- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
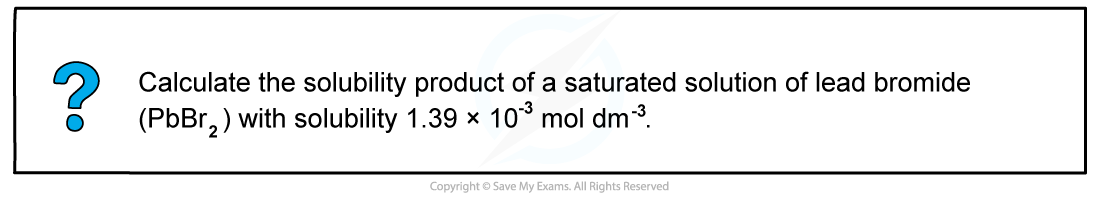
CIE A Level Chemistry复习笔记5.5.7 Solubility Product Calculations
Calculating the Solubility Product
- Calculations involving the solubility product (Ksp) may include::
- Calculating the solubility product of a compound from its solubility
- Calculating the solubility of a compound from the solubility product
Worked example: Calculating the solubility product of a compound from its solubility
Answer
- Step 1: Write down the equilibrium equation
PbBr2 (s) ⇌ Pb2+ (aq) + 2Br- (aq)
- Step 2: Write down the equilibrium expression
Ksp = [Pb2+(aq)] [Br- (aq)]2
- Step 3: Calculate the ion concentrations in the solution
[PbBr2(s)] = 1.39 x 10-3 mol dm-3
The ratio of PbBr2 to Pb2+ is 1:1
[Pb2+(aq)] = [PbBr2(s)] = 1.39 x 10-3 mol dm-3
The ratio of PbBr2 to Br- is 1:2
[Br-(aq)] = 2 x [PbBr2(s)] = 2 x 1.39 x 10-3 mol dm-3
= 2.78 x 10-3 mol dm-3
- Step 4: Substitute the values into the expression to find the solubility product
Ksp = (1.39 x 10-3) x (2.78 x 10-3)2
= 1.07 x 10-8
- Step 6: Determine the correct units of Ksp
Ksp = (mol dm-3) x (mol dm-3)2
= mol3 dm-9
The solubility product is therefore 1.07 x 10-8 mol3 dm-9
Worked example: Calculating the solubility of a compound from its solubility product

Answer
- Step 1: Write down the equilibrium equation
CuO (s) ⇌ Cu2+ (aq) + O2- (aq)
- Step 2: Write down the equilibrium expression
Ksp = [Cu2+ (aq)] [O2- (aq)]
- Step 3: Simplify the equilibrium expression
The ratio of Cu2+ to O2- is 1:1
[Cu2+(aq)] = [O2-(aq)] so the expression can be simplified to:
Ksp = [Cu2+ (aq)]2
- Step 4: Substitute the value of Ksp into the expression to find the concentration
5.9 x 10-36 = [Cu2+ (aq)]2
![]()
= 2.4 x 10-18 mol dm-3
Since [CuO(s)] = [Cu2+ (aq)] the solubility of copper oxide is 2.4 x 10-18 mol dm-3
Exam Tip
Remember that the solubility product is only applicable to very slightly soluble salts and cannot be used for soluble salts such as:
- Group 1 element salts
- All nitrates salts
- All ammonium salts
- Many sulfate salts
- Many halide salts (except for lead(II) halides and silver halides)
转载自savmyexams

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









