- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel A Level Chemistry:复习笔记5.2.4 Ionic Product of Water
Ionic Product of Water, Kw
- In all aqueous solutions, an equilibrium exists in water where a few water molecules dissociate into protons and hydroxide ions
- We can derive an equilibrium constant for the reaction:
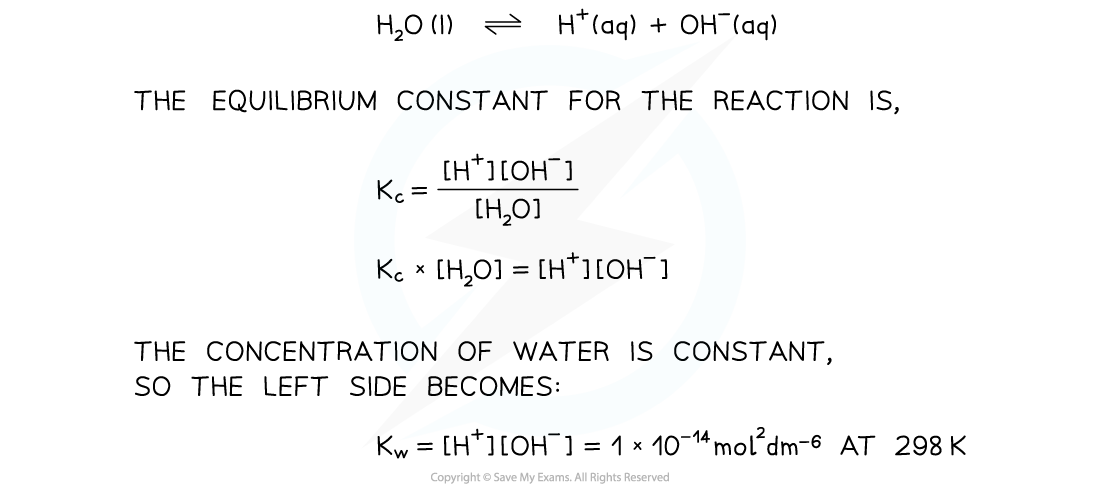
- This is a specific equilibrium constant called the ionic product for water
- The product of the two ion concentrations is always 1 x 10-14 mol2 dm-6
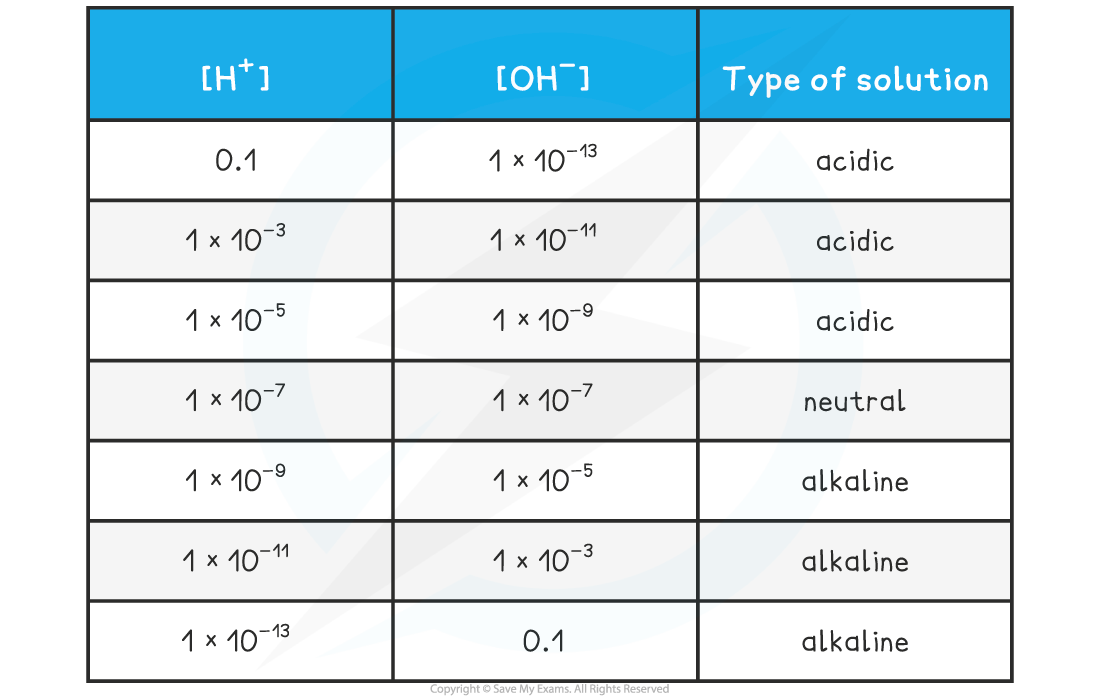
- This makes it straightforward to see the relationship between the two concentrations and the nature of the solution:
[H+] & [OH–] Table
The relationship between Kw and pKw is given by the following equation:
pKw = -logKw
pKa
- The range of values of Ka is very large and for weak acids, the values themselves are very small numbers
Table of Ka values
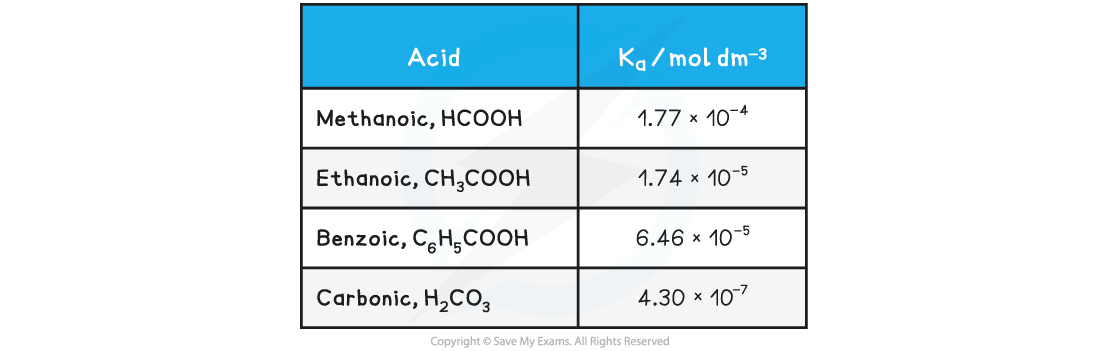
- For this reason it is easier to work with another term called pKa
- The pKa is the negative log of the Ka value, so the concept is analogous to converting [H+] into pH values
pKa = -logKa
- Looking at the pKa values for the same acids:
Table of pKa values
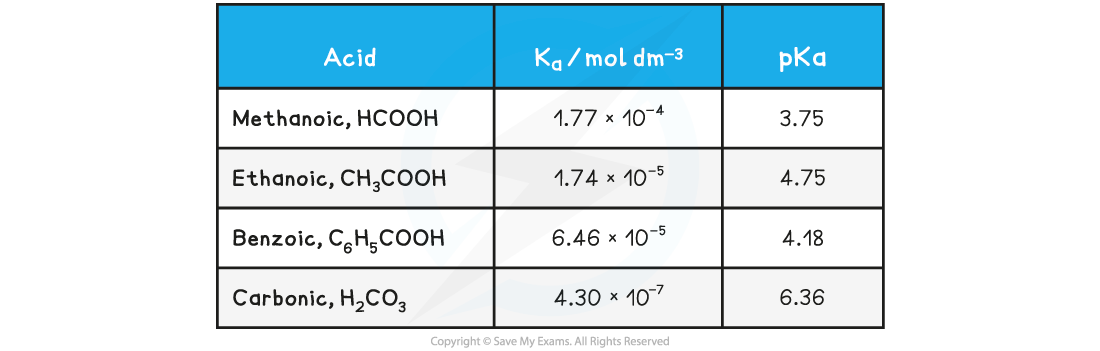
- The range of pKa values for most weak acids lies between 3 and 7
pH Calculation of a Strong Base
- Strong bases are completely ionised in solution
BOH (aq) → B+ (aq) + OH- (aq)
- Therefore, the concentration of hydroxide ions [OH-] is equal to the concentration of base [BOH]
- Even strong alkalis have small amounts of H+ in solution which is due to the ionisation of water
- The concentration of OH- in solution can be used to calculate the pH using the ionic product of water
- Once the [H+] has been determined, the pH of the strong alkali can be founding using pH = -log[H+]
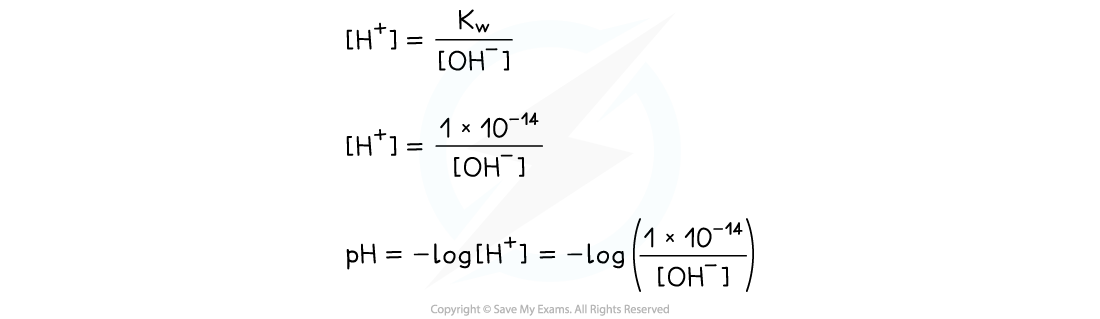
- Similarly, the ionic product of water can be used to find the concentration of OH- ions in solution if [H+] is known, simply by dividing Kw by the [H+]
Worked Example
pH calculations of a strong alkali
Question 1:
Calculate the pH of 0.15 mol dm-3 sodium hydroxide, NaOH
Question 2:
Calculate the hydroxide concentration of a solution of sodium hydroxide when the pH is 10.50
Answer
Sodium hydroxide is a strong base which ionises as follows:
NaOH (aq) → Na+ (aq) + OH- (aq)
Answer 1:
The pH of the solution is:
[H+] = Kw ÷ [OH-]
[H+] = (1 x 10-14) ÷ 0.15 = 6.66 x 10-14
pH = -log[H+]
= -log 6.66 x 10-14 = 13.17
Answer 2
Step 1: Calculate hydrogen concentration by rearranging the equation for pH
pH = -log[H+]
[H+]= 10-pH
[H+]= 10-10.50
[H+]= 3.16 x 10-11 mol dm-3
Step 2: Rearrange the ionic product of water to find the concentration of hydroxide ions
Kw = [H+] [OH-]
[OH-]= Kw ÷ [H+]
Step 3: Substitute the values into the expression to find the concentration of hydroxide ions
Since Kw is 1 x 10-14 mol2 dm-6,
[OH-]= (1 x 10-14) ÷ (3.16 x 10-11)
[OH-]= 3.16 x 10-4 mol dm-3
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








