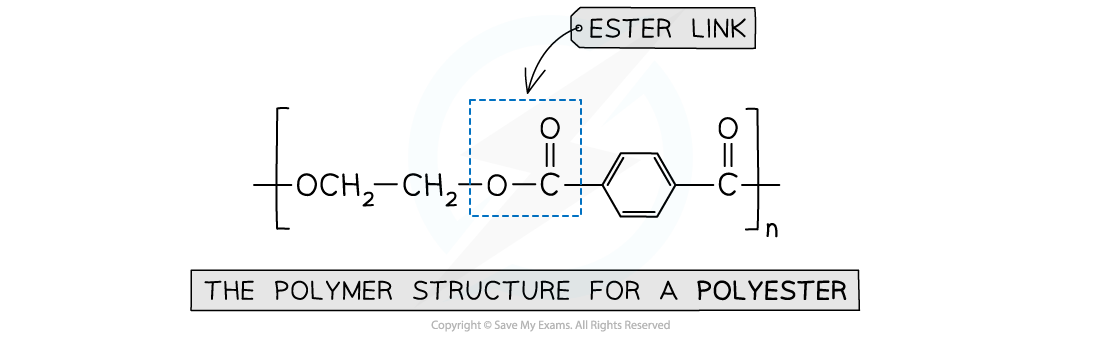
This polymer structure shows an ester functional group linking monomers together
Formation of polyesters
- A diol and a dicarboxylic acid are required to form a polyester
- A diol contains 2 -OH groups
- A dicarboxylic acid contains 2 -COOH groups
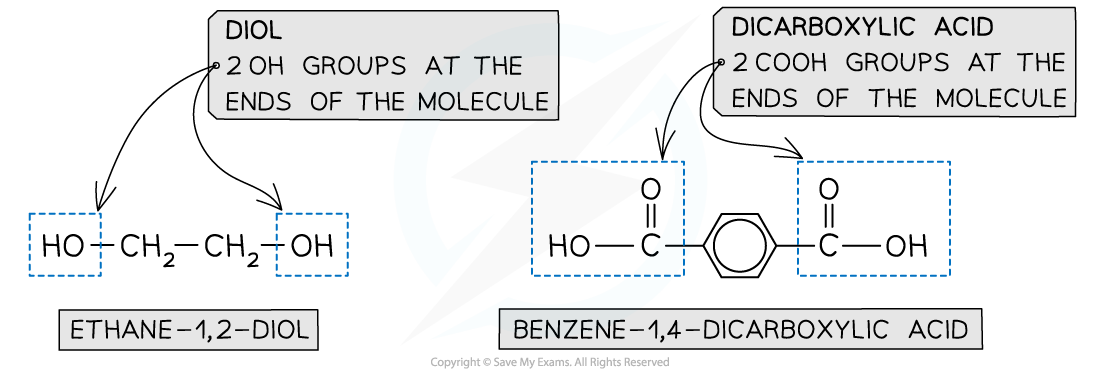
The position of the functional groups on both of these molecules allows condensation polymerisation to take place effectively
- When the polyester is formed, one of the -OH groups on the diol and the hydrogen atom of the -COOH are expelled as a water molecule (H2O)
- The resulting polymer is a polyester
- In this example, the polyester is poly(ethylene terephthalate) or PET, which is sometimes known by its brand names of Terylene or Dacron
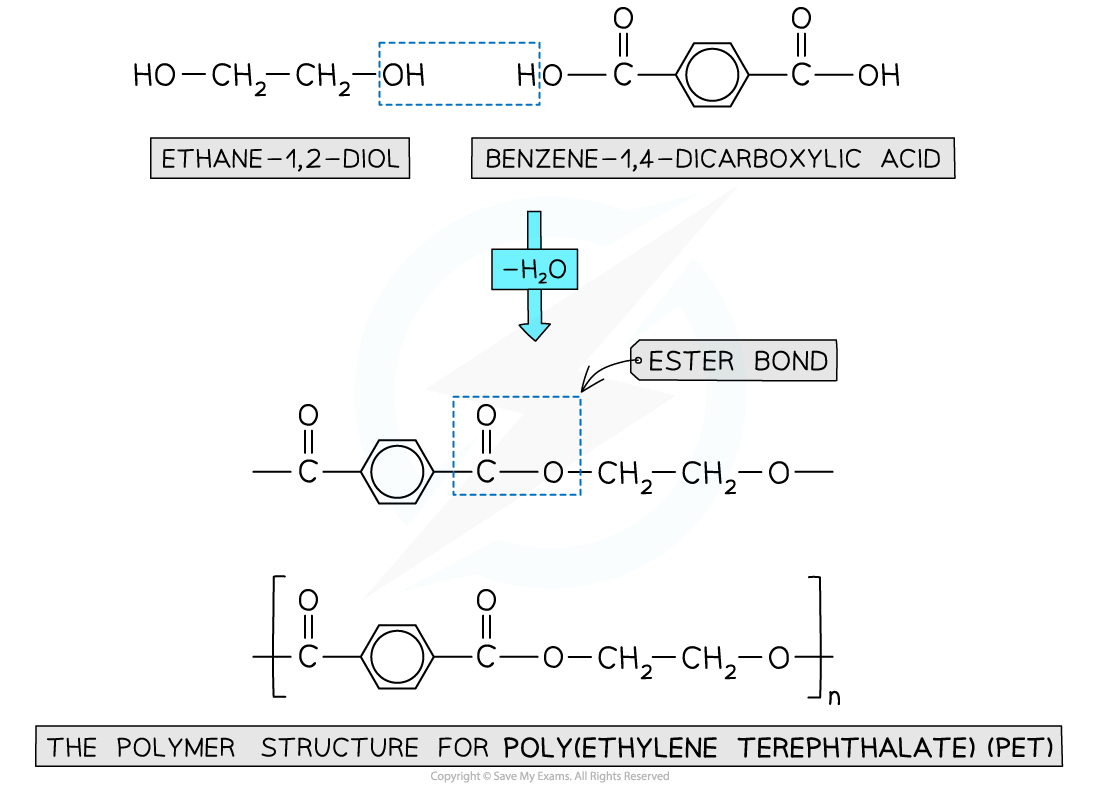
Expulsion of a water molecule in this condensation polymerisation forms the polyester called (ethylene terephthalate) (PET)
Formation of polyesters - hydroxycarboxylic acids
- So far the examples of making polyesters have focused on using 2 separate monomers for the polymerisation
- There is another route to making polyesters
- A single monomer containing both of the key functional groups can also be used
- These monomers are called hydroxycarboxylic acids
- They contain an alcohol group (-OH) at one end of the molecule while the other end is capped by a carboxylic acid group (-COOH)
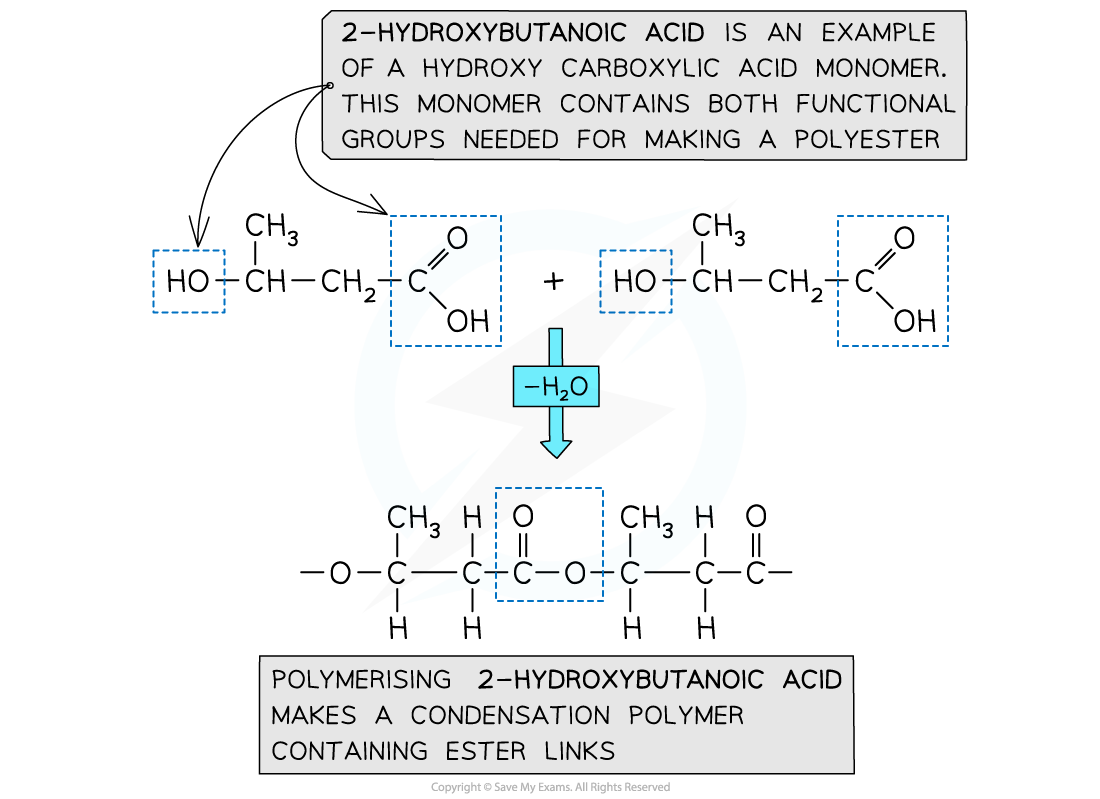
Both functional groups that are needed to make the polyester come from the same monomer
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








