- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
CIE A Level Chemistry复习笔记7.5.3 Relative Acidities of Carboxylic Acids, Phenols & Alcohols
Relative Acidities of Carboxylic Acids, Phenols & Alcohols
- Carboxylic acids are compounds with a -COOH functional group
- They can act as acids and lose a proton (H+ ion) in an aqueous solution to form carboxylate salts and water
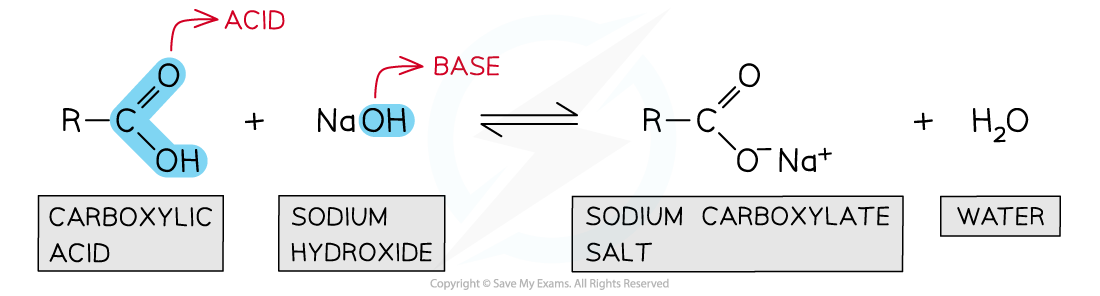 Carboxylic acids dissociate in aqueous solutions to form carboxylate salts and water
Carboxylic acids dissociate in aqueous solutions to form carboxylate salts and water
- However, carboxylic acids are only weak acids as the position of equilibrium lies well over to the left-hand side
- The pKa values of carboxylic acids, phenols, and alcohols suggest that carboxylic acids are stronger acids than alcohols and phenols
- The pKa is a measure of the relative strength of a species as an acid
- The smaller the pKa value, the stronger the acid
Relative acidity of ethanol, phenol & carboxylic acids table
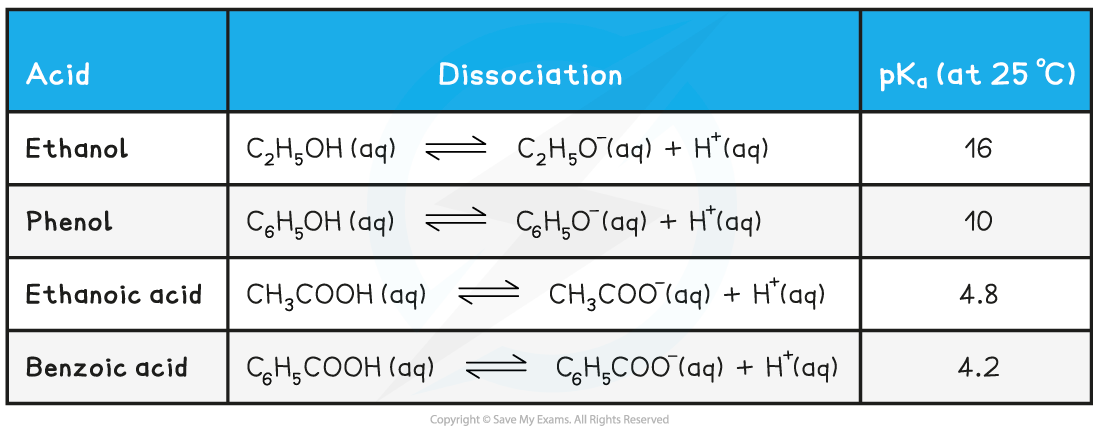
- This order of relative acidities can be explained by looking at the strength of the O-H bond and the stability of the conjugate bases of the acids
Strength of O-H bond
- In carboxylic acids, the electrons in the O-H bond are drawn towards the C-O bond
- The electrons in the C-O bond are drawn towards the C=O bond
- Overall, the O-H bond is weakened due to the carbonyl (C=O) group removing electron density from it and drawing it towards itself
- Carboxylic acids can therefore more easily lose a proton compared to phenols and alcohols which lack this electron-withdrawing carbonyl group
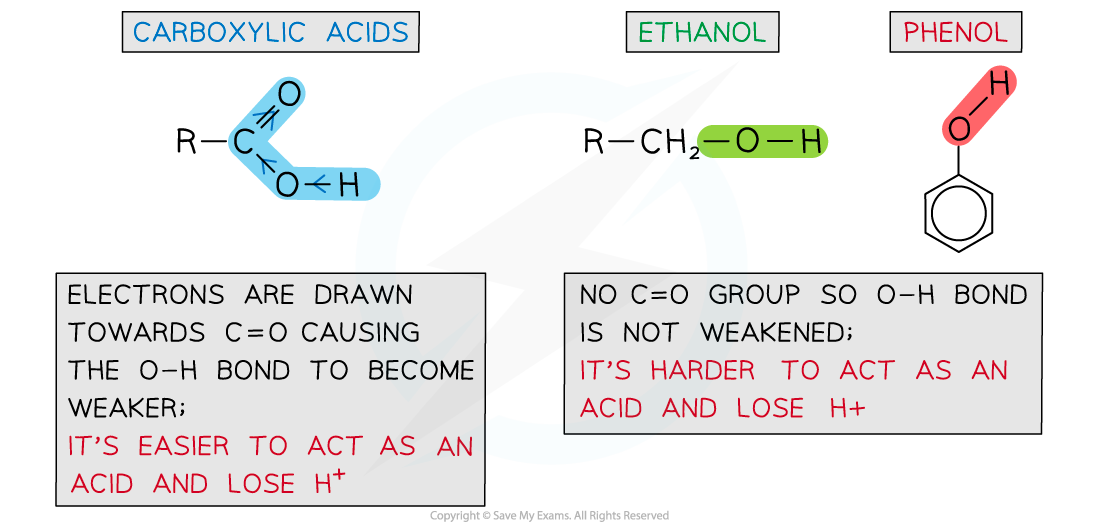
The carbonyl group in carboxylic acids draws the electrons away from the O-H bond causing it to become weaker compared to the O-H bond in phenols and alcohols
Stability of carboxylate ions
- The conjugate base of carboxylic acids is the carboxylate ion
- The charge density on the oxygen atom is spread out over the carboxylate ion
- This is because the charge is delocalised on an electronegative carbonyl oxygen atom
- As a result, the electrons on the oxygen atom are less available for bond formation with an H+ ion to reform the undissociated acid molecule with -COOH group
- The position of the dissociation equilibrium lies more to the right compared to alcohols and phenols

The carboxylate ion is stable due to delocalisation of the charge density on the electronegative oxygen
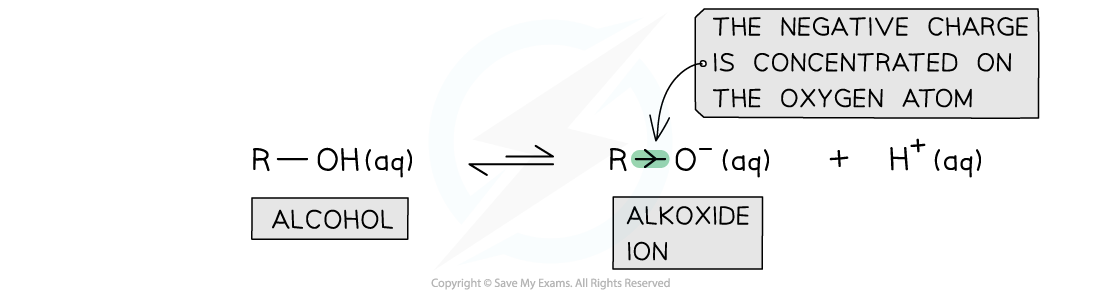
Stability of alkoxide ions
- The conjugate base of alcohols is the alkoxide ion
- The alkyl group in the ion is an electron-donating group that donates electron density to the oxygen atom
- As a result, the electron density on the oxygen atom is more readily available for bond formation with an H+ ion
- Alkoxide ions also lack the ability to delocalise the charge density on the entire ion
- The conjugate bases of alcohols are therefore less stable than the alcohols themselves and are more likely to reform the alcohol
- This means that alcohols are weaker acids compared to carboxylic acids and phenols
- The position of the dissociation equilibrium lies more to the left
The electron-donating alkyl groups in alkoxide ions increase the electron density on the oxygen atom which is, therefore, more likely to bond an H+ ion and reform the alcohol
Stability of phenoxide ions
- In the phenoxide ion (which is the conjugate base of phenol) the charge density on the oxygen atom is spread out over the entire ion
- This delocalisation of electrons stabilises the phenoxide ion
- As a result, the electrons on the oxygen atom are less available for bond formation with a proton (H+ ion)
- The conjugate base of phenols is therefore more stable than phenol
- However, since the delocalisation of charge density is on carbon atoms and not on electronegative oxygen atoms like in the carboxylate ion, phenoxide ions are less stable than carboxylate ions
- Therefore, phenols are weaker acids relative to carboxylic acids
- The position of the dissociation equilibrium lies more to the right compared to alcohols and more to the left compared to carboxylic acids
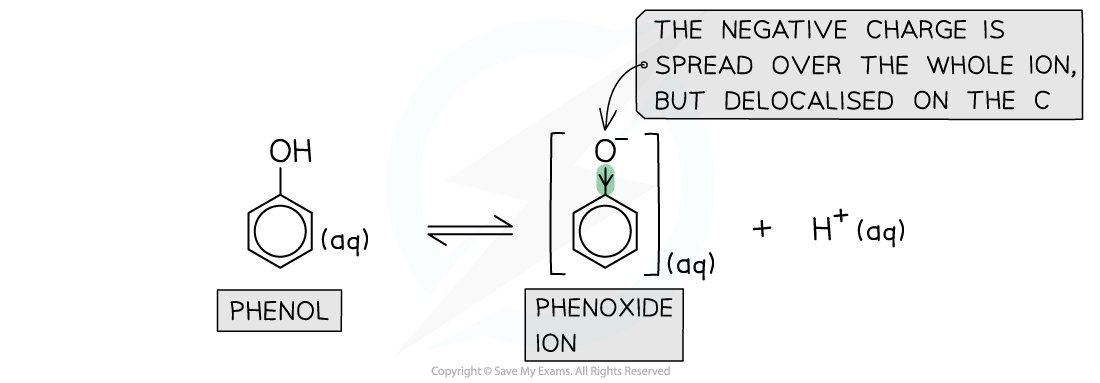
The charge density is delocalised on the entire benzene ring in the phenoxide ions
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









