- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
CIE A Level Chemistry复习笔记5.3.2 Faraday's Law & Avogadro
Faraday's Law
- The amount of substance that is formed at an electrode during electrolysis is proportional to:
- The amount of time where a constant current to passes
- The amount of electricity, in coulombs, that passes through the electrolyte (strength of electric current)
- The relationship between the current and time is:
Q = I x t
Q = charge (coulombs, C)
I = current (amperes, A)
t = time, (seconds, s)
- The amount or the quantity of electricity can also be expressed by the faraday (F) unit
- One faraday is the amount of electric charge carried by 1 mole of electrons or 1 mole of singly charged ions
- 1 faraday is 96 500 C mol-1
- Thus, the relationship between the Faraday constant and the Avogadro constant (L) is:
F = L x e
F = Faraday’s constant (96 500 C mol-1)
L = Avogadro’s constant (6.022 x 1023 mol-1)
e = charge on an electron
Worked example: Determining the amount of electricity required
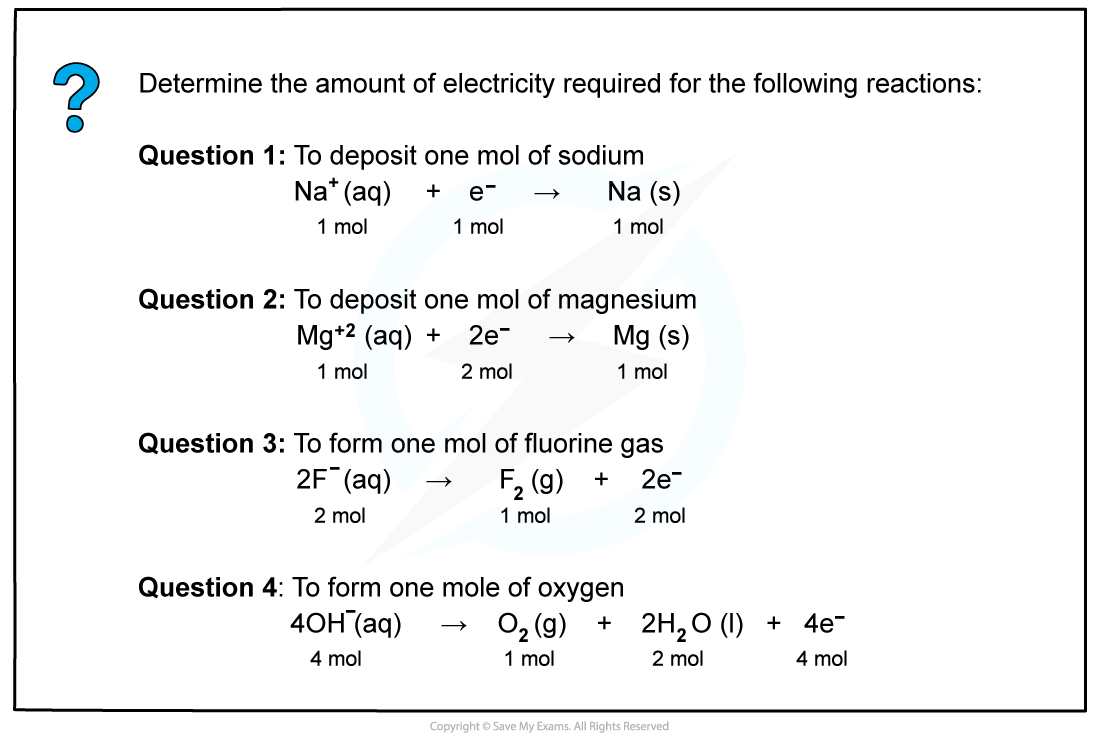
Answer
One Faraday is the amount of charge (96 500 C) carried by 1 mole of electrons
Answer 1
As there is one mole of electrons, one faraday of electricity (96 500 C) is needed to deposit one mole of sodium.
Answer 2
Now, there are two moles of electrons, therefore, two faradays of electricity (2 x 96 500 C) are required to deposit one mole of magnesium.
Answer 3
Two moles of electrons are released, so it requires two faradays of electricity (2 x 96 500 C) to form one mole of fluorine gas.
Answer 4
Four moles of electrons are released, therefore it requires four faradays of electricity (4 x 96 500 C) to form one mole of oxygen gas.
Determining Avogadro's Constant by Electrolysis
- The Avogadro’s constant (L) is the number of entities in one mole
- L = 6.02 x 1023 mol-1
- For example, four moles of water contains 2.41 x 1024 (6.02 x 1023 x 4) molecules of H2O
- The value of L (6.02 x 1023 mol-1) can be experimentally determined by electrolysis using the following equation:
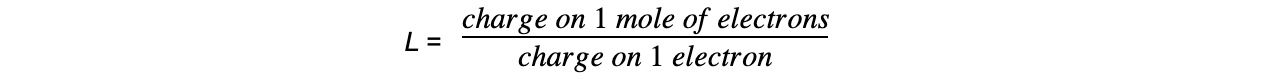
Finding L experimentally
- The charge on one mole of electrons is found by using a simple electrolysis experiment using copper electrodes
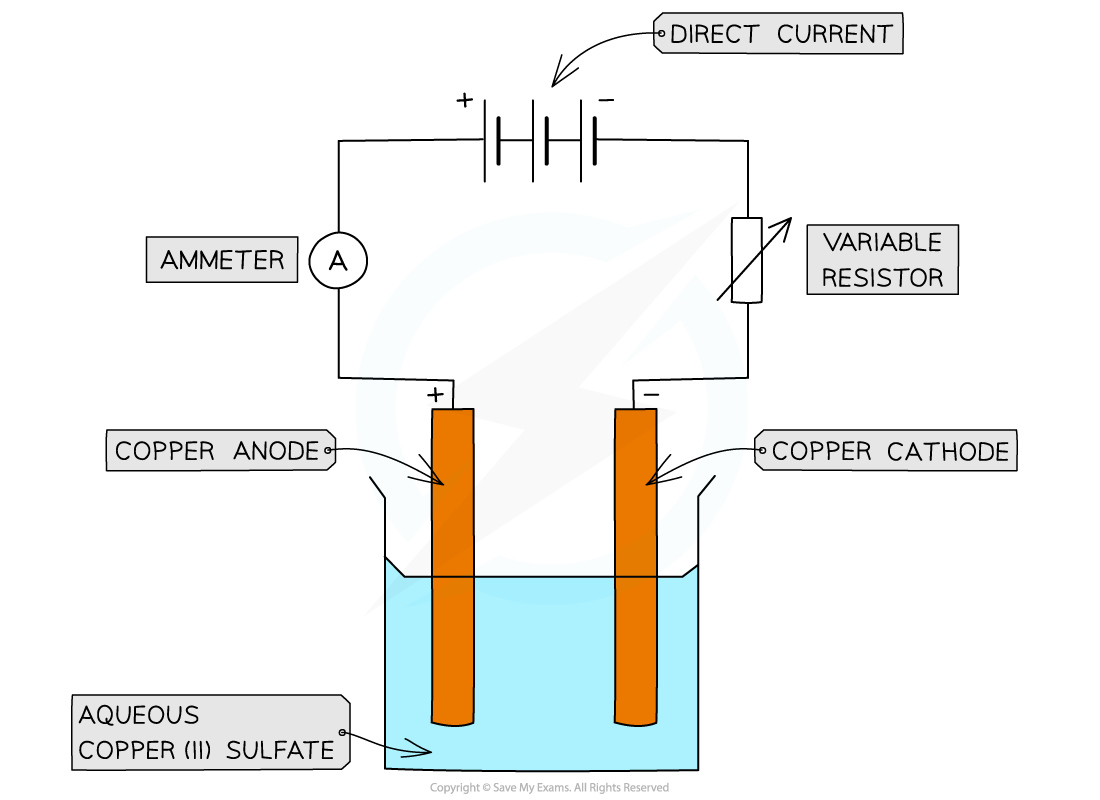
Apparatus set-up for finding the value of L experimentally
- Method
- The pure copper anode and pure copper cathode are weighed
- A variable resistor is kept at a constant current of about 0.17 A
- An electric current is then passed through for a certain time interval (e.g. 40 minutes)
- The anode and cathode are then removed, washed with distilled water, dried with propanone, and then reweighed
- Results
- The cathode has increased in mass as copper is deposited
- The anode has decreased in mass as the copper goes into solution as copper ions
- Often, it is the decreased mass of the anode which is used in the calculation, as the solid copper formed at the cathode does not always stick to the cathode properly
- Let’s say the amount of copper deposited in this experiment was 0.13 g
- Calculation:
- The amount of charge passed can be calculated as follows:
Q = I x t
= 0.17 x (60 x 40)
= 408 C
- To deposit 0.13 g of copper (2.0 x 10-3 mol), 408 C of electricity was needed
- The amount of electricity needed to deposit 1 mole of copper can therefore be calculated using simple proportion using the relative atomic mass of Cu
Calculating the amount of charge required to deposit one mole of copper table
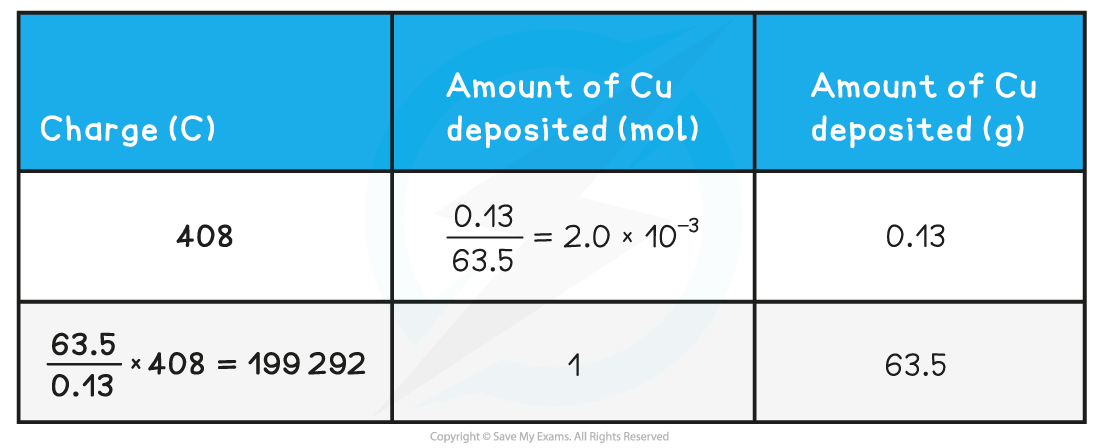
- Therefore, 199 292 C of electricity is needed to deposit 1 mole of Cu
- The half-equation shows that 2 mol of electrons are needed to deposit one mol of copper:
Cu2+(aq) + 2e- → Cu(s)
- So, the charge on 1 mol of electrons is:
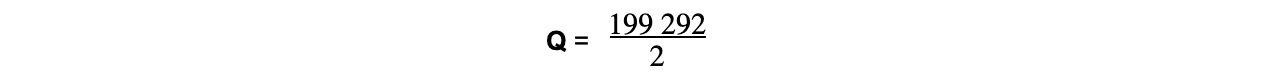
= 99 646 C
- Given that the charge on one electron is 1.60 x 10-19 C, then L equals:
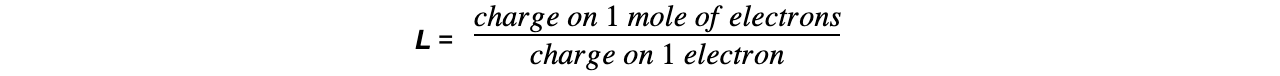
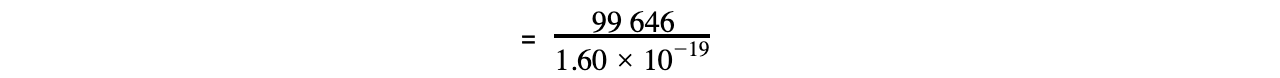
= 6.23 x 1023 mol-1
- The experimentally determined value for L of 6.23 x 1023 mol-1 is very close to the theoretical value of 6.02 x 1023 mol-1
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









