- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
CIE A Level Physics复习笔记3.2.1 Conservation of Momentum
The Principle of Conservation of Momentum
- The principle of conservation of momentum is:
- The total momentum of a system remains constant provided no external force acts on it
- For example if two objects collide:
the total momentum before the collision = the total momentum after the collision
- Remember momentum is a vector quantity. This allows oppositely-directed vectors to cancel out so the momentum of the system as a whole is zero
- Momentum is always conserved over time
External and Internal Forces
- External forces are forces that act on a structure from outside e.g. friction and weight
- Internal forces are forces exchanged by the particles in the system e.g. tension in a string
- Which forces are internal or external will depend on the system itself, as shown in the diagram below:

Internal and external forces on a mass on a spring
- You may also come across a system with no external forces being described as a ‘closed’ or ‘isolated’ system
- These all still refer to a system that is not affected by external forces
- For example, a swimmer diving from a boat:
- The diver will move forward, and, to conserve momentum, the boat will move backwards
- This is because the momentum beforehand was zero and no external forces are present to affect the motion of the diver or the boat
Collisions in One & Two Dimensions
One-dimensional momentum problems
- Momentum (p) is equal to: p = m × v
- Using the conversation of linear momentum, it is possible to calculate missing velocities and masses of components in the system. This is shown in the example below
Worked Example
Trolley A of mass 0.80 kg collides head-on with stationary trolley B at a velocity of 3.0 ms-1.Trolley B has twice the mass of trolley A.The trolleys stick together. Using the conservation of momentum, calculate the common velocity of both trolleys after the collision. Determine whether this is an elastic or inelastic collision.
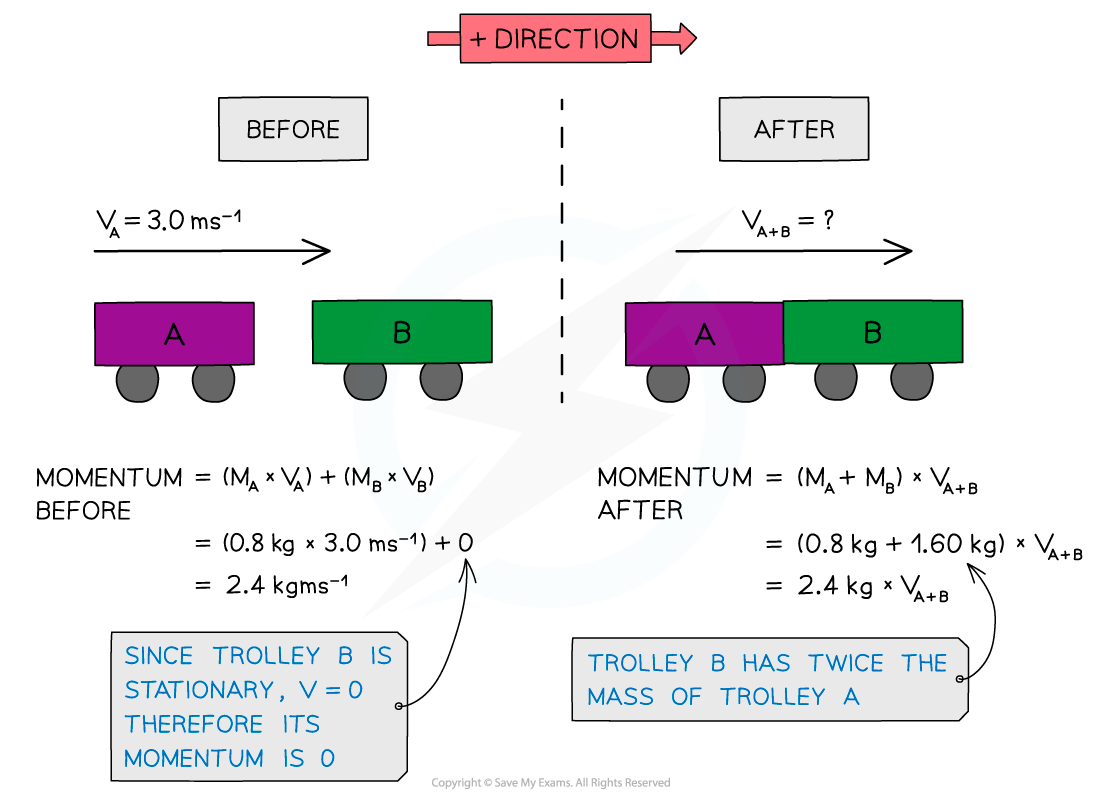
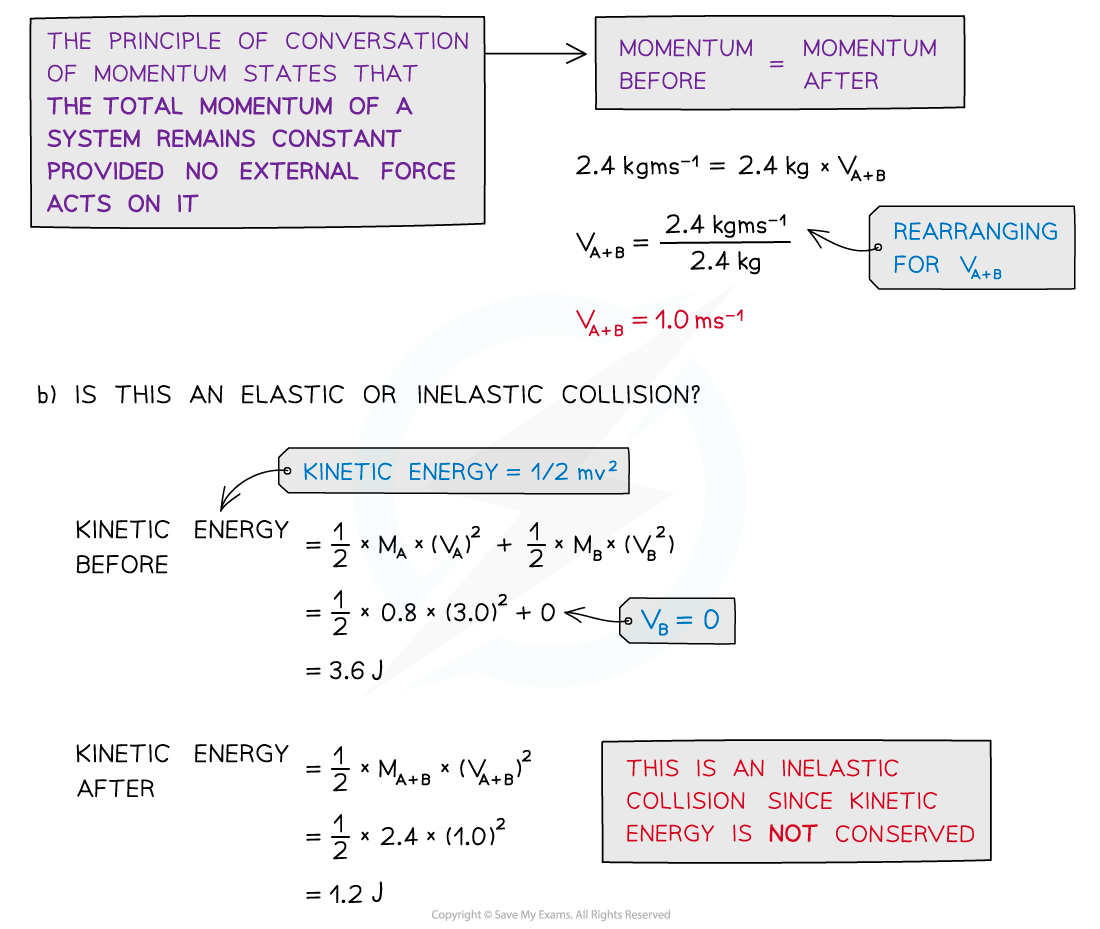
- To find out whether a collision is elastic or inelastic, compare the kinetic energy before and after the collision
- If the kinetic energy is conserved, it is an elastic collision
- If the kinetic energy is not conserved, it is an inelastic collision
- Elastic collisions are commonly those where objects colliding do not stick together and then move in opposite directions
- Inelastic collision are where objects collide and stick together after the collision
Two-dimensional momentum problems
- Since momentum is a vector, in 2D it can be split up into its x and y components
- Review revision notes 1.3 Scalars & Vectors on how to resolve vectors
Worked Example
A ball is thrown at a vertical wall. The path of the ball is shown below
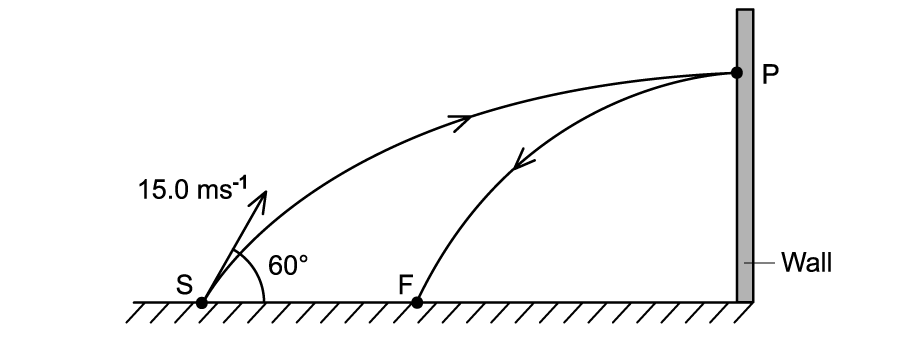
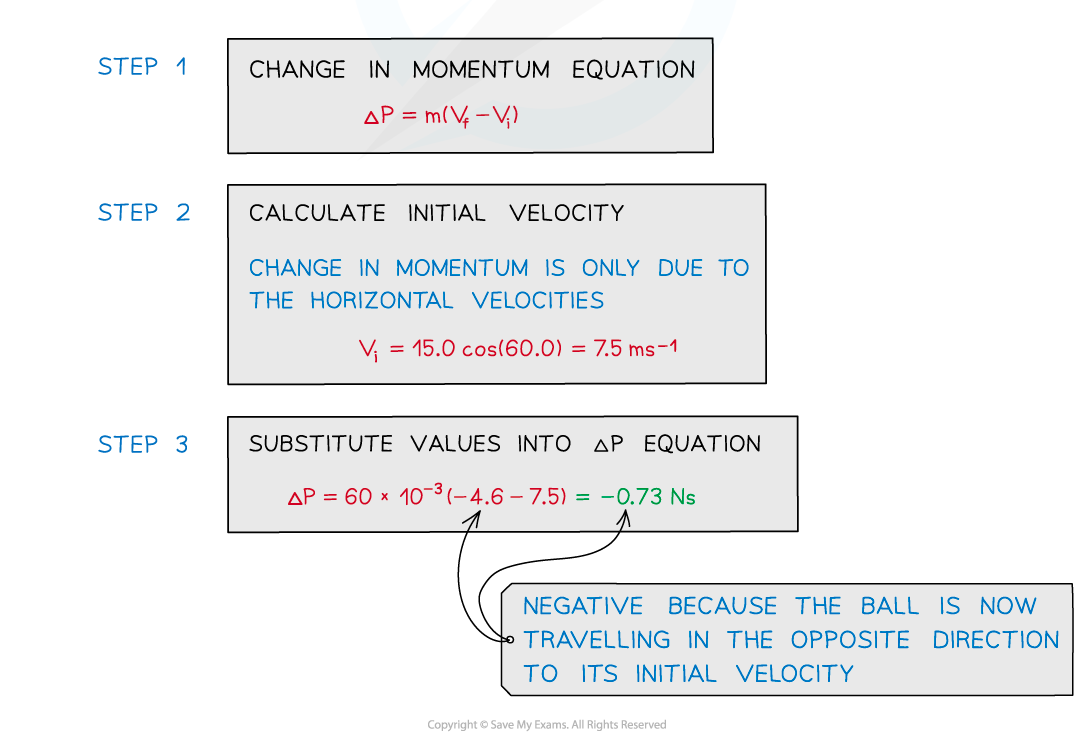
The ball is thrown from S with an initial velocity of 15.0 m s-1 at 60.0° to the horizontal. The mass of the ball is 60 × 10-3 kg and rebounds at a velocity of 4.6 m s-1.Calculate the change in momentum of the ball if it rebounds off the wall.
Exam Tip
If an object is stationary or at rest, it’s velocity equals 0, therefore, the momentum and kinetic energy are also equal to 0.When a collision occurs in which two objects are stuck together, treat the final object as a single object with a mass equal to the sum of the two individual objects.In 2D problems, make sure you’re confident resolving vectors. Here is a small trick to remember which component is cosine or sine of the angle for a vector R:
Resolving vectors with sine and cosine
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









