- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
CIE A Level Chemistry复习笔记2.2.4 Group 2: Physical & Chemical Trends
Group 2: Physical & Chemical Trends
Chemical trends
- All elements in Group 2 (also called alkali earth metals) have the two electrons in their outermost principal quantum shell
- All Group 2 metals can form ionic compounds in which they donate these two outermost electrons (so they act as reducing agents) to become an ion with +2 charge (so they themselves become oxidised)
- Going down the group, the metals become more reactive
- This can be explained by looking at the Group 2 ionisation energies:
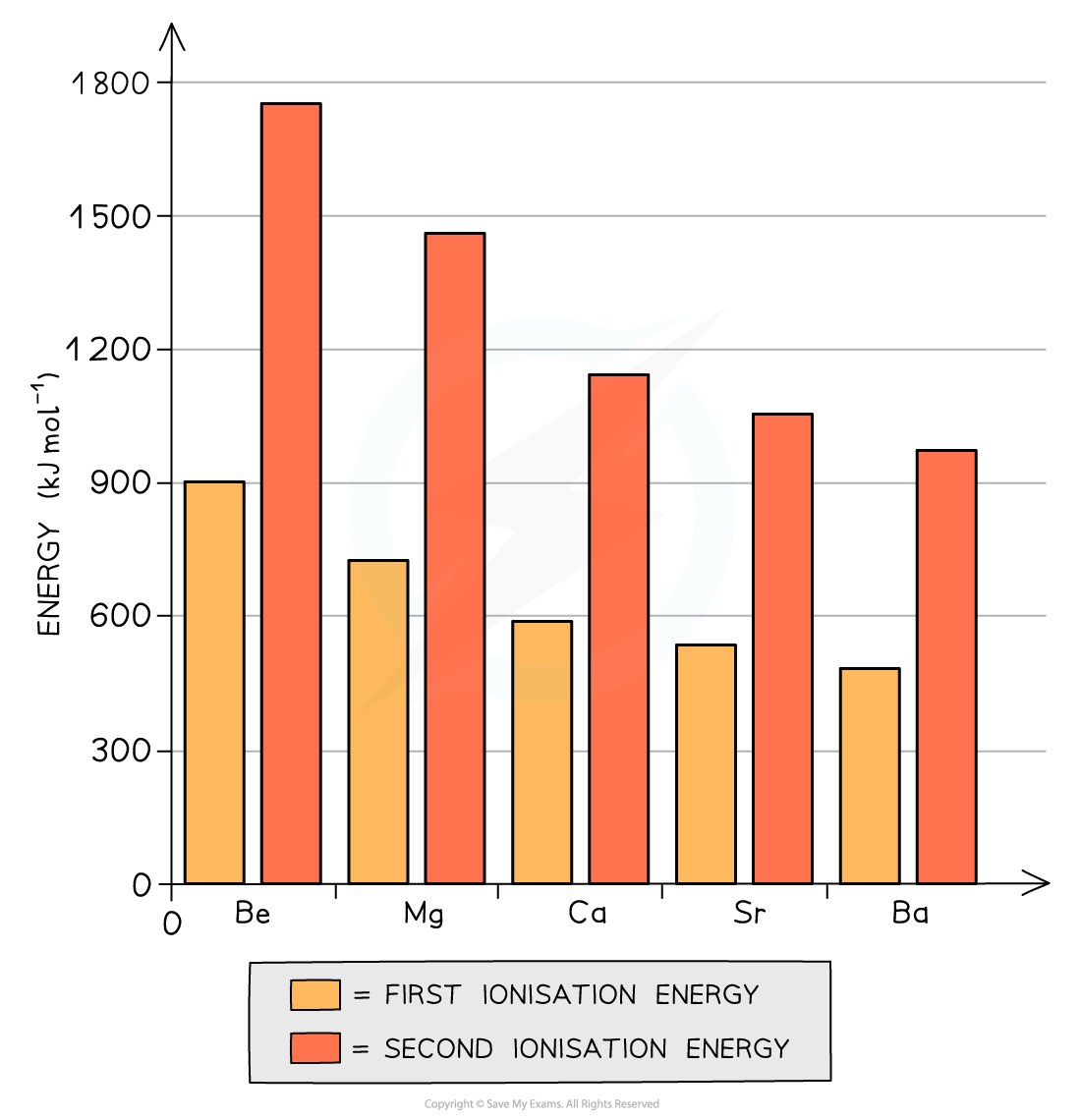
The graph shows that both the first and second ionization energies decrease going down the table
- The first ionisation energy is the energy needed to remove the first outer electron of an atom
- The second ionisation energy is the energy needed to remove the second outer electron of an atom
- The graph above shows that going down the group, it becomes easier to remove the outer two electrons of the metals
- Though the nuclear charge on the nucleus increases going down the group (because there are more protons), factors such as an increased shielding effect and a larger distance between the outermost electrons and nucleus outweigh the attraction of the higher nuclear charge
- As a result of this, the elements become more reactive going down the group as it gets easier for the atoms to lose two electrons and become 2+ ions
- This trend is shown by looking at reactions of the Group 2 metals:
- With dilute hydrochloric acid: bubbles of hydrogen gas are given off much faster indicating that the reactions become more vigorous
- With oxygen hydrochloric acid: the metals get more reactive with oxygen down the group (Ba is so reactive, that it must be stored in oil to prevent it from reacting with oxygen in air)
Physical trends
- Going down the group, the elements become larger as the outer two electrons occupy a new principal quantum shell which is further away from the nucleus
 The atomic radius of the Group 2 elements increases going down the group due to the addition of an extra principal quantum shell
The atomic radius of the Group 2 elements increases going down the group due to the addition of an extra principal quantum shell
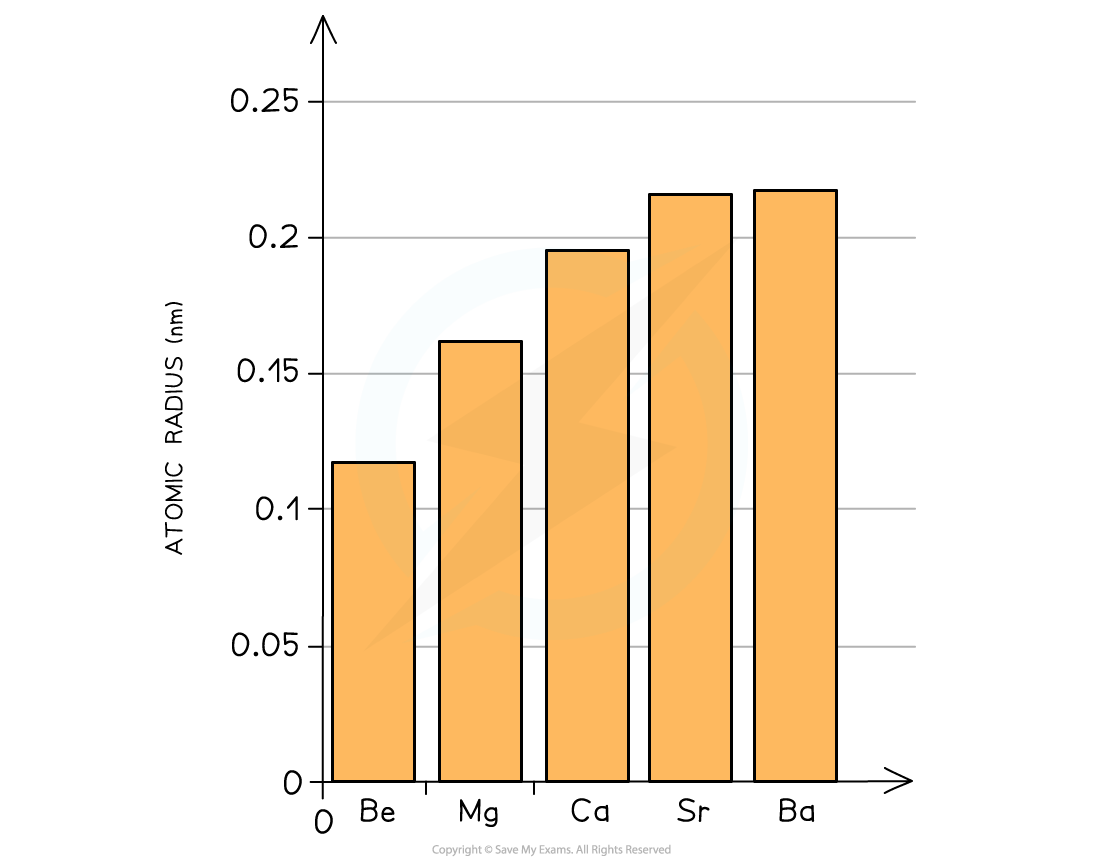
The graph shows a increase in atomic radius going down the group
- The melting point of the elements decreases going down the group as the outer electrons get further away from the nucleus
- This means that the attraction between the nucleus and the bonding electrons decreases causing a decrease in melting point
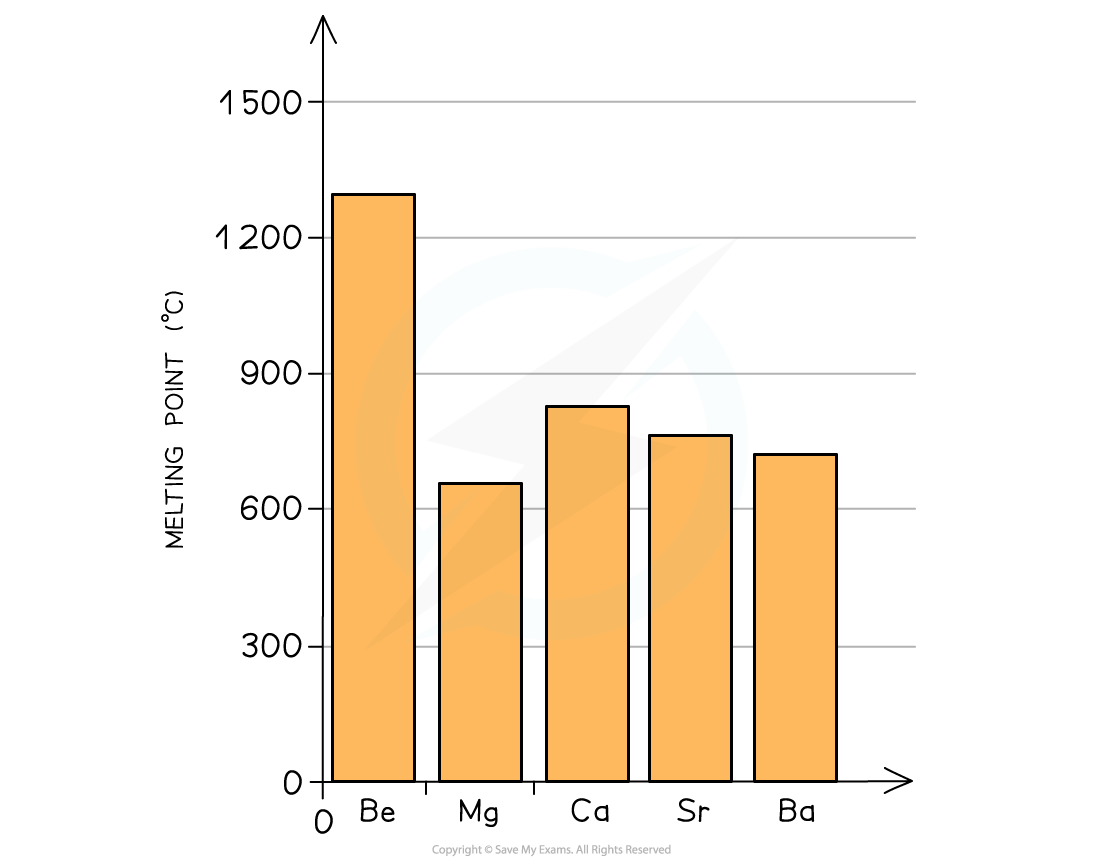 The graph shows a decrease in melting point going down the group
The graph shows a decrease in melting point going down the group
- As you go down the group, the density of the alkali earth metals increases
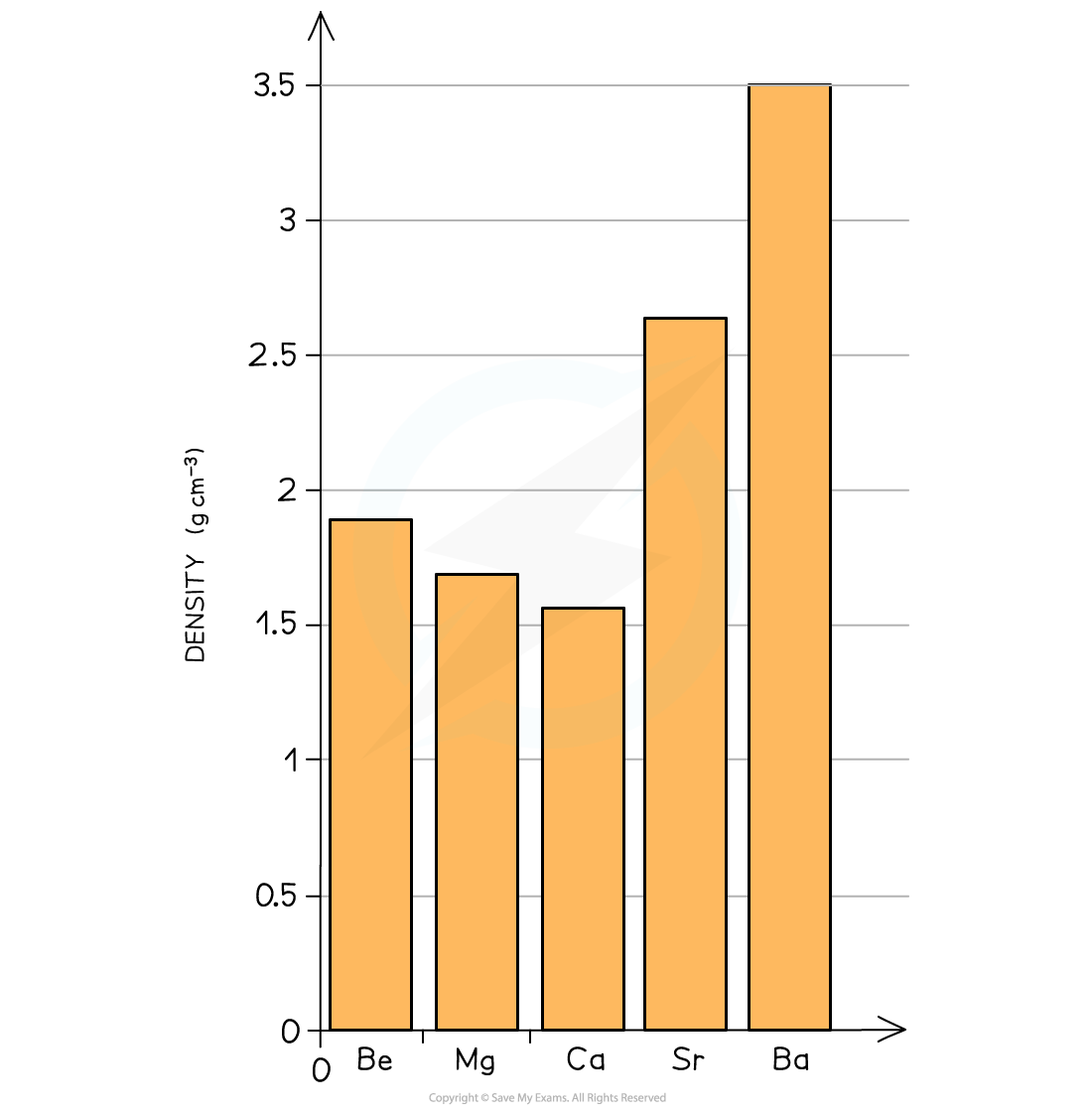
The graph shows an increase in density going down the group
Worked example: Predicting properties of radium

Answer
Property 1:
Since, Ra is in Group 2, it will form an ion with +2 charge to give Ra2+Property 2:
The Group 2 oxides and hydroxides have general formula XO and X(OH)2 respectively where X is the Group 2 element.Therefore, radium oxide is RaO and radium hydroxide is Ra(OH)2
Property 3:
Radium is below barium so its atomic radius is larger than the atomic radius of barium.
This means that radium’s outermost electrons are even further away and are therefore even more easily removed than barium’s outermost electron pair.The first ionization energy is between 450-480 kJ mol-1
Property 4:
Radium’s outermost electrons are even further away than in barium and are therefore more easily removed making radium more reactive than barium.
Property 5:
The Group 2 hydroxides become more soluble going down the group.
Radium hydroxide will therefore be more soluble than calcium hydroxide.Property 6:
The Group 2 sulfates become less soluble going down the group.Radium sulfate will therefore be less soluble than strontium sulfate.
Property 7:
The general equation for the reaction of Group 2 oxides with dilute hydrochloric acid is:
XO(s) + 2HCl(aq) → XCl2(aq) + H2O(l)
where X is the Group 2 element
The reaction of radium oxide with dilute hydrochloric acid is therefore:
RaO(s) + 2HCl(aq) → RaCl2(aq) + H2O(l)
Property 8:
Radium sulfate will be formed in this reaction, however the solubility of Group 2 sulfates decreases going down the group, therefore a white precipitate of radium sulfate will be formed in this reaction
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









