- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
CIE A Level Chemistry复习笔记3.1.8 Hybridisation in Organic Molecules
Hybridised Atoms: Shapes & Bond Angles in Molecules
- Each carbon atom has four electrons in its outer shell (electronic configuration: 1s22s22p2)
- Carbon atoms share these four electrons in four covalent bonds with other atoms to achieve a full outer shell configuration
- These electrons are found in orbitals within the respective atoms
- When forming a covalent bond, the orbitals overlap in such a way to form two types of bonds
- Sigma bonds (σ)
- Pi bonds (π)
Hybridisation: sp3
- The electron pair in a σ bond is found in a region of space between the nuclei of the two atoms that are sharing the electrons
- The electrostatic attraction between the electrons (negatively charged) and the two nuclei (positively charged) holds the two atoms together
- Carbon atoms that form four σ bonds are said to be sp3 hybridised
- The four pairs of electrons around each carbon repel each other forcing the molecule to adopt a configuration in which the bonding pairs of electrons are as far away from each other as possible
- The molecule adopts a tetrahedral arrangement with bond angles of 109.5 o

The diagram shows a molecule of ethane in which each carbon atom forms four σ bonds to adopt a tetrahedral configuration and minimise the repulsion between the bonding pairs of electrons
Hybridisation: sp2
- When carbon atoms use only three of their electron pairs to form a σ bond, they are said to be sp2 hybridised
- Each carbon atom will have a p orbital with contains one spare electron
- When the p orbitals of two carbon atoms overlap with each other, a π bond is formed (the π bond contains two electrons)
- The two orbitals that form the π bond lie above and below the plane of the two carbon atoms to maximise bond overlap
- The three bonding pair of electrons are in the plane of the molecule and repel each other
- The molecule adopts a planar arrangement with bond angles of 120o
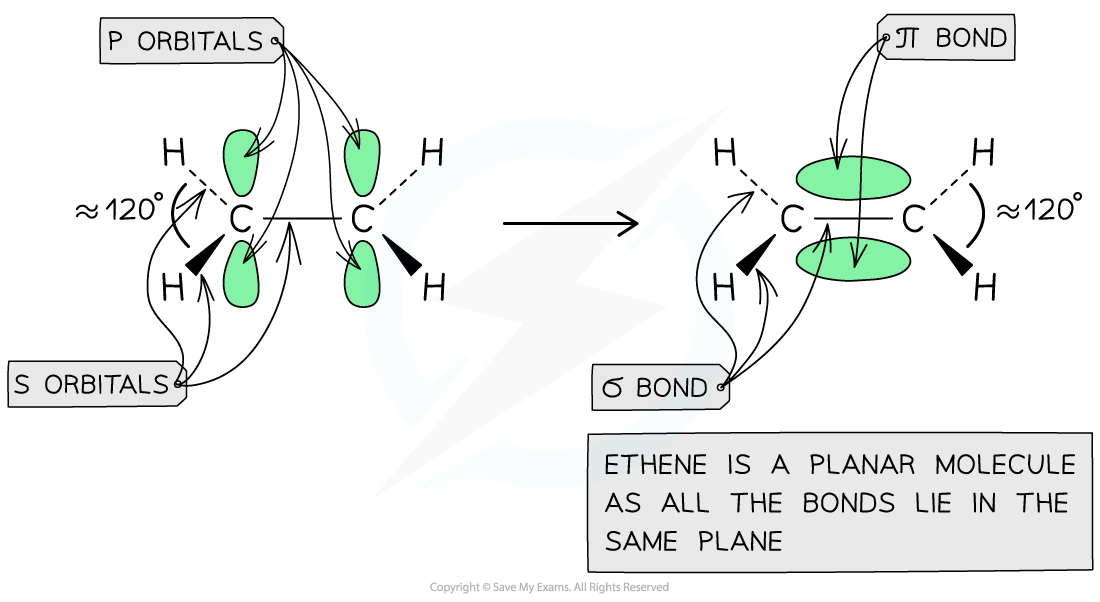 The overlap of the two p orbitals results in the formation of a π bond in ethene (sp2 hybridised molecule) in which the bonding pair of electrons repel each other to force the molecule into a planar configuration with bond angles of 120o
The overlap of the two p orbitals results in the formation of a π bond in ethene (sp2 hybridised molecule) in which the bonding pair of electrons repel each other to force the molecule into a planar configuration with bond angles of 120o
Hybridisation: sp
- Carbon atoms can also use only one of their electron pair to form a σ bond, in which case the carbon atoms are said to be sp hybridised
- Each carbon atom will have two p orbitals with one spare electron each
- When the four p orbitals of the carbon atoms overlap with each other, two π bonds are formed (each π bond contains two electrons)
- The two orbitals that form the π bond lie above and below the plane of the carbon atoms
- The two orbitals of the other π bond lie in front and behind the plane of the atoms
- This maximises the overlap of the four p orbitals
- The molecule adopts a linear arrangement with bond angles 180o
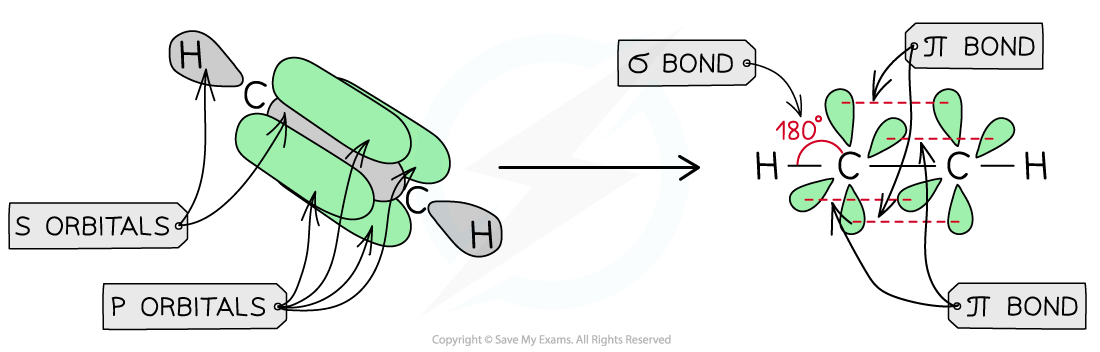 The overlap of the p orbitals results in the formation of two π bonds in ethyne (sp hybridised molecule) which adopts a linear arrangement with bond angles of 180
The overlap of the p orbitals results in the formation of two π bonds in ethyne (sp hybridised molecule) which adopts a linear arrangement with bond angles of 180
Exam Tip
A double bond is a combination of a σ and π bond and a triple bond is a combination of one σ and two π bonds.The strength of the bonds increases as follows: single < double < triple bondThis is due to the increased electron density around the C-C atom, making the bond stronger and more difficult to break.
Hybridised Atoms: σ and π Bonds in Molecules
σ bonds
- Sigma bonds are formed from the end-on overlap of atomic orbitals
- S orbitals overlap this way as well as p orbitals
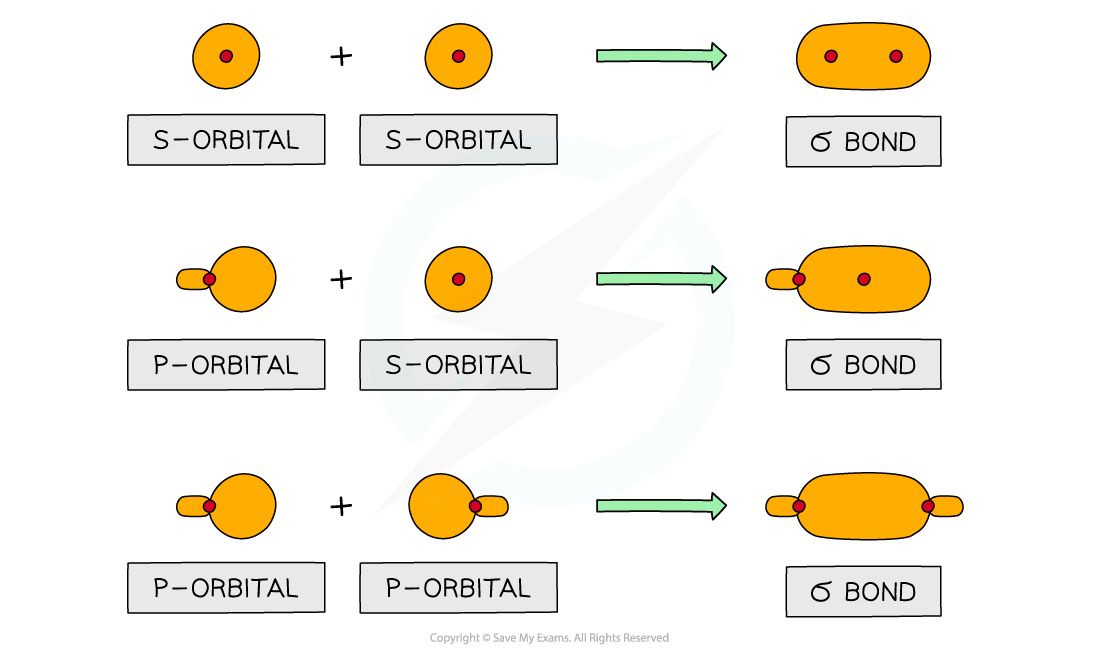 Sigma orbitals can be formed from the end-on overlap of s or p orbitals
Sigma orbitals can be formed from the end-on overlap of s or p orbitals
- The electron density in a σ bond is symmetrical about a line joining the nuclei of the atoms forming the bond
- The pair of electrons is found between the nuclei of the two atoms
- The electrostatic attraction between the electrons and nuclei bonds the atoms to each other
- The diagram below shows the arrangement of the σ bond in sp3, sp2 and sp hybridised carbon atoms
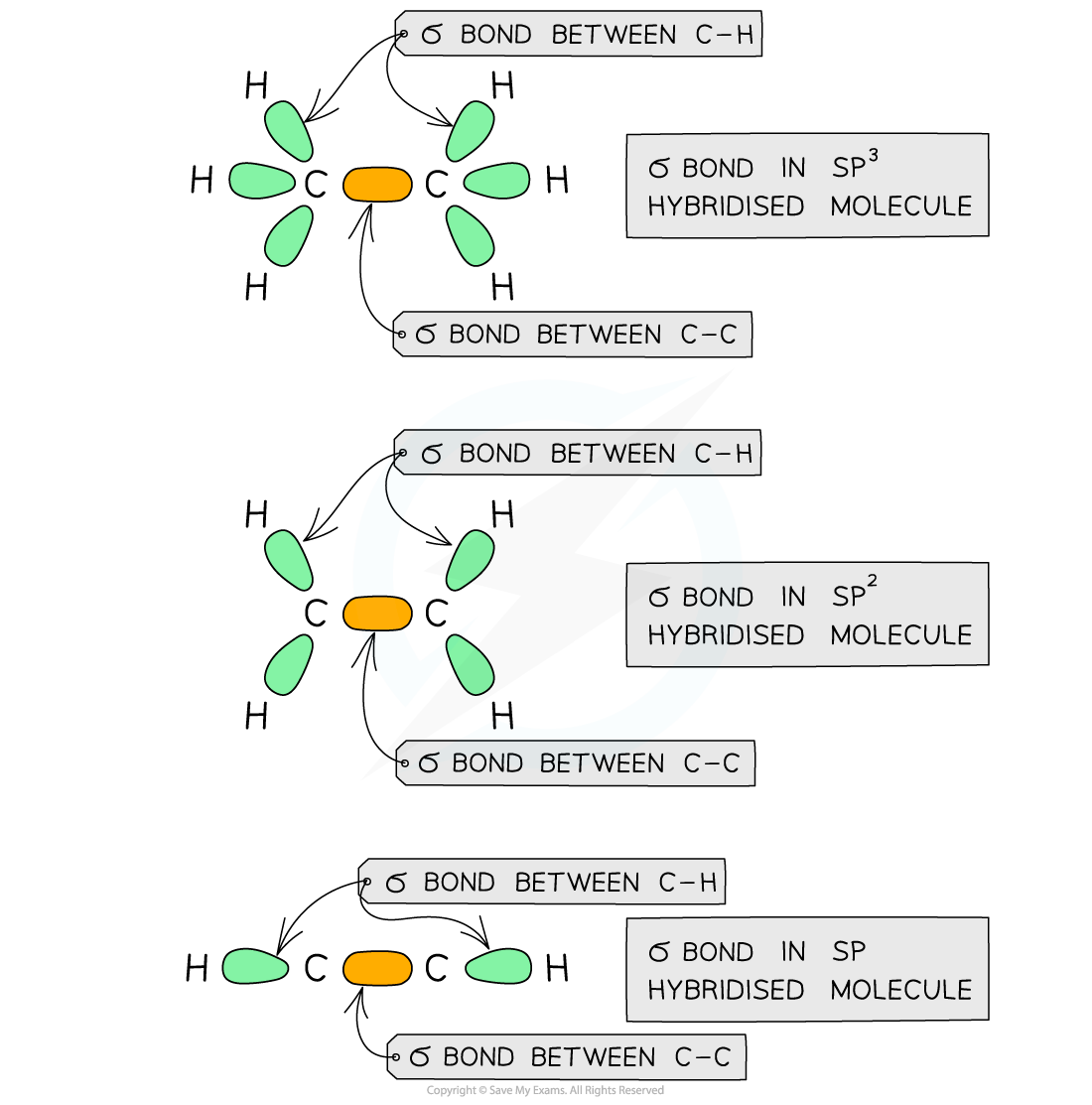
The σ orbitals are formed from the end-on overlap of the atomic orbitals resulting in symmetrical electron density on the atoms
π bonds
- Pi (π) bonds are formed from the sideways overlap of p orbitals
- The two lobes that make up the π bond lie above and below the plane of the atoms
- This maximises overlap of the p orbitals
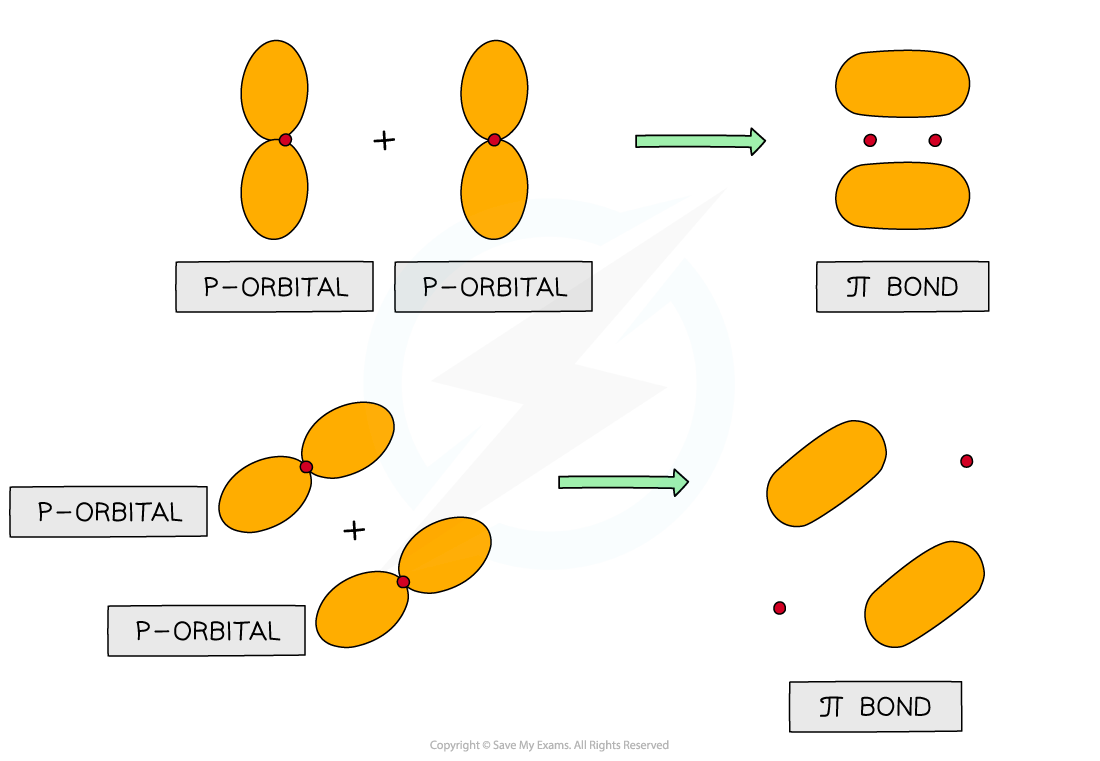
π orbitals can be formed from the end-on overlap of p orbitals
- In triple bonds, there is an additional overlap of p orbital
- The two lobes of the π bond lie in front of and behind the plane of the atoms in the molecule
- This maximises overlap of the p orbitals
- The diagram below shows the arrangement of the π bond in sp3, sp2 and sp hybridised carbon atoms
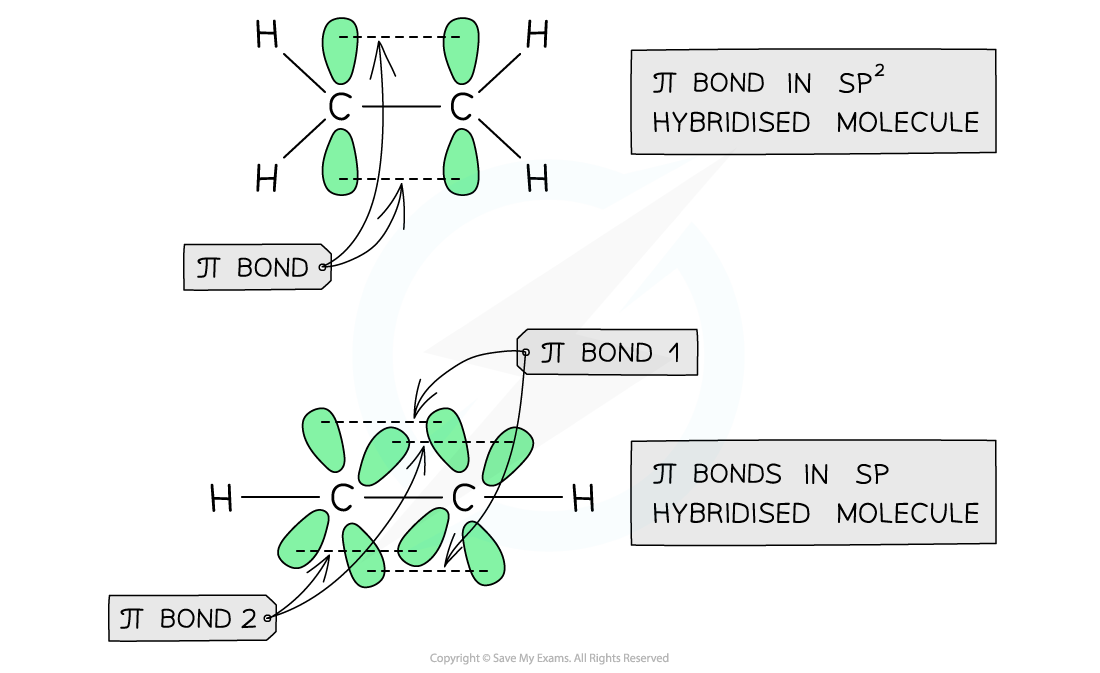
The π orbitals are formed from the sideway overlap of the atomic orbitals
Exam Tip
π bonds are drawn as two electron clouds, one arising from each lobe of the p orbitals.The two clouds of electrons in a π bond represent one bond consisting of two electrons (one from each orbital).
转载自savemyexams


最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








