- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
CIE A Level Chemistry复习笔记5.5.2 pH, Ka, pKa & Kw Calculations
Calculating pH, Ka, pKA & Kw
pH
- The pH indicates the acidity or basicity of an acid or alkali
- The pH scale goes from 0 to 14
- Acids have pH between 0-7
- Pure water is neutral and has a pH of 7
- Bases and alkalis have pH between 7-14
- The pH can be calculated using: pH = -log10 [H+]
where [H+] = concentration of H+ ions (mol dm-3)
- The pH can also be used to calculate the concentration of H+ ions in solution by rearranging the equation to:
[H+] = 10-pH
Worked Example: Calculating the pH of acids

Answer
pH = -log [H+]
= -log 1.32 x 10-3
= 2.9
Ka & pKa
- The Ka is the acidic dissociation constant
- It is the equilibrium constant for the dissociation of a weak acid at 298 K
- For the partial ionisation of a weak acid HA the equilibrium expression to find Ka is as follows:
HA (aq) ⇌ H+ (aq) + A- (aq)
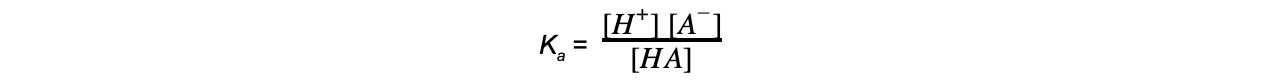
- When writing the equilibrium expression for weak acids, the following assumptions are made:
- The concentration of hydrogen ions due to the ionisation of water is negligible
- The dissociation of the weak acid is so small that the concentration of HA is approximately the same as the concentration of A-
- The value of Ka indicates the extent of dissociation
- A high value of Ka means that:
- The equilibrium position lies to the right
- The acid is almost completely ionised
- The acid is strongly acidic
- A low value of Ka means that:
- The equilibrium position lies to the left
- The acid is only slightly ionised (there are mainly HA and only a few H+ and A- ions)
- The acid is weakly acidic
- A high value of Ka means that:
- Since Ka values of many weak acids are very low, pKa values are used instead to compare the strengths of weak acids with each other
pKa = -log10 Ka
- The less positive the pKa value the more acidic the acid is
Worked Example: Calculating the Ka & pKa of weak acids
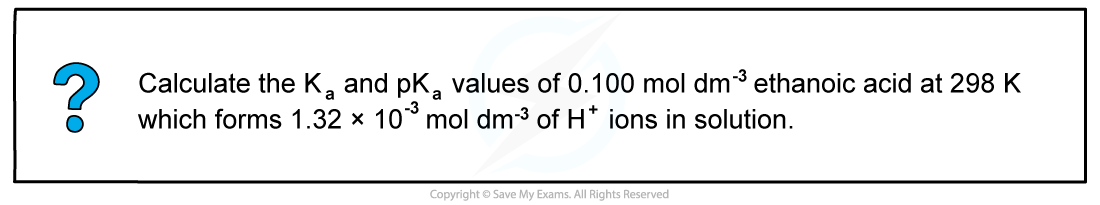
Answer
- Step 1: Write down the equation for the partial dissociation of ethanoic acid
CH3COOH (aq) ⇌ H+ (aq) + CH3COO- (aq)
- Step 2: Write down the equilibrium expression to find Ka
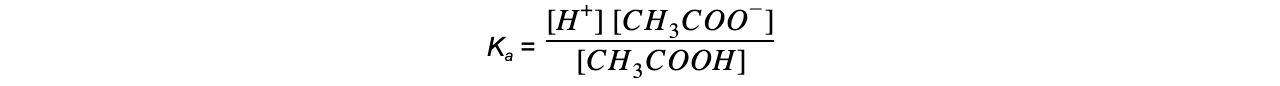
- Step 3: Simplify the expression
The ratio of H+ to CH3COO- is 1:1
The concentration of H+ and CH3COO- is, therefore, the same
The equilibrium expression can be simplified to:
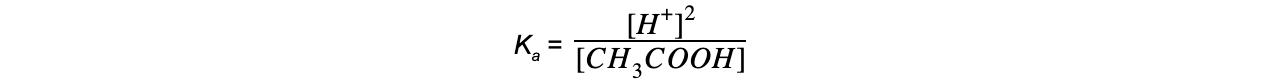
- Step 4: Substitute the values into the expression to find Ka
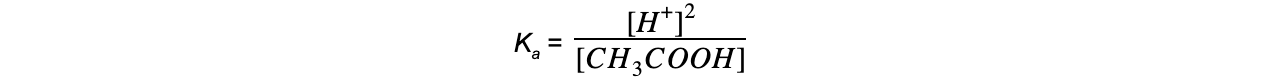
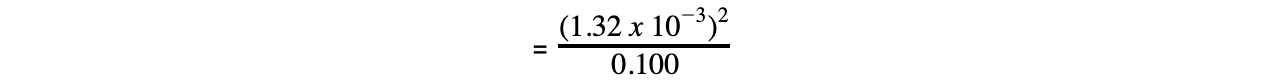 = 1.74 x 10-5
= 1.74 x 10-5
- Step 5: Determine the units of Ka
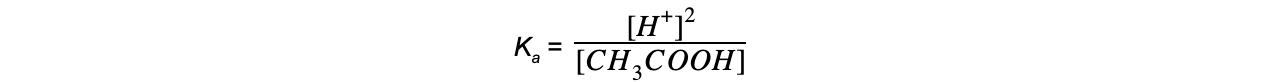
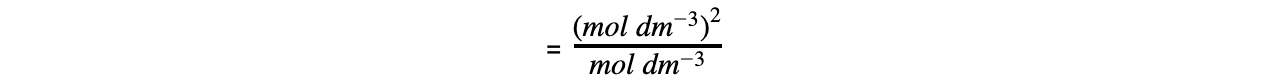
= mol dm-3
The value of Ka is therefore 1.74 x 10-5 mol dm-3
- Step 6: Find pKa
pKa = - log10 Ka
= - log10 (1.74 x 10-5)
= 4.76
Kw
- The Kw is the ionic product of water
- It is the equilibrium constant for the dissociation of water at 298 K
- Its value is 1.00 x 10-14 mol2 dm-6
- For the ionisation of water the equilibrium expression to find Kw is as follows:
H2O (l) ⇌ H+ (aq) + OH- (aq)
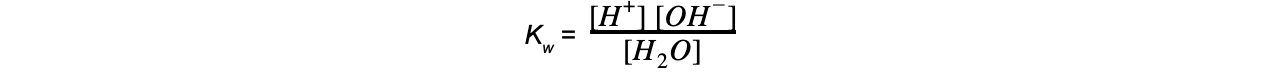
- As the extent of ionisation is very low, only small amounts of H+ and OH- ions are formed
- The concentration of H2O can therefore be regarded as constant and removed from the Kw expression
- The equilibrium expression therefore becomes:
Kw = [H+] [OH-]
- As the [H+] = [OH+] in pure water, the equilibrium expression can be further simplified to:
Kw = [H+]2
Worked Example: Calculating the concentration of H+ of pure water

Answer
- Step 1: Write down the equation for the partial dissociation of water
In pure water, the following equilibrium exists:
H2O (l) ⇌ H+ (aq) + OH- (aq)
- Step 2: Write down the equilibrium expression to find Kw
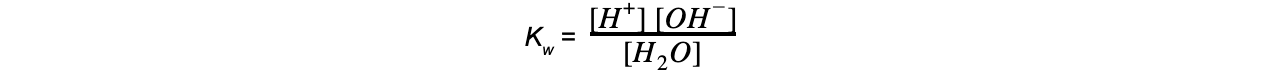
- Step 3: Simplify the expression
Since the concentration of H2O is constant, this expression can be simplified to:
Kw = [H+] [OH-]
- Step 4: Further simplify the expression
The ratio of H+ to OH- is 1:1
The concentration of H+ and OH- is, therefore, the same and the equilibrium expression can be further simplified to:
Kw = [H+]2
- Step 5: Rearrange the equation to find [H+]
Kw = [H+]2
- Step 6: Substitute the values into the expression to find Kw
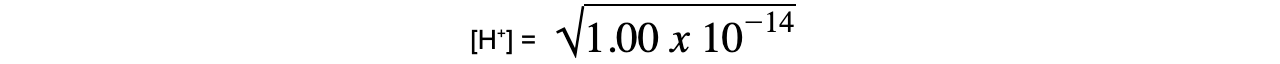
= 1.00 x 10-7 mol dm-3
Exam Tip
Remember:The greater the Kavalue, the more strongly acidic the acid is.The greater the pKa value, the less strongly acidic the acid is.Also, you should be able to rearrange the following expressions:
pH = -log10 [H+] TO [H+] = 10-pH
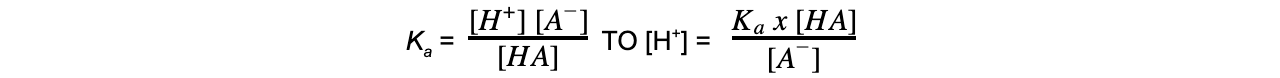
pKa = - log10 KaTO Ka = 10-pKa
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









