- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
CIE A Level Physics复习笔记6.1.3 The Young Modulus
Stress, Strain & the Young Modulus
Stress
- Tensile stress is the applied force per unit cross sectional area of a material
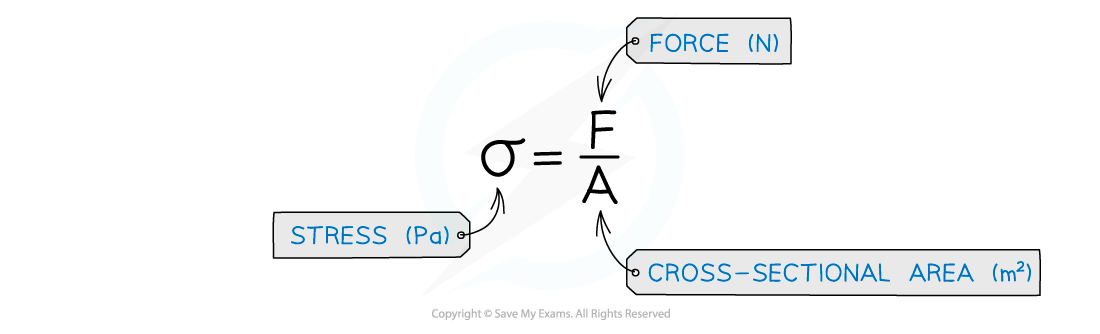
Stress equation
- The ultimate tensile stress is the maximum force per original cross-sectional area a wire is able to support until it breaks
Strain
- Strain is the extension per unit length
- This is a deformation of a solid due to stress in the form of elongation or contraction
- Note that strain is a dimensionless unit because it’s the ratio of lengths
 Strain equation
Strain equation
Young’s Modulus
- The Young modulus is the measure of the ability of a material to withstand changes in length with an added load ie. how stiff a material is
- This gives information about the elasticity of a material
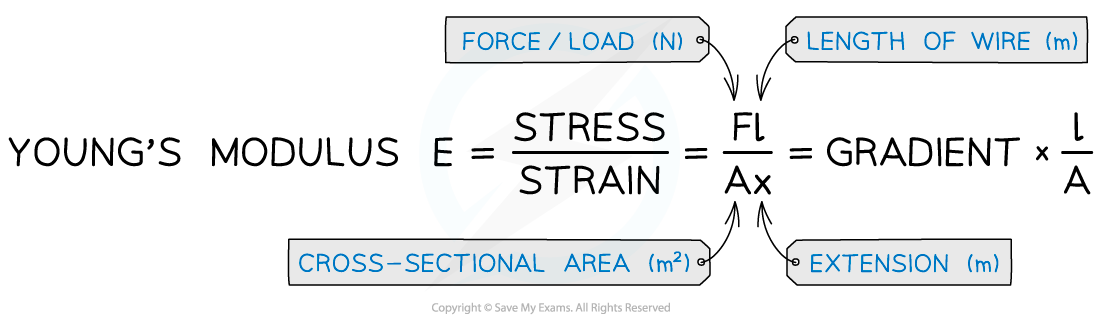
- The Young Modulus is defined as the ratio of stress and strain
 Young Modulus equation
Young Modulus equation
- Its unit is the same as stress: Pa (since strain is unitless)
- Just like the Force-Extension graph, stress and strain are directly proportional to one another for a material exhibiting elastic behaviour
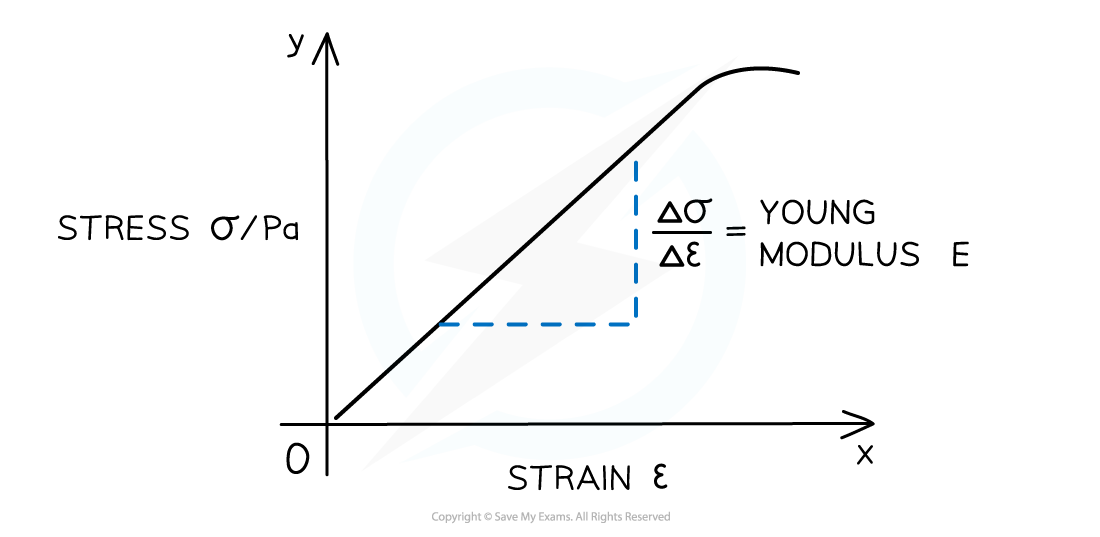
A stress-strain graph is a straight line with its gradient equal to Young modulus
- The gradient of a stress-stress graph when it is linear is the Young Modulus
Worked Example
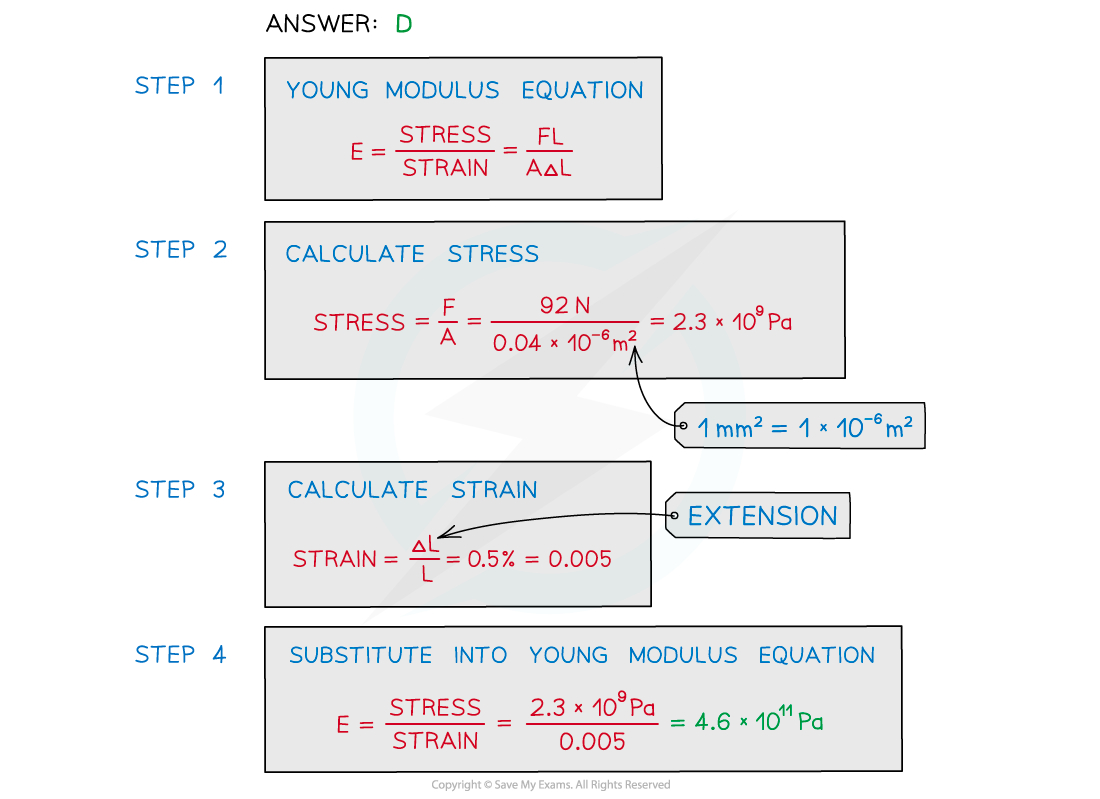
A metal wire that is supported vertically from a fixed point has a load of 92 N applied to the lower end.
The wire has a cross-sectional area of 0.04 mm2 and obeys Hooke’s law.
The length of the wire increases by 0.50%.What is the Young modulus of the metal wire?
A. 4.6 × 107Pa B. 4.6 × 1012 Pa C. 4.6 × 109 Pa D. 4.6 × 1011 Pa
Exam Tip
To remember whether stress or strain comes first in the Young modulus equation, try thinking of the phrase ‘When you’re stressed, you show the strain’ ie. Stress ÷ strain.
Young's Modulus Experiment
- To measure the Young’s Modulus of a metal in the form of a wire requires a clamped horizontal wire over a pulley (or vertical wire attached to the ceiling with a mass attached) as shown in the diagram below
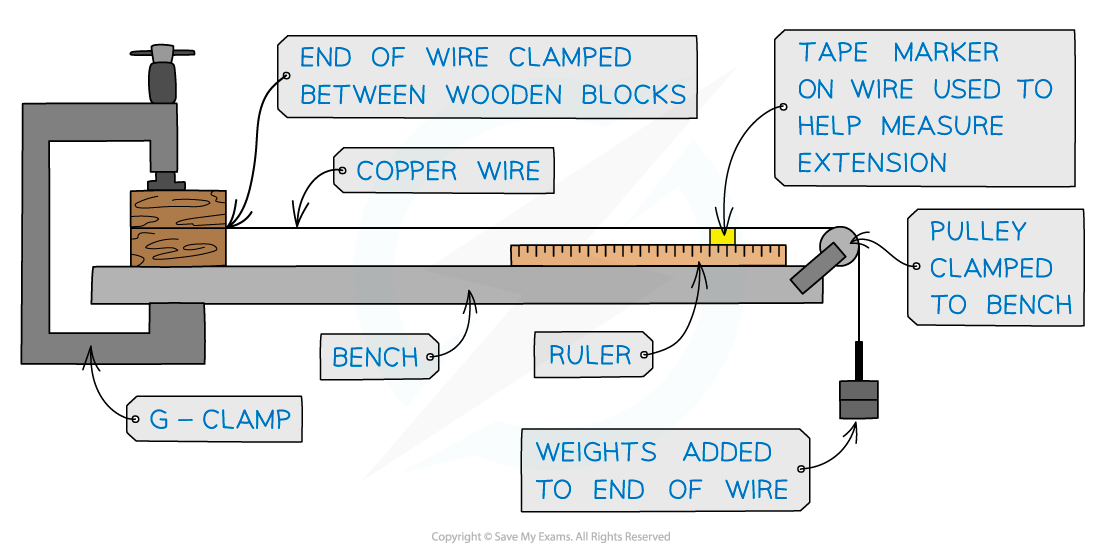
- A reference marker is needed on the wire. This is used to accurately measure the extension with the applied load
- The independent variable is the load
- The dependent variable is the extension
Method
- Measure the original length of the wire using a metre ruler and mark this reference point with tape
- Measure the diameter of the wire with micrometer screw gauge or digital calipers
- Measure or record the mass or weight used for the extension e.g. 300 g
- Record initial reading on the ruler where the reference point is
- Add mass and record the new scale reading from the metre ruler
- Record final reading from the new position of the reference point on the ruler
- Add another mass and repeat method
Improving experiment and reducing uncertainties:
- Reduce uncertainty of the cross-sectional area by measuring the diameter d in several places along the wire and calculating an average
- Remove the load and check wire returns to original limit after each reading
- Take several readings with different loads and find average
- Use a Vernier scale to measure the extension of the wire
Measurements to determine Young’s modulus
1. Determine extension x from final and initial readings
Example table of results:
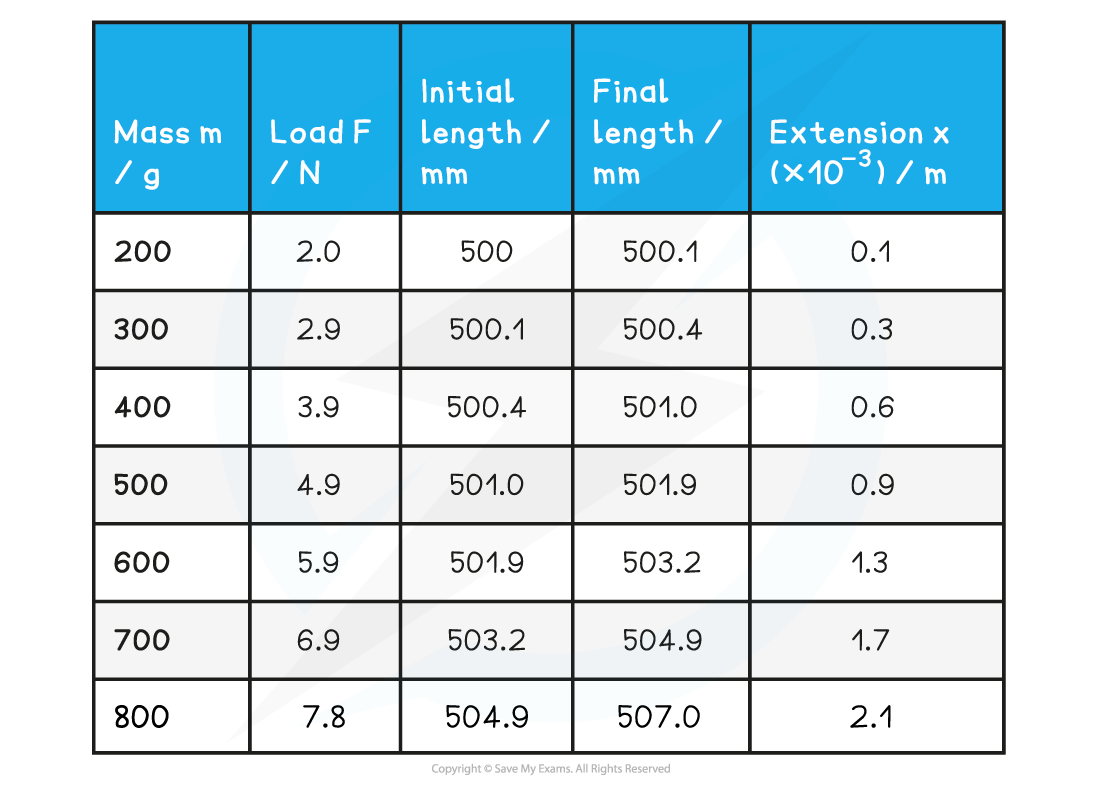
Table with additional data
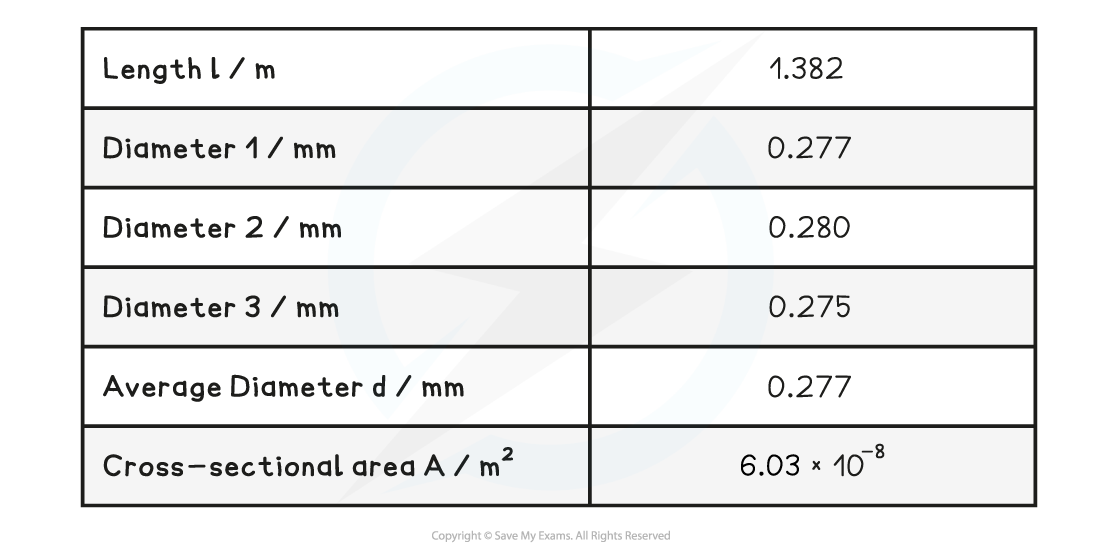
2. Plot a graph of force against extension and draw line of best fit
3. Determine gradient of the force v extension graph

4. Calculate cross-sectional area from:

5. Calculate the Young’s modulus from:
Exam Tip
Although every care should be taken to make the experiment as reliable as possible, you will be expected to suggest improvements in producing more accurate and reliable results (e.g. repeat readings and use a longer length of wire)
转载自savemyexams


最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








