- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
CIE A Level Physics复习笔记22.1.1 The Photon
The Particle Nature of Light
- In classical wave theory, electromagnetic (EM) radiation is assumed to behave as a wave
- This is demonstrated by the fact EM radiation exhibits phenomena such as diffraction and interference
- However, experiments from the last century, such as the photoelectric effect and atomic line spectra, can only be explained if EM radiation is assumed to behave as particles
- These experiments have formed the basis of quantum theory, which will be explored in detail in this section
The Photon
- Photons are fundamental particles which make up all forms of electromagnetic radiation
- A photon is a massless “packet” or a “quantum” of electromagnetic energy
- What this means is that the energy is not transferred continuously, but as discrete packets of energy
- In other words, each photon carries a specific amount of energy, and transfers this energy all in one go, rather than supplying a consistent amount of energy
Exam Tip
Make sure you learn the definition for a photon: discrete quantity / packet / quantum of electromagnetic energy are all acceptable definitions
Calculating Photon Energy
- The energy of a photon can be calculated using the formula:
E = hf
- Using the wave equation, energy can also be equal to:
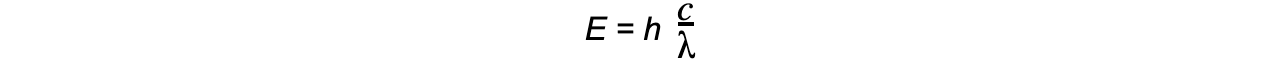
- Where:
- E = energy of the photon (J)
- h = Planck's constant (J s)
- c = the speed of light (m s-1)
- f = frequency in Hertz (Hz)
- λ = wavelength (m)
- This equation tells us:
- The higher the frequency of EM radiation, the higher the energy of the photon
- The energy of a photon is inversely proportional to the wavelength
- A long-wavelength photon of light has a lower energy than a shorter-wavelength photon
Worked Example
Light of wavelength 490 nm is incident normally on a surface, as shown in the diagram.
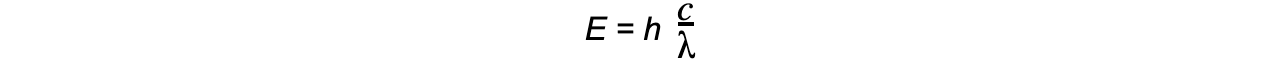
The power of the light is 3.6 mW. The light is completely absorbed by the surface.Calculate the number of photons incident on the surface in 2.0 s.
Step 1: Write down the known quantities
Wavelength, λ = 490 nm = 490 × 10-9 m
Power, P = 3.6 mW = 3.6 × 10-3 W
Time, t = 2.0 s
Step 2: Write the equations for wave speed and photon energy
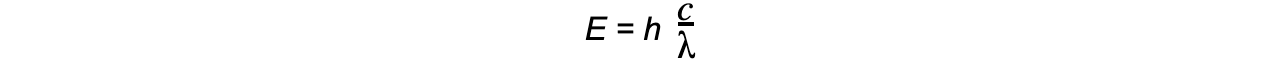
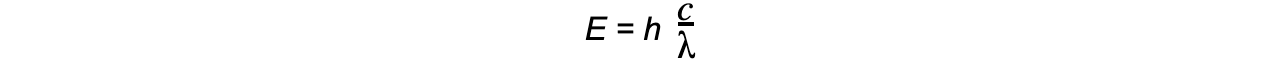
Step 3: Calculate the energy of one photon
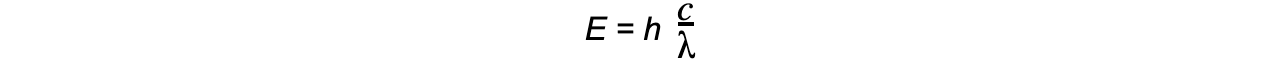
Step 4: Calculate the number of photons hitting the surface every second
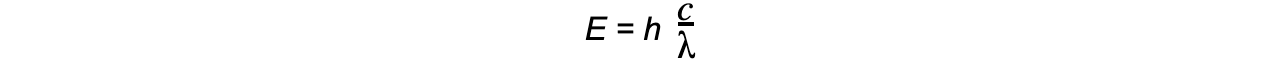
Step 5: Calculate the number of photons that hit the surface in 2 s
(8.9 × 1015) × 2 = 1.8 × 1016
Exam Tip
The values of Planck’s constant and the speed of light will always be given to you in an exam, however, it helps to memorise them to speed up calculation questions!
Photon Momentum
- Einstein showed that a photon travelling in a vacuum has momentum, despite it having no mass
- The momentum (p) of a photon is related to its energy (E) by the equation:
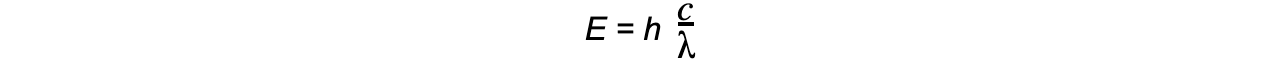
-
- Where c is the speed of light
Worked Example
A 5.0 mW laser beam is incident normally on a fixed metal plate. The cross-sectional area of the beam is 8.0 × 10-6 m2. The light from the laser has frequency 5.6 × 1014 Hz.Assuming that all the photons are absorbed by the plate, calculate the momentum of the photon, and the pressure exerted by the laser beam on the metal plate.
Step 1: Write down the known quantities
Power, P = 5.0 mW = 5.0 × 10-3 W
Frequency, f = 5.6 × 1014 Hz
Cross-sectional area, A = 8.0 × 10-6 m2
Step 2: Write the equations for photon energy and momentum
photon energy: E = hf
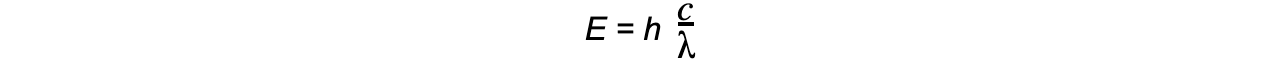
Step 3: Calculate the photon momentum
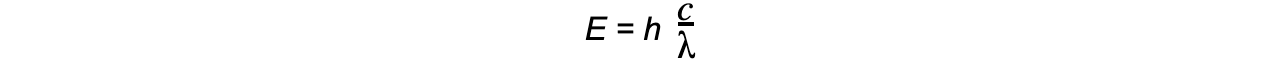
Step 4: Calculate the number of photons incident on the plate every second
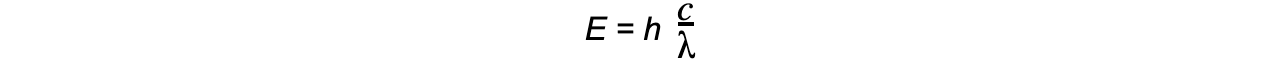
Step 5: Calculate the force exerted on the plate in a 1.0 s time interval
Force = rate of change of momentum
= number of photons per second × momentum of each photon
= (1.35 × 1016) × (1.24 × 10-27)
= 1.67 × 10-11 N
Step 6: Calculate the pressure
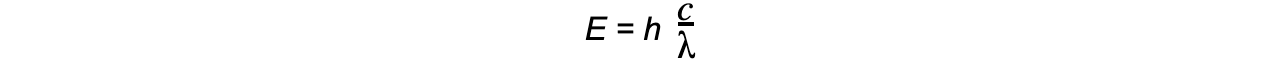
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









