- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
CIE A Level Maths: Probability & Statistics 2复习笔记2.4.1 Choosing Distributions
Choosing Distributions
When should I use a Poisson distribution?
- A random variable that follows a Poisson distribution is a discrete random variable
- A Poisson distribution is used when the random variable counts something
- The number of occurrences of an event in a given interval of time or space
- There are three conditions that must fulfil to follow a Poisson distribution
- The mean number of occurrences is known and finite (λ)
- The events occur at random
- The events occur singly and independently
When should I use a normal distribution?
- A random variable that follows a normal distribution is a continuous random variable
- A normal distribution is used when the random variable measures something and the distribution is:
- Symmetrical
- Bell-shaped
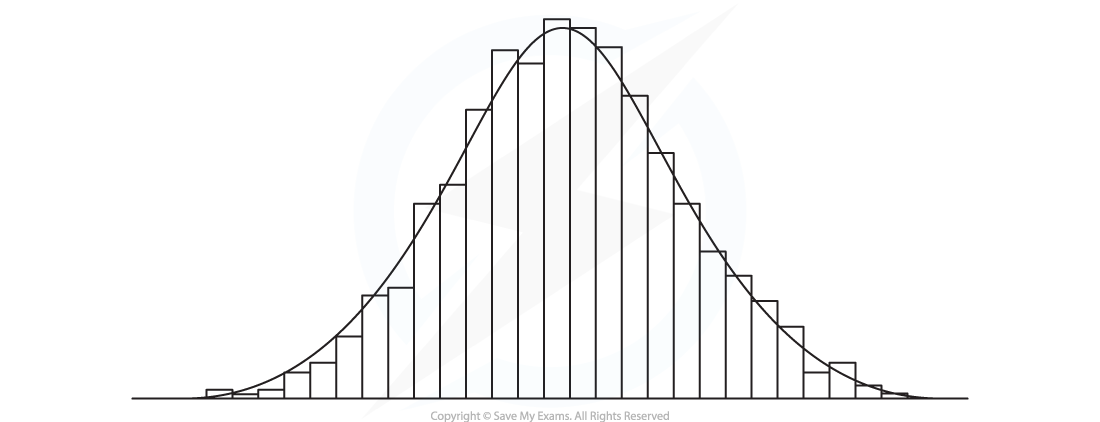
- A normal distribution can be used to model real-life data provided the histogram for this data is roughly symmetrical and bell-shaped
- If the variable is normally distributed then as more data is collected the outline of the histogram should get smoother and resemble a normal distribution curve
Will I still be expected to use the binomial and geometric distribution
- Knowledge of using the binomial and geometric distribution is expected for Statistics 2
- Remember the three conditions for both distributions
- The trials are independent
- There are exactly two outcomes of each trial (success or failure)
- The probability of success(p) is constant
- You will be expected to recognise when a random variable follows a binomial or geometric distribution and use their properties
- A binomial distribution will have a fixed finite number of trials(n)
- A geometric distribution will continue the trials until the first success
Exam Tip
- Always state what your variables and parameters represent. Make sure you know the conditions for when each distribution is (or is not) a suitable model.
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









