- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel A Level Chemistry:复习笔记5.3.4 Enthalpy of Solution
Solution & Hydration Definitions
Enthalpy of solution
- The standard enthalpy change of solution (ΔHsolꝋ) is the enthalpy change when 1 mole of an ionic substance dissolves in sufficient water to form an infinitely dilute solution
- The symbol (aq) is used to show that the solid is dissolved in sufficient water
- For example, the enthalpy changes of solution for potassium chloride are described by the following equations:
KCl (s) + aq → KCl (aq)
OR
KCl (s) + aq → K+ (aq) + Cl- (aq)
- ΔHsolꝋ can be exothermic (negative) or endothermic (positive)
Enthalpy of hydration
- The standard enthalpy change of hydration (ΔHhydꝋ) is the enthalpy change when 1 mole of a specified gaseous ion dissolves in sufficient water to form an infinitely dilute solution
- For example, the enthalpy change of hydration for magnesium ions is described by the following equation:
Mg2+(g) + aq → Mg2+(aq)
-
- Hydration enthalpies are the measure of the energy that is released when there is an attraction formed between the ions and water molecules
- Hydration enthalpies are exothermic
- When an ionic solid dissolves in water, positive and negative ions are formed
- Water is a polar molecule with a δ- oxygen (O) atom and δ+ hydrogen (H) atoms which will form ion-dipole attractions with the ions present in the solution
- The oxygen atom in water will be attracted to the positive ions and the hydrogen atoms will be attracted to the negative ions
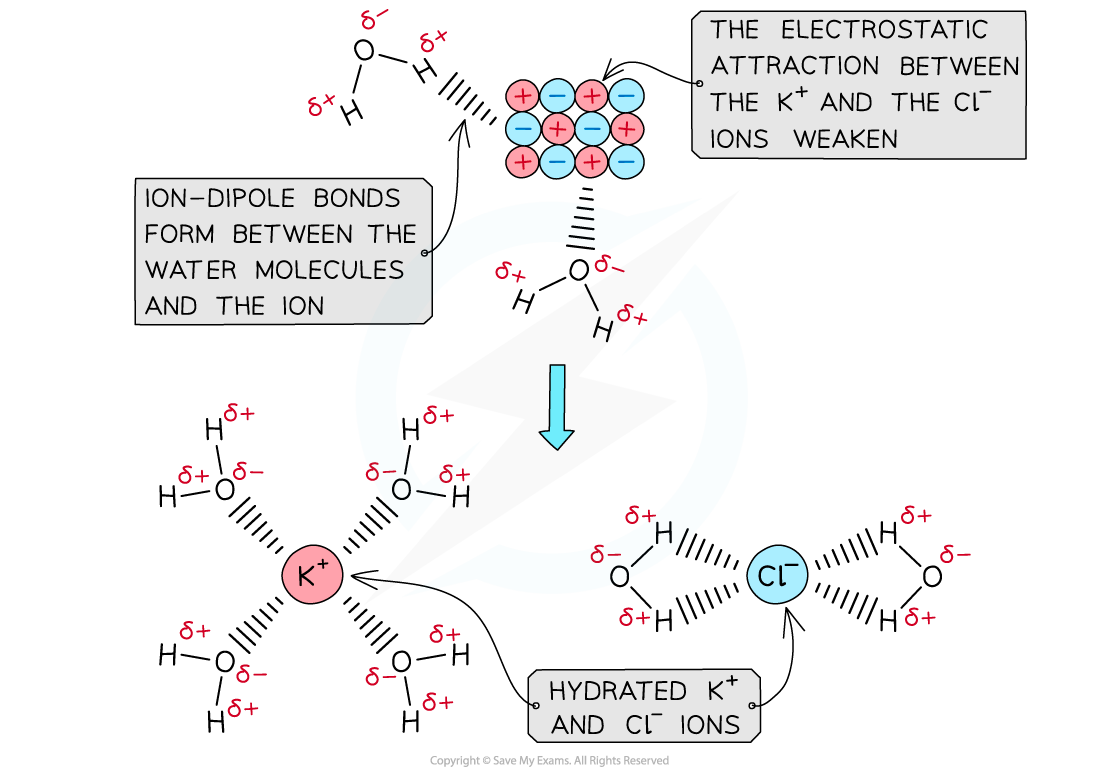
The polar water molecules will form ion-dipole bonds with the ions in solution causing the ions to become hydrated
How are enthalpy of solution and hydration enthalpies related?
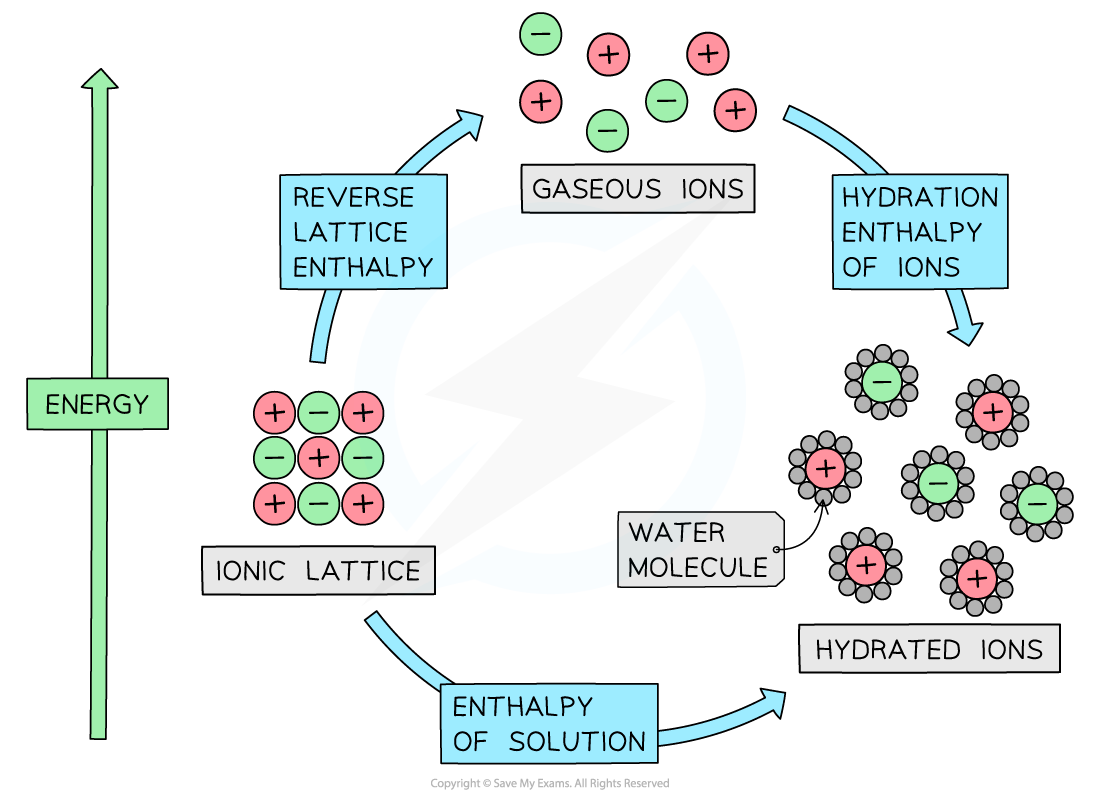
The relationship between lattice enthalpy, hydration enthalpies and enthalpy of solution
- From the diagram we can see that the relationship is
Enthalpy of solution = reverse lattice enthalpy* + hydration enthalpy
- The hydration enthalpy is the sum of the hydration enthalpies of each ion
- If there is more than one cation or anion, such as in MgCl2, then you must multiply by the appropriate coefficient for that ion
*To be consistent with lattice formation enthalpy
Cycles & Energy Level Diagrams
- Questions in this topic typically ask you to calculate the hydration enthalpy of one of the ions, given the lattice enthalpy, enthalpy of solution and hydration enthalpy of the other ion.
- This can be done by constructing an appropriate energy cycle and using Hess's Law to find the unknown energy value
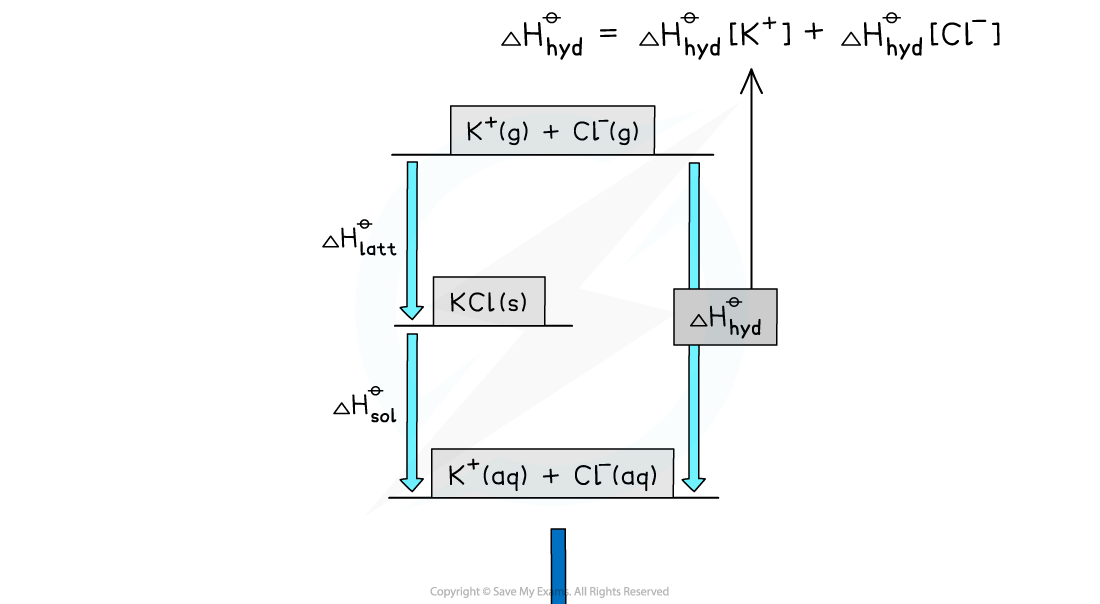
- The energy cycle above shows that there are two routes to go from the gaseous ions to the ions in an aqueous solution:
-
- Route 1: going from gaseous ions → ionic solid → ions in aqueous solution (this is the indirect route)
- Route 2: going from gaseous ions → ions in aqueous solution (this is the direct route)
-
- According to Hess’s law, the enthalpy change for both routes is the same, such that:
ΔHhydꝋ = ΔHlattꝋ + ΔHsolꝋ
- Each ion will have its own enthalpy change of hydration, ΔHhydꝋ, which will need to be taken into account during calculations
- The total ΔHhydꝋ is found by adding the ΔHhydꝋ values of both anions and cations together
Worked Example
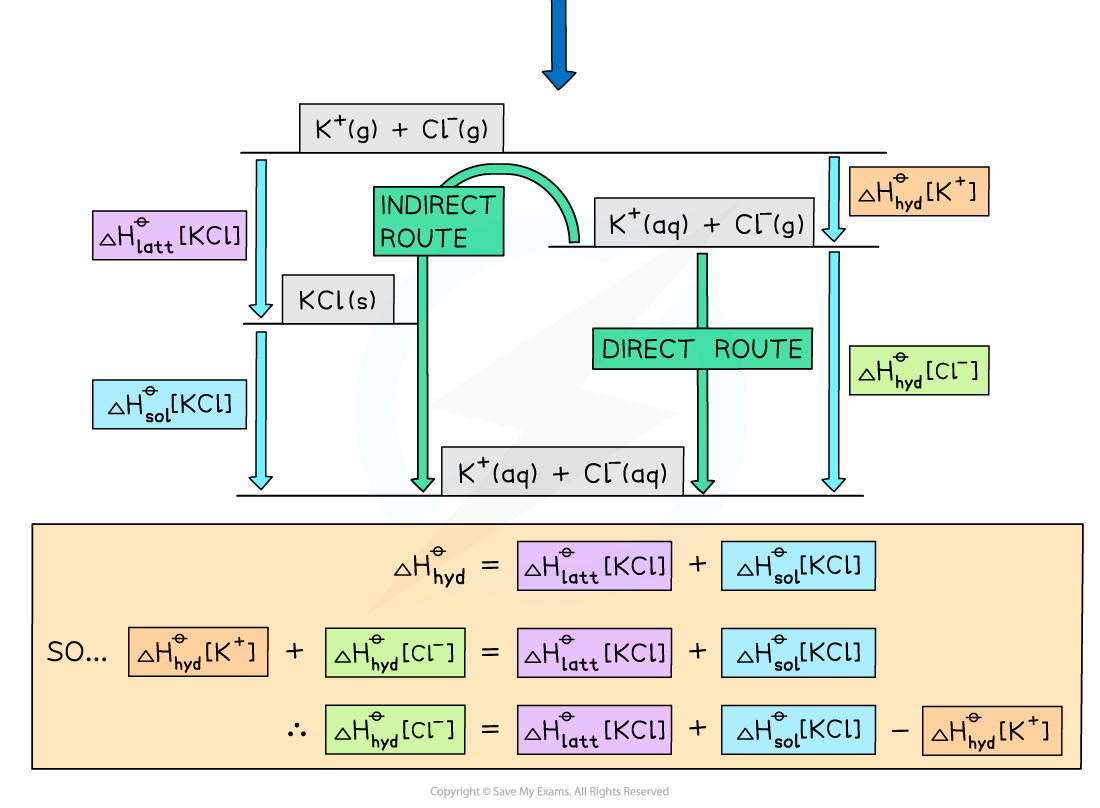
Constructing an energy cycle for KClCalculate the enthalpy of hydration of the chloride ion given the following data:
ΔHlattꝋ [KCl] = -711 kJ mol-1
ΔHsolꝋ [KCl] = +26 kJ mol-1
ΔHhydꝋ [K+] = -322 kJ mol-1
Answer
Step 1: Draw the energy cycle and make ΔHhyd[Cl-] the subject of the formula:
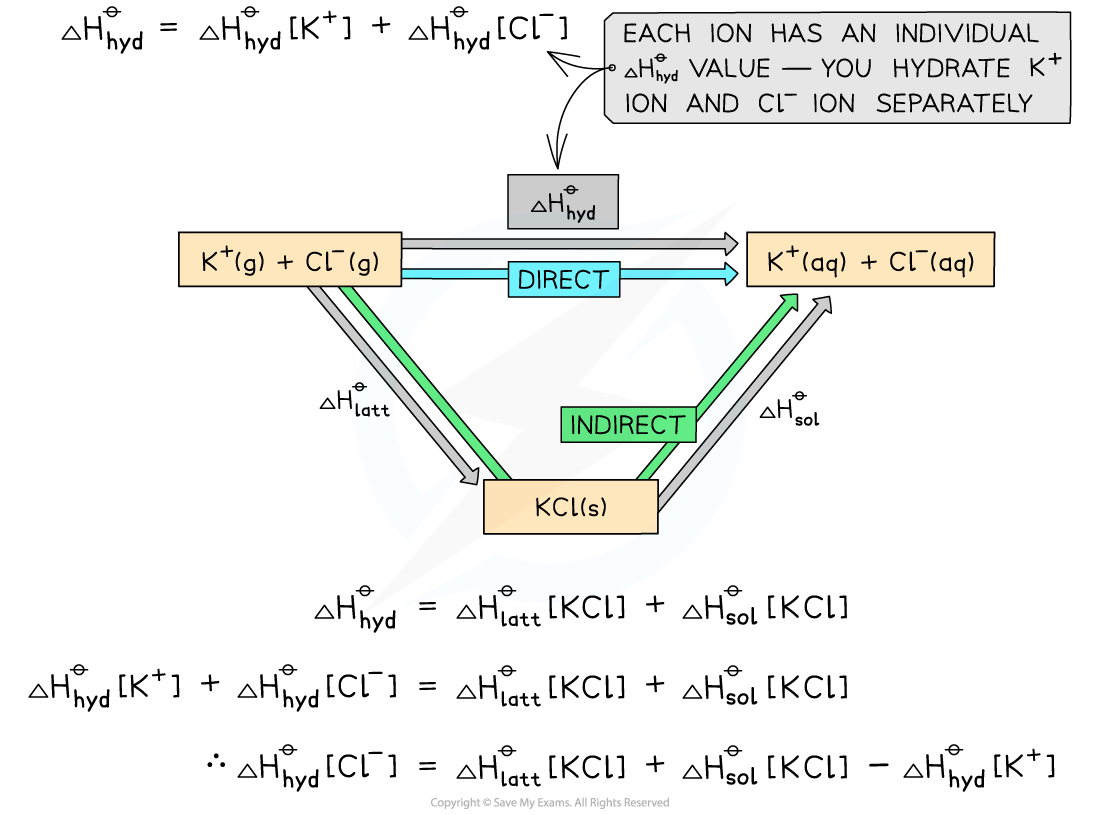
Step 2: Substitute the values to find ΔHhydꝋ [Cl-]
ΔHhydꝋ [Cl-] = (-711) + (+26) - (-322) = -363 kJ mol-1
Alternative Diagram
- You can also draw a Born-Haber cycle as an alternative approach to the same problem
Energy level diagram:
Worked Example
Constructing an energy cycle and energy level diagram of MgCl2
Construct an energy cycle to calculate the ΔHhydꝋof magnesium ions in magnesium chloride, given the following data:
ΔHlatt [MgCl2] = -2592 kJ mol-1
ΔHsol [MgCl2] = -55 kJ mol-1
ΔHhyd [Cl-] = -363 kJ mol-1
Answer
Step 1: Draw an energy cycle:
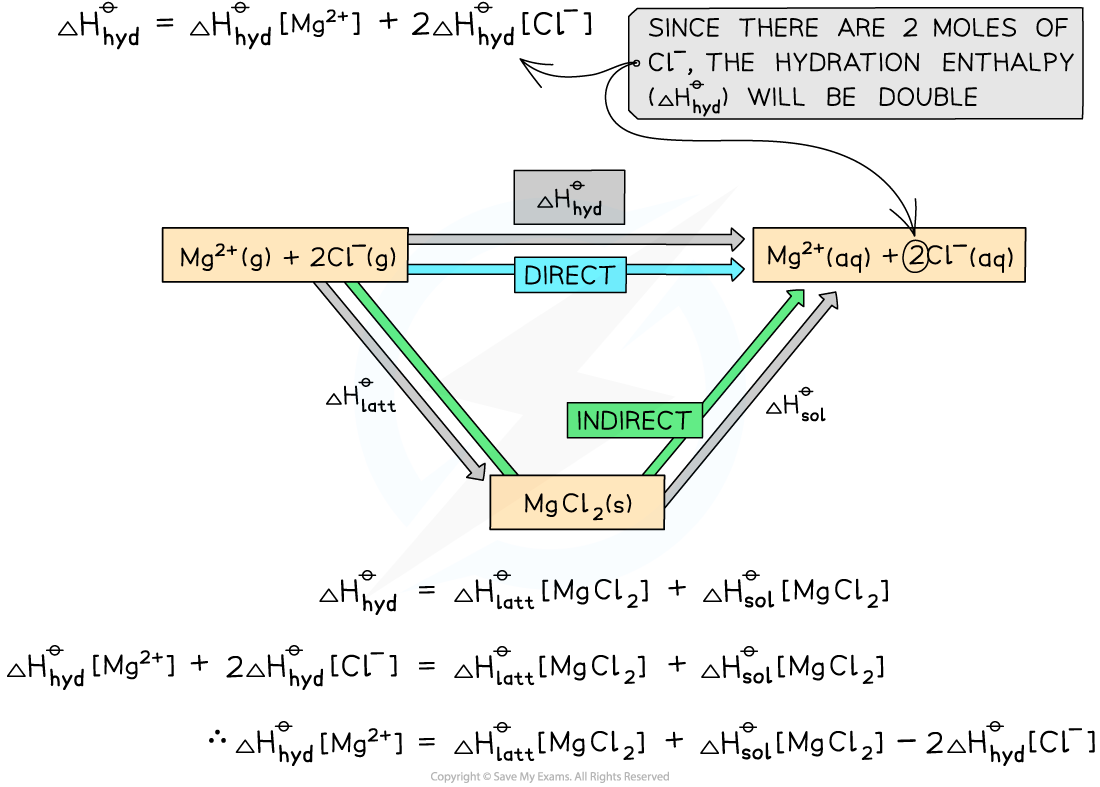
Step 2: Substitute the values to find ΔHhydꝋ [Mg2+]
ΔHhydꝋ[Mg2+] = (-2592) + (-55) - (2 x -363) = -1921 kJ mol-1
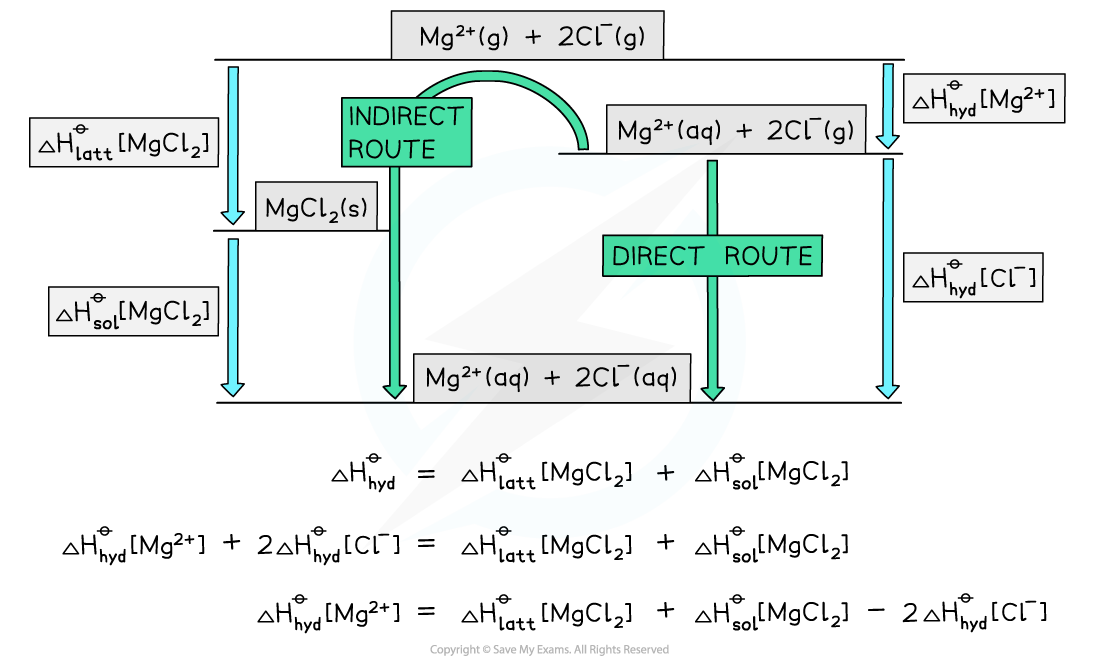
Alternative route to find ΔHhydꝋ[Mg2+]
- Here is the same solution using a Born-Haber cycle
Exam Tip
It doesn't matter whether you use Hess cycles or Born-Haber style cycles to solve these problems as long as the information is correctly labelled and the direction of the arrows matches the definitions.Exam problems in this topic often show diagrams with missing labels which you have to complete and find unknown values.The key to success in energy cycle calculations is not to panic, but have a careful step-by-step approach, show your workings and use brackets to separate mathematical operations from the enthalpy changes.
The Effects of Ionic Charge & Radius
Factors affecting lattice enthalpy
- The two key factors which affect lattice energy, ΔHlattꝋ, are the charge and radius of the ions that make up the crystalline lattice
Ionic radius
- The lattice energy becomes less exothermic as the ionic radius of the ions increases
- This is because the charge on the ions is more spread out over the ion when the ions are larger
- The ions are also further apart from each other in the lattice
- The attraction between ions is between the centres of the ions involved, so the bigger the ions the bigger the distance between the centre of the ions
- Therefore, the electrostatic forces of attraction between the oppositely charged ions in the lattice are weaker
- For example, the lattice energy of caesium fluoride (CsF) is less exothermic than the lattice energy of potassium fluoride (KF)
- Since both compounds contain a fluoride (F-) ion, the difference in lattice energy must be due to the caesium (Cs+) ion in CsF and potassium (K+) ion in KF
- Potassium is a Group 1 and Period 4 element
- Caesium is a Group 1 and Period 6 element
- This means that the Cs+ ion is larger than the K+ ion
- There are weaker electrostatic forces of attraction between the Cs+ and F- ions compared to K+ and F- ions
- As a result, the lattice energy of CsF is less exothermic than that of KF
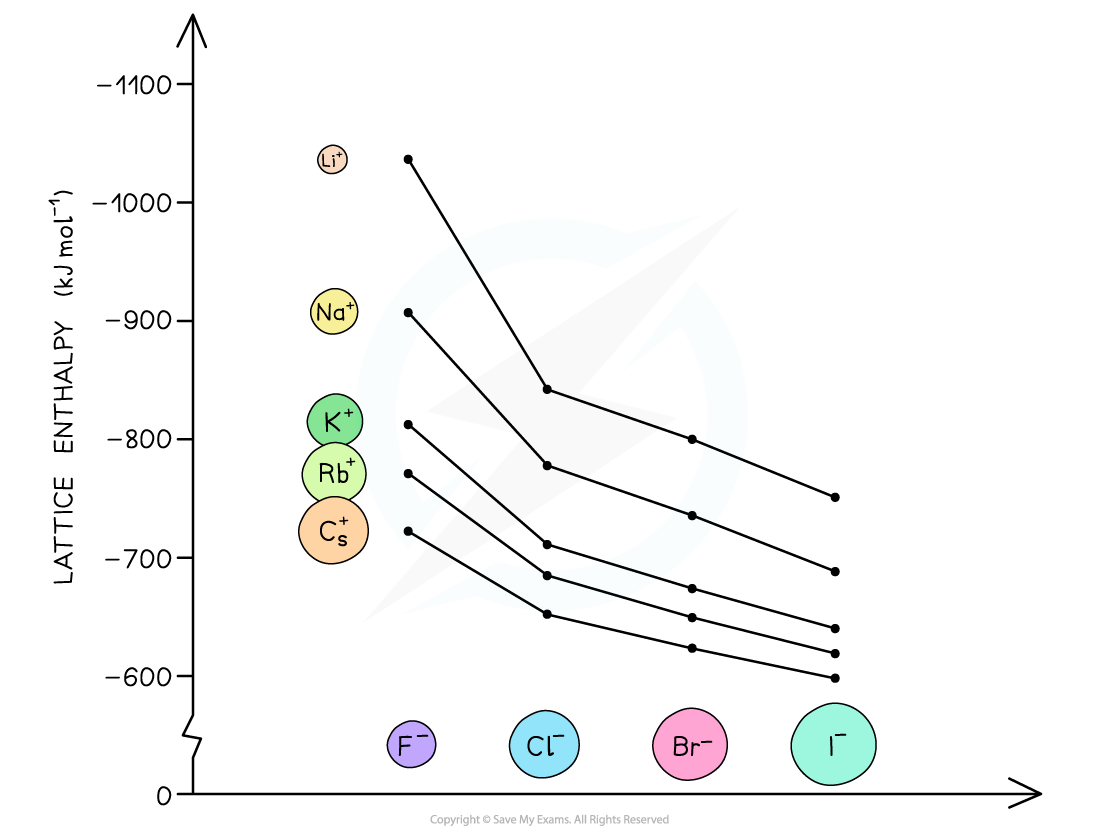
The lattice energies get less exothermic as the ionic radius of the ions increases
Ionic charge
- The lattice energy gets more exothermic as the ionic charge of the ions increases
- The greater the ionic charge, the higher the charge density
- This results in stronger electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions in the lattice
- As a result, the lattice energy is more exothermic
- For example, the lattice energy of calcium oxide (CaO) is more exothermic than the lattice energy of potassium chloride (KCl)
- Calcium oxide is an ionic compound which consists of calcium (Ca2+) and oxide (O2-) ions
- Potassium chloride is formed from potassium (K+) and chloride (Cl-) ions
- The ions in calcium oxide have a greater ionic charge than the ions in potassium chloride
- This means that the electrostatic forces of attraction are stronger between the Ca2+and O2- compared to the forces between K+ and Cl-
- Therefore, the lattice energy of calcium oxide is more exothermic, as more energy is released upon its formation from its gaseous ions
- Ca2+ and O2- are also smaller ions than K+ and Cl-, so this also adds to the value for the lattice energy being more exothermic
Factors affecting enthalpy of hydration
- Hydration enthalpies are exothermic as energy is given out as water molecules bond to the metal ions
- The negative ions are attracted to the δ+ hydrogens on the polar water molecules and the positive ions are attracted to the δ- oxygen on the polar water molecules
- The higher the charge density the greater the hydration enthalpy (e.g. smaller ions or ions with larger charges) as the ions attract the water molecules more strongly, for example:
- Fluoride ions, F-, have more negative hydration enthalpies than chloride ions, Cl-
- Magnesium ions, Mg2+, have a more negative hydration enthalpy than barium ion, Ba2+
转载自savemyexams
在线登记
最新发布
翰林课程体验,退费流程快速投诉邮箱: yuxi@linstitute.net 沪ICP备2023009024号-1