- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel A Level Chemistry:复习笔记7.2.2 Testing for Carbonyls
Reactions of Carbonyls
- Carbonyl compounds can undergo a number of reactions, some of which allow you to distinguish between an aldehyde and a ketone
- Oxidation - with acidified potassium dichromate(VI) solution, Tollens' reagent or Fehling's / Benedict's solution
- Reduction - with lithium tetrahydridoaluminate / lithium aluminium hydride in dry ether
- Nucleophilic addition - with HCN or acidified KCN
- Non-specific carbonyl testing
- 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine (2,4-DNPH) - to identify a carbonyl compound
- Iodoform test - iodine in the presence of alkali
Acidified potassium dichromate(VI)
- Aldehydes can be oxidised to form carboxylic acids using acidified potassium dichromate(VI) solution
- K2Cr2O7 (aq) with sulfuric acid, H2SO4

General reaction of an aldehyde with an oxidising agent
- Ketones are very resistant to being oxidised
- This is because ketones do not have a readily available hydrogen atom, like aldehydes do
- An extremely strong oxidising agent would be needed for oxidation of a ketone to take place
- Such oxidation will likely oxidise a ketone in a destructive way, breaking a C-C bond
- Heating with acidified potassium dichromate can distinguish between an aldehyde and a ketone
- The aldehyde would be oxidised, and you would see an orange to green colour change
- The ketone would not be oxidised, so you would see no colour change
Tollens' reagent
- Tollens' reagent contains the silver(I) complex ion [Ag(NH3)2]+
- This is formed when aqueous ammonia is added to a solution of silver nitrate
- Tollens' reagent is also known as ammoniacal silver nitrate
- If gently warmed with Tollens' reagent, an aldehyde will become oxidised
- The silver(I) complex ion solution, [Ag(NH3)2]+, is colourless
- As the aldehyde is oxidised, it causes the [Ag(NH3)2]+ ions to become reduced to solid metallic silver, Ag
- This is why a positive test result is called a "silver mirror"
Positive Test Result:
- When Tollens' reagent is gently warmed with an aldehyde, the silver mirror is formed
- This is the positive test result
- When Tollens' reagent is gently warmed with a ketone, no silver mirror will be seen, as the ketone cannot be oxidised by Tollens' reagent, so no reaction takes place
- This is a negative test result
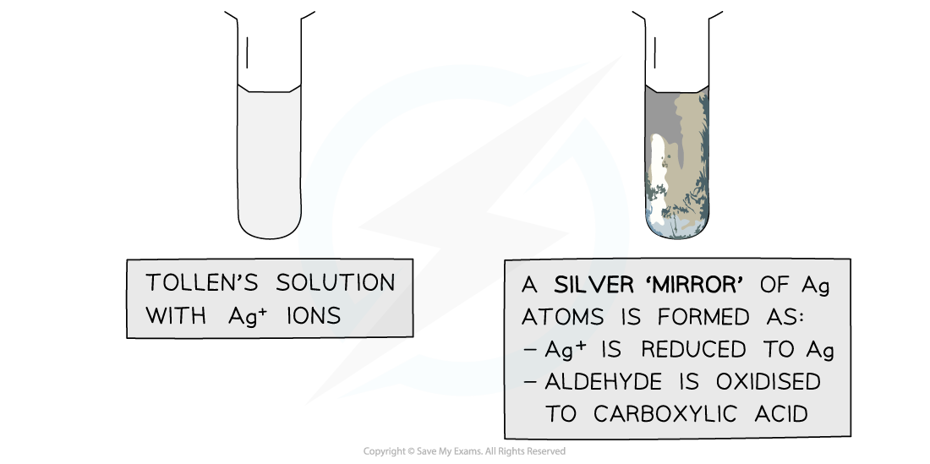
The Ag+ ions in Tollens’ reagent are oxidising agents, oxidising the aldehyde to a carboxylic acid and getting reduced themselves to silver atoms
Fehling's Solution
- Fehling’s solution is a solution containing copper(II) ions dissolved in sodium hydroxide, which act as the oxidising agent
- Benedict's solution is exactly the same as Fehling's solution but the copper(II) ions are dissolved in sodium carbonate
- If an aldehyde is warmed with Fehling's solution, the aldehyde will be oxidised and a colour change will take place
- Fehling's solution is blue, because of the copper(II) complex ions present
- During the reaction, as the aldehyde is oxidised to a carboxylic acid, the blue Cu2+ ions are reduced to Cu+ ions and a brick red precipitate is formed
- The brick red precipitate is copper(I) oxide
- If a ketone is warmed with Fehling's solution, no reaction takes place as the ketone will not be oxidised, so the solution will remain blue
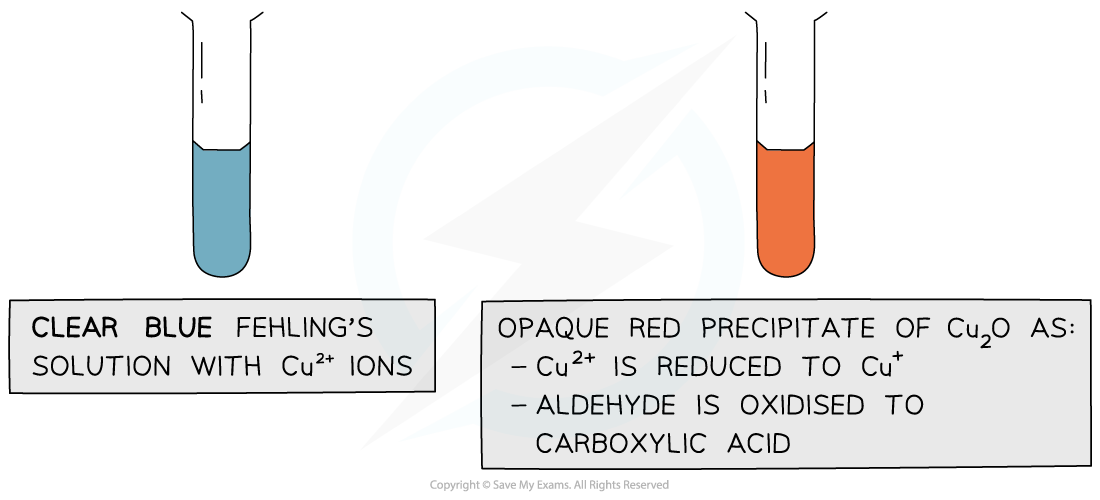
The copper(II) ions in Fehling’s solution are oxidising agents, oxidising the aldehyde to a carboxylic acid and getting reduced themselves to copper(I) ions in the Cu2O precipitate
Exam Tip
You are expected to know all of the above methods which can be used to distinguish between an aldehyde and a ketone! However, Tollens' reagent is the most commonly used method, if trying to identify an unknown sample for example.
Reduction of Carbonyls
- Aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols and ketones are reduced to secondary alcohols
- This is done with lithium tetrahydridoaluminate / lithium aluminium hydride, LiAlH4, in dry ether
- The LiAlH4 generates a hydride ion nucleophile, :H-
- The hydride ion reduces the carbonyl group in an aldehyde or a ketone
- When this reaction takes place, it is an example of a nucleophilic addition reaction
Reduction equation for an aldehyde
Reduction equation for a ketone
Nucleophilic addition
- Many of the reactions which carbonyl compounds undergo are nucleophilic addition reactions
- The carbonyl group -C=O, in aldehydes and ketones is polarised
- The oxygen atom is more electronegative than carbon drawing electron density towards itself
- This leaves the carbon atom slightly positively charged and the oxygen atom slightly negatively charged
- The carbonyl carbon is therefore susceptible to attack by a nucleophile, such as the cyanide ion

General Mechanism with an aldehyde
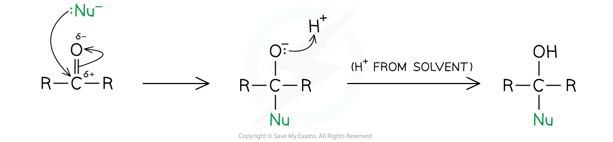
General Mechanism with a ketone
- In both reactions, the nucleophile (Nu) attacks the carbonyl carbon to form a negatively charged intermediate which quickly reacts with a proton
Addition of HCN to carbonyl compounds
The nucleophilic addition of hydrogen cyanide to carbonyl compounds is a two-step process, as shown below
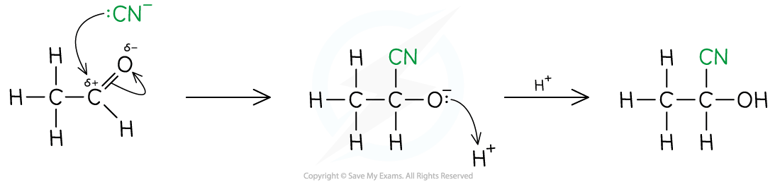
- In step 1, the cyanide ion attacks the carbonyl carbon to form a negatively charged intermediate
- In step 2, the negatively charged oxygen atom in the reactive intermediate quickly reacts with aqueous H+ (either from HCN, water or dilute acid) to form 2-hydroxynitrile compounds,
- e.g. 2-hydroxypropanenitrile
- This reaction is important in organic synthesis, because it adds a carbon atom to the chain, increasing the chain length
- The products of the reaction are hydroxynitriles
- The nitrile group is the priority functional group so it is attached to carbon 1 and results in the suffix -nitrile
- The hydroxyl group is not the priority functional group so the hydroxyl group is named using the hydroxy- prefix, rather than the -ol suffix
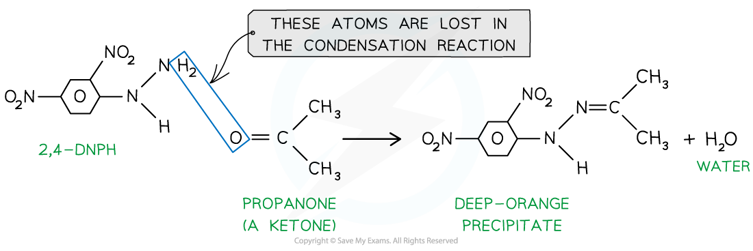
2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine (2,4-DNPH)
- 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine (also known as 2,4-DNPH) is a reagent which detects the presence of carbonyl compounds (compounds with -C=O group)
- The carbonyl group of aldehydes and ketones undergoes a condensation reaction with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine
- A condensation reaction is a reaction in which two molecules join together and a small molecule (such as H2O or HCl) is eliminated
- The product formed when 2,4-DNPH is added to a solution that contains an aldehyde or ketone is a deep-orange precipitate which can be purified by recrystallisation
- The melting point of the formed precipitate can then be measured and compared to literature values to find out which specific aldehyde or ketone had reacted with 2,4-DNPH
Ketones and aldehydes react with 2,4-DNPH in a condensation reaction

The test tube on the left shows a negative 2,4-DNPH test and the tube on the right shows a positive test
Exam Tip
The 2,4-DNPH test is especially useful as other carbonyl compounds such as carboxylic acids and esters do not give a positive result
Iodoform test
- Tri-iodomethane (also called iodoform) forms a yellow precipitate with methyl ketones
- Methyl ketones are compounds that have a CH3CO-group
- Ethanal also contains a CH3CO- group and therefore also forms a yellow precipitate with iodoform
- The reagent is heated with an alkaline solution of iodine
- This reaction involves a halogenation and hydrolysis step
- In the halogenation step, all three H-atoms in the -CH3 (methyl) group are replaced with iodine atoms, forming a -CI3 group
- The intermediate compound is hydrolysed by an alkaline solution to form a sodium salt (RCO2- Na+) and a yellow precipitate of CHI3

The reaction of ethanal with iodoform results in the formation of a yellow CHI3 precipitate
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1











