- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
CIE A Level Chemistry复习笔记5.4.1 Electrolysis: Calculations
Calculations in Electrolysis
- Faraday’s constant can be used to calculate:
- The mass of a substance deposited at an electrode
- The volume of gas liberated at an electrode
Calculating the mass of a substance deposited at an electrode
- To calculate the mass of a substance deposited at the electrode, you need to be able to:
- Write the half-equation at the electrode
- Determine the number of coulombs needed to form one mole of substance at the specific electrode using Faraday’s constant
- Calculate the charge transferred during electrolysis
- Use simple proportion and the relative atomic mass of the substance to find its mass
Worked example: Calculating the mass of a substance deposited at an electrode

Answer
The magnesium (Mg2+) ion is a positively charged cation that will move towards the cathode.
- Step 1: Write the half-equation at the cathode
Mg2+(aq) + 2e- → Mg(s)
1 mol 2 mol 1 mol
- Step 2: Determine the number of coulombs required to deposit one mole of magnesium at the cathode
For every one mole of electrons, the number of coulombs needed is 96 500 C mol-1
In this case, there are two moles of electrons required
So, the number of coulombs needed is:
F = 2 x 96 500
F = 193 000 C mol-1
- Step 3: Calculate the charge transferred during the electrolysis
Q = I x t
Q = 2.20 x (60 x 15)
= 1980 C
- Step 4: Calculate the mass of magnesium deposited by simple proportion using the relative atomic mass of Mg
Calculating the mass of a substance deposited at an electrode table
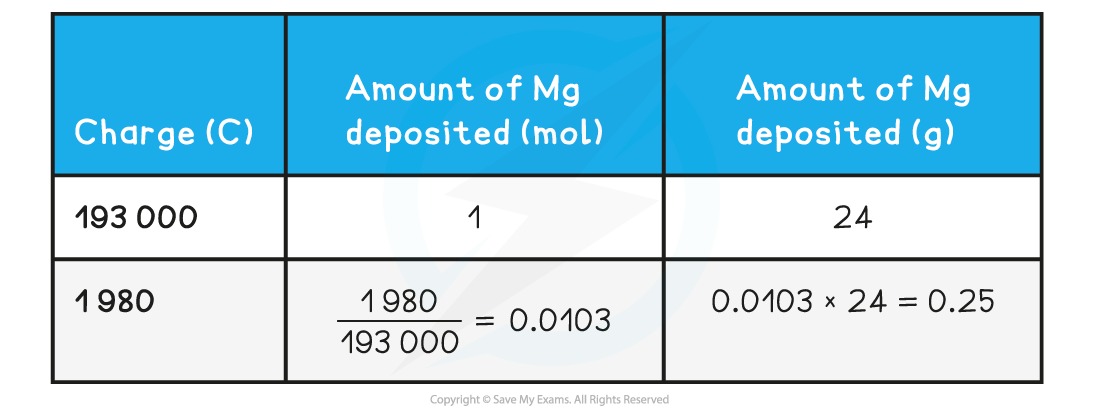
Therefore, 0.25 g of magnesium is deposited at the cathode
Calculating the volume of gas liberated at an electrode
- To calculate the volume of gas liberated at an electrode, you need to be able to:
- Write the half-equation at the electrode
- Determine the number of coulombs needed to form one mole of substance at the specific electrode using Faraday’s constant
- Calculate the charge transferred during electrolysis
- Use simple proportion and the relationship 1 mol of gas occupies 24.0 dm3 at room temperature
Worked example: Calculating the volume of a gas produced at an electrode
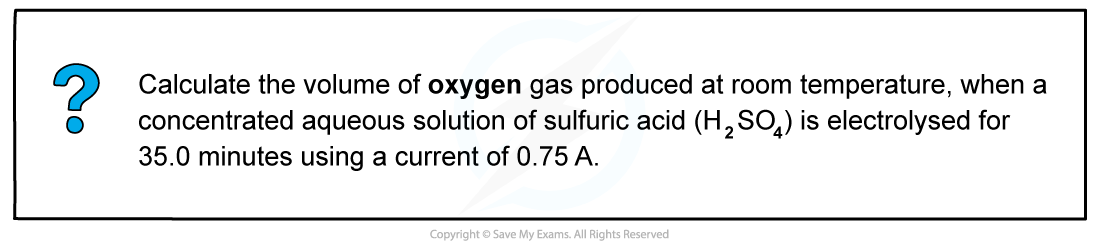
Answer
The oxygen gas is formed from the oxidation of negatively charged hydroxide (OH-) ions at the anode-
- Step 1: Write the half-equation at the anode
4OH-(aq) → O2(g) + 2H2O(l) + 4e-
4 mol 1 mol 2 mol 4 mol
- Step 2: Determine the number of coulombs required to form one mole of oxygen gas at the anode
For every one mole of electrons, the number of coulombs needed is 96 500 C mol-1
So, for four moles of electrons, the number of coulombs needed is:
F = 4 x 96 500
F = 386 000 C mol-1
- Step 3: Calculate the charge transferred during the electrolysis
Q = I x t
Q = 0.75 x (60 x 35)
= 1575 C
- Step 4: Calculate the volume of oxygen liberated by simple proportion using the relationship 1 mol of gas occupies 24.0 dm3 at room temperature
Calculating the volume of a gas liberated at an electrode table
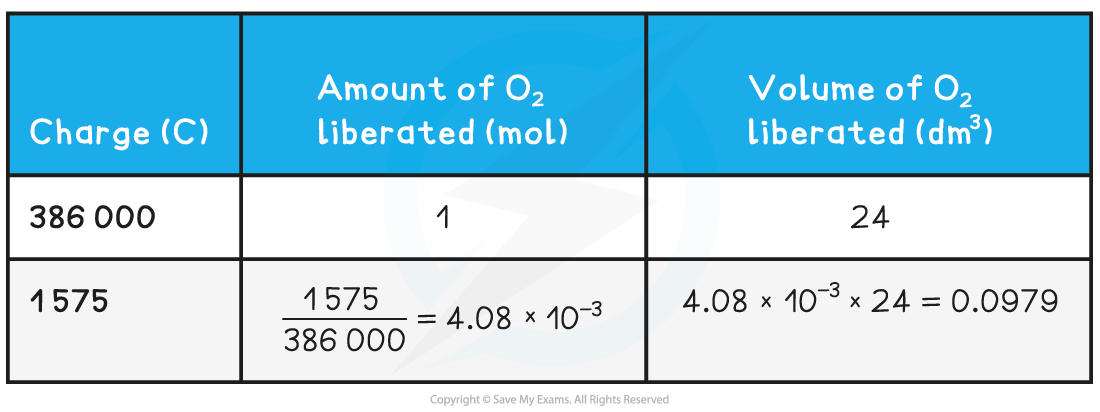
Therefore, 0.0979 dm3 of oxygen is formed at the anode
Worked example: Calculating the volume of hydrogen gas produced at an electrode
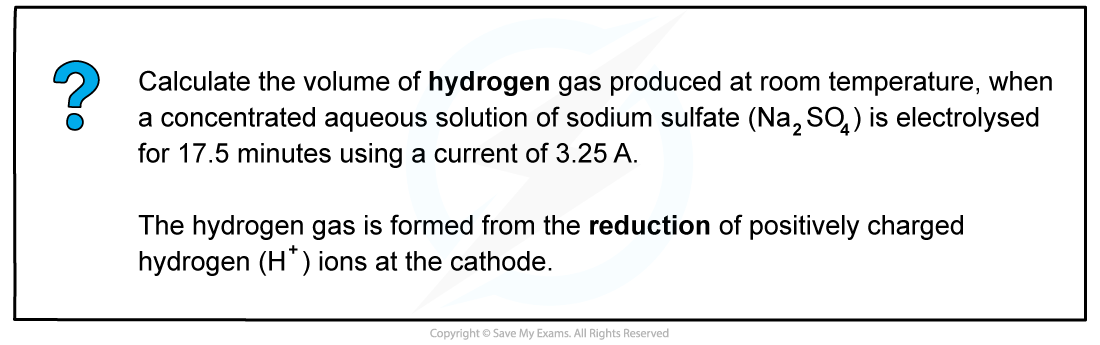
The hydrogen gas is formed from the reduction of positively charged hydrogen (H+) ions at the cathode
- Step 1: Write the half-equation at the cathode
2H+ (aq) + 2e- → H2 (g)
2 mols 2 mols 1 mol
- Step 2: Determine the number of coulombs required to form one mole of hydrogen gas at the cathode
For every one mole of electrons, the number of coulombs needed is:
F = 96 500 C mol-1
F = 1 x 96 500
F = 96 500 C
So, for two moles of electrons, the number of coulombs needed is:
F = 2 x 96 500
F = 193 000 C
- Step 3: Calculate the charge transferred during the electrolysis
Q = I x t
Q = 3.25 x (60 x 17.5)
= 3 413 C
- Step 4: Calculate the volume of hydrogen liberated by simple proportion using the relationship 1 mol of gas occupies 24.0 dm3 at room temperature
Calculating the volume of hydrogen gas produced at an electrode table
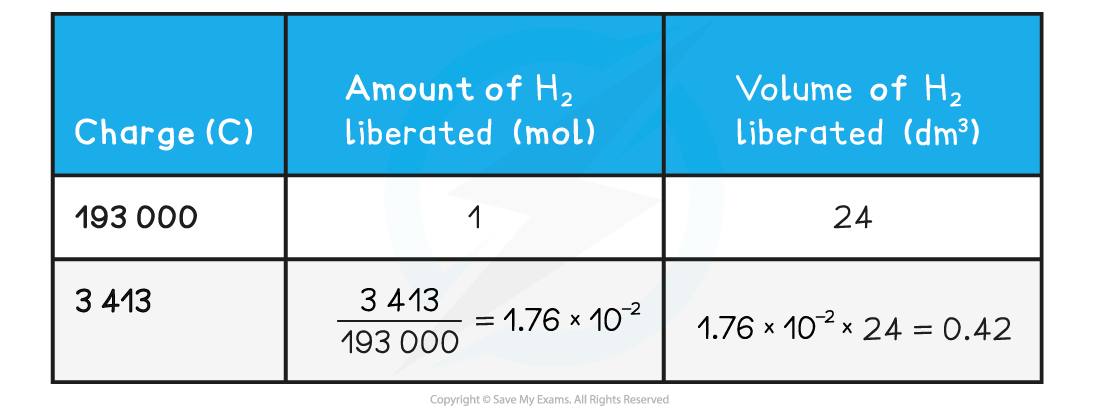
Therefore, 0.42 dm3 of hydrogen is formed at the cathode
转载自savemyexams


最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








